Understanding Target Heart Rate.jpg
... tensity levels. ACSM recommends that your intensity levels stay between 55 to 80 percent of your maximum heart rate, for 20 to 60 minutes (or 10 minutes bouts through the day) 3 to 5 days a week. When begining a cardiovascular training program, you must consider the importance of intensity. It is re ...
... tensity levels. ACSM recommends that your intensity levels stay between 55 to 80 percent of your maximum heart rate, for 20 to 60 minutes (or 10 minutes bouts through the day) 3 to 5 days a week. When begining a cardiovascular training program, you must consider the importance of intensity. It is re ...
Chapters 7 and 8
... • congestive heart failure (CHF), heart failure‐ when the work demanded on the heart is greater than the hearts ability to perform • heart murmur – soft blowing or rasping sound heard when listening to heart with a stethoscope ...
... • congestive heart failure (CHF), heart failure‐ when the work demanded on the heart is greater than the hearts ability to perform • heart murmur – soft blowing or rasping sound heard when listening to heart with a stethoscope ...
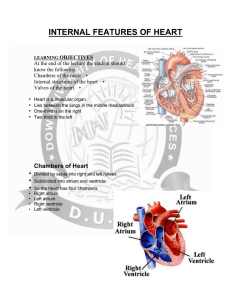
Chambers and internal features of heart
... At the end of the lecture the student should know the following Chambers of the heart • Internal structures of the heart • Valves of the heart • ...
... At the end of the lecture the student should know the following Chambers of the heart • Internal structures of the heart • Valves of the heart • ...
Sheep Heart Dissection Lab
... the preservative as possible. Also run water into the larger blood vessels to force any blood clots out of the heart chambers. 2. Place the heart in a dissecting tray with its ventral surface up (See Figure 36.4 below). Proceed as follows: a. Locate the visceral pericardium, which appears as a thin, ...
... the preservative as possible. Also run water into the larger blood vessels to force any blood clots out of the heart chambers. 2. Place the heart in a dissecting tray with its ventral surface up (See Figure 36.4 below). Proceed as follows: a. Locate the visceral pericardium, which appears as a thin, ...
4.12 To dissect, display and identify an ox`s or sheep`s heart
... Identify the opening at the base of the aorta, above the semi-lunar valves, leading to the coronary arteries ...
... Identify the opening at the base of the aorta, above the semi-lunar valves, leading to the coronary arteries ...
File the circulatory system
... – Two closely related conditions: Angina pectoris: pain that occurs when heart muscle is deprived of oxygen Myocardial infarction: heart attack; part of the heart muscle dies Heart failure – Heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs – Types Cor pulmonale (right-sided heart ...
... – Two closely related conditions: Angina pectoris: pain that occurs when heart muscle is deprived of oxygen Myocardial infarction: heart attack; part of the heart muscle dies Heart failure – Heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs – Types Cor pulmonale (right-sided heart ...
Look after your heart - The Brookside Group Practice
... Along with the change in lifestyle came a change in diet. Fried foods, like crisps, hamburgers and chips became staples in many diets. The combination of a sedentary lifestyle and a rich diet led to an increase in clogged blood vessels, heart attacks, and strokes. The rate of heart disease increased ...
... Along with the change in lifestyle came a change in diet. Fried foods, like crisps, hamburgers and chips became staples in many diets. The combination of a sedentary lifestyle and a rich diet led to an increase in clogged blood vessels, heart attacks, and strokes. The rate of heart disease increased ...
hypoplastic left heart syndrome
... upon the ductus arteriosus (DA) remaining open. The DA is a vessel between the pulmonary arteries (arteries going to the lungs) and aorta which bypasses the left side of the heart The DA normally closes after the baby is born. The baby will often appear well in the first few hours to days of life as ...
... upon the ductus arteriosus (DA) remaining open. The DA is a vessel between the pulmonary arteries (arteries going to the lungs) and aorta which bypasses the left side of the heart The DA normally closes after the baby is born. The baby will often appear well in the first few hours to days of life as ...
Congestive Heart Failure
... • Cardiac output insufficient for metabolic requirements of the body • Systolic dysfunction – decreased myocardial contractility • Diastolic dysfunction – insufficient expansion for ventricular volume • Problems are accentuated by increased demand – high output heart failure ...
