Chapter 12.1 - Evidence for Continental Drift
... • Wilson then unified the ideas of Wegener and Hess into the plate tectonic theory. Continental drift occurs because of areas like these ridges, that push along tectonic plates floating on Earth’s surface. geologic hot spots are anywhere magma rises to Earth’s surface. See pages 512 - 513 ...
... • Wilson then unified the ideas of Wegener and Hess into the plate tectonic theory. Continental drift occurs because of areas like these ridges, that push along tectonic plates floating on Earth’s surface. geologic hot spots are anywhere magma rises to Earth’s surface. See pages 512 - 513 ...
Resource 1
... route’.) There must be a connection from each end of the battery to two points on the bulb holder (i.e. the metal, not the glass) for the bulb to light. Misconception: current is ‘used up’ as it flows round the circuit Current is not used up: the current is the same all the way round a series circui ...
... route’.) There must be a connection from each end of the battery to two points on the bulb holder (i.e. the metal, not the glass) for the bulb to light. Misconception: current is ‘used up’ as it flows round the circuit Current is not used up: the current is the same all the way round a series circui ...
Matter Unit - Griffin Middle School
... Essential Question(s): Unit: How do the forces within the earth affect the formations of the Earth’s surface? Lesson: How are the earth’s layers alike and different? • What challenges stand in the way of sending explorers to the center of the earth? • How does the movement of lithospheric plates cau ...
... Essential Question(s): Unit: How do the forces within the earth affect the formations of the Earth’s surface? Lesson: How are the earth’s layers alike and different? • What challenges stand in the way of sending explorers to the center of the earth? • How does the movement of lithospheric plates cau ...
File
... • Describe the interior of the Earth (in terms of crust, mantle, and inner and outer cores) and where the magnetic field of the Earth is generated. • Explain how scientists infer that the Earth has internal layers with discernable properties using patterns of primary (P) and secondary (S) seismic wa ...
... • Describe the interior of the Earth (in terms of crust, mantle, and inner and outer cores) and where the magnetic field of the Earth is generated. • Explain how scientists infer that the Earth has internal layers with discernable properties using patterns of primary (P) and secondary (S) seismic wa ...
1 Magnetism 2 Magnetic Field and Magnetic Force
... Physics 1214 — Chapter 20: Magnetic Field and Magnetic Forces ...
... Physics 1214 — Chapter 20: Magnetic Field and Magnetic Forces ...
1 Magnetism 2 Magnetic Field and Magnetic Force
... Physics 1214 — Chapter 20: Magnetic Field and Magnetic Forces — 02/08 ...
... Physics 1214 — Chapter 20: Magnetic Field and Magnetic Forces — 02/08 ...
Document
... 11. The outermost layer of the Earth is called the __________________________. 12. The ___________________________ is solid nickel and iron; under extreme heat and pressure. 13. The __________________________ is melted nickel and iron. 14. A _____________________________ is when plates are moving ap ...
... 11. The outermost layer of the Earth is called the __________________________. 12. The ___________________________ is solid nickel and iron; under extreme heat and pressure. 13. The __________________________ is melted nickel and iron. 14. A _____________________________ is when plates are moving ap ...
Name
... 1. How do most fossils form? Living things die and their remains are buried by sediment. 2. The relative age of a rock is its age generally; its age compared to the ages of other rocks. 3. The law of superposition states that, in horizontal layers of sedimentary rock, each layer is older than the la ...
... 1. How do most fossils form? Living things die and their remains are buried by sediment. 2. The relative age of a rock is its age generally; its age compared to the ages of other rocks. 3. The law of superposition states that, in horizontal layers of sedimentary rock, each layer is older than the la ...
Lesson plans- 3/20/17 - Williston School District 29
... Explain why some objects are magnetic and how some objects can be magnetized. ...
... Explain why some objects are magnetic and how some objects can be magnetized. ...
Earth
... 3. Transform boundaries- plates slide past each other: strike slip fault, oceanic transforms ...
