- Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapy
... Figure 1 Cardiovascular diseases represented in the Cardiac Centre of St. Elizabeth Catholic General hospital. Abbreviations: HTN, Hypertension; CHF, Congestive Heart Failure; Arrh., Arrhythmia; Misc., Miscellaneous; IHD, Ischemic Heart Disease; CHD, Congenital Heart Disease. ...
... Figure 1 Cardiovascular diseases represented in the Cardiac Centre of St. Elizabeth Catholic General hospital. Abbreviations: HTN, Hypertension; CHF, Congestive Heart Failure; Arrh., Arrhythmia; Misc., Miscellaneous; IHD, Ischemic Heart Disease; CHD, Congenital Heart Disease. ...
The left atrium: an old `barometer` which can reveal great secrets
... Two-dimensional speckle tracking-derived strain, an angle independent tool, overcomes the main drawbacks of tissue Doppler imaging and thus provides more accurate quantification of LA function.10 Compared with normal subjects, the different components of LA function—reservoir, conduit and active con ...
... Two-dimensional speckle tracking-derived strain, an angle independent tool, overcomes the main drawbacks of tissue Doppler imaging and thus provides more accurate quantification of LA function.10 Compared with normal subjects, the different components of LA function—reservoir, conduit and active con ...
heart valves
... ATRIA IN DIASTOLE FOR REMAINDER VENTRICLES DEPOLARIZE, CONTRACT VENTRICULAR PRESSURE INCREASES AV VALVES CLOSE HEART SOUND S1 NO BLOOD EJECTED YET ...
... ATRIA IN DIASTOLE FOR REMAINDER VENTRICLES DEPOLARIZE, CONTRACT VENTRICULAR PRESSURE INCREASES AV VALVES CLOSE HEART SOUND S1 NO BLOOD EJECTED YET ...
A Case of Left Atrial Sarcoma Presenting with Mitral Valve
... Introduction: Primary cardiac tumors are extremely rare with an incidence ranging from 0.0017 to 0.019% [1]. Myxoma, a benign tumor, represent by far almost three quarters of them while the remaining are malignant, predominantly sarcomas [2], [3]. On the other hand, metastatic tumors in the heart ar ...
... Introduction: Primary cardiac tumors are extremely rare with an incidence ranging from 0.0017 to 0.019% [1]. Myxoma, a benign tumor, represent by far almost three quarters of them while the remaining are malignant, predominantly sarcomas [2], [3]. On the other hand, metastatic tumors in the heart ar ...
Chapter 14 PP PDF
... Serves as a point if attachment for the myocardium Serves as electrical insulation between the atria and the ventricles ...
... Serves as a point if attachment for the myocardium Serves as electrical insulation between the atria and the ventricles ...
Chapter 20
... Functions of the Heart --generating blood pressure --routing blood: seperates pulmonary and systemic circulations --ensuring one-way flow of blood --regulating blood supply: changes in contraction rate and force match blood delivery to changing metabolic needs Location of the Heart --behind rib cage ...
... Functions of the Heart --generating blood pressure --routing blood: seperates pulmonary and systemic circulations --ensuring one-way flow of blood --regulating blood supply: changes in contraction rate and force match blood delivery to changing metabolic needs Location of the Heart --behind rib cage ...
Detection and management of preclinical heart failure
... 3. Proof of Principle – TasELF study 4. Lessons about community-based RCTs ...
... 3. Proof of Principle – TasELF study 4. Lessons about community-based RCTs ...
Congestion in Heart Failure - Open Secret Communications
... Lower threshold for arrhythmias Progression of LV dysfunction/remodeling ...
... Lower threshold for arrhythmias Progression of LV dysfunction/remodeling ...