... • Cardiac output insufficient for metabolic requirements of the body • Systolic dysfunction – decreased myocardial contractility • Diastolic dysfunction – insufficient expansion for ventricular volume • Problems are accentuated by increased demand – high output heart failure ...
Ventricular Septal Defect - Children`s Heart Federation
... A VSD may also occur in association with other heart Defects. In some cases the VSD is necessary to allow mixing of blood in some forms of congenital heart disease such as Pulmonary Atresia. ...
... A VSD may also occur in association with other heart Defects. In some cases the VSD is necessary to allow mixing of blood in some forms of congenital heart disease such as Pulmonary Atresia. ...
Fetal Pig Dissection Assignment
... 4. What age is your pig______________________________________ 5. How many toes are on the feet? _____________________ Do they have an odd or even number of toes? _________________________________ 6. Locate the hard palate and soft palate epiglottis pharynx Internal anatomy organ checklist Check the ...
... 4. What age is your pig______________________________________ 5. How many toes are on the feet? _____________________ Do they have an odd or even number of toes? _________________________________ 6. Locate the hard palate and soft palate epiglottis pharynx Internal anatomy organ checklist Check the ...
2017 cpt codes for left heart catheterization
... policy and reimbursement information. Please click the links below to. E-mail; Print; RSS; Know your cardiac catheterization codes and guidelines by heart HCPro Coder Connection, September 7, 2005. Know your cardiac catheterization codes. Cardiac catheterization (also called heart catheterization) i ...
... policy and reimbursement information. Please click the links below to. E-mail; Print; RSS; Know your cardiac catheterization codes and guidelines by heart HCPro Coder Connection, September 7, 2005. Know your cardiac catheterization codes. Cardiac catheterization (also called heart catheterization) i ...
Ventricular Septal Defect - Children`s Heart Federation
... usually fade away to nothing. After the first year, the child will be monitored infrequently by a cardiologist. ...
... usually fade away to nothing. After the first year, the child will be monitored infrequently by a cardiologist. ...
Circulatory System
... blood away from capillaries to the heart Veins contain a muscular layer, but less elastic and muscular than arteries Thin walled veins collapse easily when not filled with blood Valves permit flow of blood only in direction of the heart Jugular vein- located in the neck ...
... blood away from capillaries to the heart Veins contain a muscular layer, but less elastic and muscular than arteries Thin walled veins collapse easily when not filled with blood Valves permit flow of blood only in direction of the heart Jugular vein- located in the neck ...
Chapter 2 - Preventing Cardiovascular Disease
... Type II (90% of all diabetes) occurs in older, overweight, sedentary adults Diabetes increases the risk of coronary artery disease 2 to 3 times in men and 3 to 7 times in women ...
... Type II (90% of all diabetes) occurs in older, overweight, sedentary adults Diabetes increases the risk of coronary artery disease 2 to 3 times in men and 3 to 7 times in women ...
This is the way to write a paper
... Norepinephrine can exert adverse effects on the circula/on, both directly and inac/va/on of the sympathe/c nervous system is one of the cardinal pathophysiologic abnormali/es in pa/ents with chronic heart failure. ...
... Norepinephrine can exert adverse effects on the circula/on, both directly and inac/va/on of the sympathe/c nervous system is one of the cardinal pathophysiologic abnormali/es in pa/ents with chronic heart failure. ...
END STAGE HEART FAILURE – TRANSPLANTATION OR LVAD?
... The right ventricular systolic dysfunction is usually due to the left ventricular systolic dysfunction. However, it can also develop as a consequence of ventricular infarction, pulmonary hypertension, chronic severe tricuspid regurgitation, or arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia. The diastoli ...
... The right ventricular systolic dysfunction is usually due to the left ventricular systolic dysfunction. However, it can also develop as a consequence of ventricular infarction, pulmonary hypertension, chronic severe tricuspid regurgitation, or arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia. The diastoli ...
The Cardiovascular System: The Heart
... Right atrium tricuspid valve right ventricle Right ventricle pulmonary semilunar valve pulmonary arteries lungs Lungs pulmonary veins left atrium Left atrium bicuspid valve left ventricle Left ventricle aortic semilunar valve aorta Aorta systemic circulation ...