... 3. Transform boundaries- plates slide past each other: strike slip fault, oceanic transforms ...
magnetism
... A practical motor armature is made up of many coils of conductors The magnetic fields of these conductors combine to form a resultant armature field with north and south poles that are interact with those of the main stator field to exert a continuous torque on the armature. ©2010, The McGraw-Hill ...
... A practical motor armature is made up of many coils of conductors The magnetic fields of these conductors combine to form a resultant armature field with north and south poles that are interact with those of the main stator field to exert a continuous torque on the armature. ©2010, The McGraw-Hill ...
Magnetic Effect of Electric Current
... Like poles of magnets repel each other while unlike poles of magnets attract each other. Similar to other effects; electric current also produces magnetic effect. The magnetic effect of electric current is known as electromagnetic effect. It is observed that when a compass is brought near a current ...
... Like poles of magnets repel each other while unlike poles of magnets attract each other. Similar to other effects; electric current also produces magnetic effect. The magnetic effect of electric current is known as electromagnetic effect. It is observed that when a compass is brought near a current ...
History of Climate Change
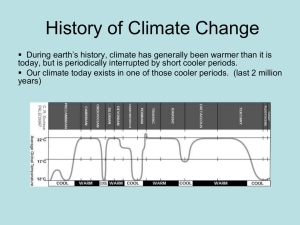
... History of Climate Change During earth’s history, climate has generally been warmer than it is today, but is periodically interrupted by short cooler periods. Our climate today exists in one of those cooler periods. (last 2 million years) ...
... History of Climate Change During earth’s history, climate has generally been warmer than it is today, but is periodically interrupted by short cooler periods. Our climate today exists in one of those cooler periods. (last 2 million years) ...
Earth`s Interior Worksheet A Journey to the Center of the Earth (p. 9
... A Journey to the Center of the Earth (p. 9) 1. What happens to the temperature as you travel closer towards the center of the Earth? 2. What happens to the pressure as you travel down? 3. Name the three main layers that make up the Earth’s interior. ...
... A Journey to the Center of the Earth (p. 9) 1. What happens to the temperature as you travel closer towards the center of the Earth? 2. What happens to the pressure as you travel down? 3. Name the three main layers that make up the Earth’s interior. ...
Electricity and Magn.. - Caledonia High School
... Splits and is wired to all outlets of the house ...
... Splits and is wired to all outlets of the house ...
journey 05 - Auburn High School
... The study of seismic waves allows scientists to “see” inside the earth. Scientists have discovered that seismic waves • refract • reflect • change velocity • and become absorbed by various parts of the Earth’s interior ...
... The study of seismic waves allows scientists to “see” inside the earth. Scientists have discovered that seismic waves • refract • reflect • change velocity • and become absorbed by various parts of the Earth’s interior ...
PPT - Hss-1.us
... by magnetic fields described by Magnetic field lines as shown in the figure below. The magnetic field can be thought of as consisting of lines of force. The forces of magnetic attraction and repulsion move along the lines of force creating a North and South Pole. ...
... by magnetic fields described by Magnetic field lines as shown in the figure below. The magnetic field can be thought of as consisting of lines of force. The forces of magnetic attraction and repulsion move along the lines of force creating a North and South Pole. ...
History of geomagnetism

The history of geomagnetism is concerned with the history of the study of Earth's magnetic field. It encompasses the history of navigation using compasses, studies of the prehistoric magnetic field (archeomagnetism and paleomagnetism), and applications to plate tectonics.Magnetism has been known since prehistory, but knowledge of the Earth's field developed slowly. The horizontal direction of the Earth's field was first measured in the fourth century BC but the vertical direction was not measured until 1544 AD and the intensity was first measured in 1791. At first, compasses were thought to point towards locations in the heavens, then towards magnetic mountains. A modern experimental approach to understanding the Earth's field began with de Magnete, a book published by William Gilbert in 1600. His experiments with a magnetic model of the Earth convinced him that the Earth itself is a large magnet.