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
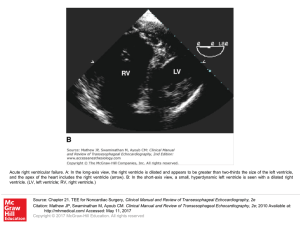
... Acute right ventricular failure. A: In the long-axis view, the right ventricle is dilated and appears to be greater than two-thirds the size of the left ventricle, and the apex of the heart includes the right ventricle (arrow). B: In the short-axis view, a small, hyperdynamic left ventricle is seen ...
... Acute right ventricular failure. A: In the long-axis view, the right ventricle is dilated and appears to be greater than two-thirds the size of the left ventricle, and the apex of the heart includes the right ventricle (arrow). B: In the short-axis view, a small, hyperdynamic left ventricle is seen ...
Computer-assisted Planning of Cardiac Interventions and Heart
... research to understand the underlying mechanisms of heart function and diseases and they help to ask the right questions for further research. They can also be used for learning and training in cardiology. ...
... research to understand the underlying mechanisms of heart function and diseases and they help to ask the right questions for further research. They can also be used for learning and training in cardiology. ...
The Nervous System
... Sympathetic fibers are always “talking” to the smooth muscle in the walls of blood vessels… this is called sympathetic “tone”. This continuous rate of action potential firing leads to continuous release of transmitter and sustained low level of contraction of the smooth muscle, and thus partial vaso ...
... Sympathetic fibers are always “talking” to the smooth muscle in the walls of blood vessels… this is called sympathetic “tone”. This continuous rate of action potential firing leads to continuous release of transmitter and sustained low level of contraction of the smooth muscle, and thus partial vaso ...
Pharmacological Management of Chronic Heart Failure with Left
... It is ideal if the heart rate is kept at around 55 bpm. However, it is uncommon for the up titration to continue when the heart rate reaches 60 bpm or below. Similarly, while the physician may exceed this limit, it is customary not to persevere with the up titration if the systolic BP is at 100 mmHg ...
... It is ideal if the heart rate is kept at around 55 bpm. However, it is uncommon for the up titration to continue when the heart rate reaches 60 bpm or below. Similarly, while the physician may exceed this limit, it is customary not to persevere with the up titration if the systolic BP is at 100 mmHg ...
pdf english - International Journal of Cardiovascular Sciences
... cardiomyopathy, hypertension and valvular disease are the major causes of heart failure due to systolic dysfunction. In diastolic dysfunction, hypertension, coronary artery disease and the restrictive and hypertrophic cardiomyopathies are the most prevalent causes11,12. The diagnostic approach in HF ...
... cardiomyopathy, hypertension and valvular disease are the major causes of heart failure due to systolic dysfunction. In diastolic dysfunction, hypertension, coronary artery disease and the restrictive and hypertrophic cardiomyopathies are the most prevalent causes11,12. The diagnostic approach in HF ...
01. CVS,angina, MI & HTN. 2010
... demand, such as that produced by physical activity, emotional excitement, or any other cause of increased cardiac workload. Episodic chest pain associated with exertion or some other form of stress. ...
... demand, such as that produced by physical activity, emotional excitement, or any other cause of increased cardiac workload. Episodic chest pain associated with exertion or some other form of stress. ...
Valves of the Heart
... presses back against the valves during ventricular contraction, the valves may not remain closed. If many of these connections are ruptured or if the thicker ones are affected, the valves can open in the reverse direction, and blood can backflow into the atria. This results in increased pressure in ...
... presses back against the valves during ventricular contraction, the valves may not remain closed. If many of these connections are ruptured or if the thicker ones are affected, the valves can open in the reverse direction, and blood can backflow into the atria. This results in increased pressure in ...
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFTING
... Blood comes back to heart for reoxygenation via SVC and IVC entering the RA>tricuspid valve>RV> pulmonic valve into the pulmonary trunk>R/L pulmonary arteries>Lungs (reoxygenated)>returns to heart via the pulmonic veins (two per side/four total) into the LA>mitral (bicuspid)valve LV through the aort ...