... Right atrium tricuspid valve right ventricle Right ventricle pulmonary semilunar valve pulmonary arteries lungs Lungs pulmonary veins left atrium Left atrium bicuspid valve left ventricle Left ventricle aortic semilunar valve aorta Aorta systemic circulation ...
pics
... Heart valves ensure unidirectional blood flow through the heart Atrioventricular (AV) valves lie between the atria and the ventricles AV valves prevent backflow into the atria when ventricles contract Chordae tendineae anchor AV valves to papillary ...
... Heart valves ensure unidirectional blood flow through the heart Atrioventricular (AV) valves lie between the atria and the ventricles AV valves prevent backflow into the atria when ventricles contract Chordae tendineae anchor AV valves to papillary ...
Cardiac Muscle
... • Abnormalities in the shape of the waves and changes in their timing send signals that something may be wrong with the intrinsic conduction system or may indicate a myocardial infarct (present or past). • A myocardial infarct is an area of heart tissue in which the cardiac cells have died; it is g ...
... • Abnormalities in the shape of the waves and changes in their timing send signals that something may be wrong with the intrinsic conduction system or may indicate a myocardial infarct (present or past). • A myocardial infarct is an area of heart tissue in which the cardiac cells have died; it is g ...
Pre op Assessment - Iowa Society of PeriAnesthesia Nurses
... Increased oxygen demand: sympathetic stimulation, surgical stress/pain ...
... Increased oxygen demand: sympathetic stimulation, surgical stress/pain ...
– H F R
... The fellow should be an active participant on rounds. With attending supervision, the fellow will lead the HF team that is composed of nurse practitioners, pharmacists, and case managers. The fellow will guide clinical decision-making, educate team members and patients when necessary, and explain th ...
... The fellow should be an active participant on rounds. With attending supervision, the fellow will lead the HF team that is composed of nurse practitioners, pharmacists, and case managers. The fellow will guide clinical decision-making, educate team members and patients when necessary, and explain th ...
Heart failure

Heart failure (HF), often referred to as congestive heart failure (CHF), occurs when the heart is unable to pump sufficiently to maintain blood flow to meet the body's needs. The terms chronic heart failure (CHF) or congestive cardiac failure (CCF) are often used interchangeably with congestive heart failure. Signs and symptoms commonly include shortness of breath, excessive tiredness, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath is usually worse with exercise, while lying down, and may wake the person at night. A limited ability to exercise is also a common feature.Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease including a previous myocardial infarction (heart attack), high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excess alcohol use, infection, and cardiomyopathy of an unknown cause. These cause heart failure by changing either the structure or the functioning of the heart. There are two main types of heart failure: heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure with normal ejection fraction depending on if the ability of the left ventricle to contract is affected, or the heart's ability to relax. The severity of disease is usually graded by the degree of problems with exercise. Heart failure is not the same as myocardial infarction (in which part of the heart muscle dies) or cardiac arrest (in which blood flow stops altogether). Other diseases that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver problems, anemia and thyroid disease.The condition is diagnosed based on the history of the symptoms and a physical examination with confirmation by echocardiography. Blood tests, electrocardiography, and chest radiography may be useful to determine the underlying cause. Treatment depends on the severity and cause of the disease. In people with chronic stable mild heart failure, treatment commonly consists of lifestyle modifications such as stopping smoking, physical exercise, and dietary changes, as well as medications. In those with heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers along with beta blockers are recommended. For those with severe disease, aldosterone antagonists, or hydralazine plus a nitrate may be used. Diuretics are useful for preventing fluid retention. Sometimes, depending on the cause, an implanted device such as a pacemaker or an implantable cardiac defibrillator may be recommended. In some moderate or severe cases cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) may be suggested or cardiac contractility modulation may be of benefit. A ventricular assist device or occasionally a heart transplant may be recommended in those with severe disease despite all other measures.Heart failure is a common, costly, and potentially fatal condition. In developed countries, around 2% of adults have heart failure and in those over the age of 65, this increases to 6–10%. In the year after diagnosis the risk of death is about 35% after which it decreases to below 10% each year. This is similar to the risks with a number of types of cancer. In the United Kingdom the disease is the reason for 5% of emergency hospital admissions. Heart failure has been known since ancient times with the Ebers papyrus commenting on it around 1550 BCE.