... Blood comes back to heart for reoxygenation via SVC and IVC entering the RA>tricuspid valve>RV> pulmonic valve into the pulmonary trunk>R/L pulmonary arteries>Lungs (reoxygenated)>returns to heart via the pulmonic veins (two per side/four total) into the LA>mitral (bicuspid)valve LV through the aort ...
Positive Inotropes
... combination confers additional clinical benefits. The inotropic effect of pimobendan is significantly greater than that seen with digoxin, and pimobendan has supplanted digoxin as the first choice for inotropic support in CHF in dogs. There is some debate regarding the use of pimobendan in cats, and ...
... combination confers additional clinical benefits. The inotropic effect of pimobendan is significantly greater than that seen with digoxin, and pimobendan has supplanted digoxin as the first choice for inotropic support in CHF in dogs. There is some debate regarding the use of pimobendan in cats, and ...
The Heart and Associated Blood Vessels
... • The low pitched, quieter, long lasting ‘lub’ sound is due to the bicuspid and tricuspid valves being forced shut when the ventricles contract. • The higher pitched, louder much shorter ‘dub’ sound is due to the semilunar valves snapping shut. ...
... • The low pitched, quieter, long lasting ‘lub’ sound is due to the bicuspid and tricuspid valves being forced shut when the ventricles contract. • The higher pitched, louder much shorter ‘dub’ sound is due to the semilunar valves snapping shut. ...
Reaxys Database Information
... and diastole, and to cyclins B, D1, D3 and E expression. Conclusion: These results agree with the notion that IGF1/IGF-1R and cyclins are involved in the hypertrophic response observed in cardiomyopathies. © 2009 Mahmoudabady et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. ...
... and diastole, and to cyclins B, D1, D3 and E expression. Conclusion: These results agree with the notion that IGF1/IGF-1R and cyclins are involved in the hypertrophic response observed in cardiomyopathies. © 2009 Mahmoudabady et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. ...
File - Dr. Jerry Cronin
... – Adjusts heart rate in response to venous return – Stretch receptors in right atrium • Trigger increase in heart rate ...
... – Adjusts heart rate in response to venous return – Stretch receptors in right atrium • Trigger increase in heart rate ...
PATIENT INFORMATION SHEET Holter (24hr) ECG recording Why
... activities. It is very important that we know what medications are being taken at the time we do the test. An easy way is to bring all your medications with you to the first appointment. The recorder and connecting wires are usually hidden under your normal clothing. The appointment time takes about ...
... activities. It is very important that we know what medications are being taken at the time we do the test. An easy way is to bring all your medications with you to the first appointment. The recorder and connecting wires are usually hidden under your normal clothing. The appointment time takes about ...
Cardiovascular - Daphne - A Palomar College Web Server
... • < 1mm in diameter • Endothelium and smooth muscle • Metarterioles regulate flow of blood into capillaries • Help regulate blood pressure ...
... • < 1mm in diameter • Endothelium and smooth muscle • Metarterioles regulate flow of blood into capillaries • Help regulate blood pressure ...
Clinical Pharmacy Program Guidelines for Multaq Program Prior
... Multaq (dronedarone) is indicated to reduce the risk of hospitalization for atrial fibrillation in patients in sinus rhythm with a history of paroxysmal or persistent atrial fibrillation (AF). 2 . Coverage Criteria: A. Multaq 1. Diagnosis of one of the following: a. Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (A ...
... Multaq (dronedarone) is indicated to reduce the risk of hospitalization for atrial fibrillation in patients in sinus rhythm with a history of paroxysmal or persistent atrial fibrillation (AF). 2 . Coverage Criteria: A. Multaq 1. Diagnosis of one of the following: a. Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (A ...
Heart failure

Heart failure (HF), often referred to as congestive heart failure (CHF), occurs when the heart is unable to pump sufficiently to maintain blood flow to meet the body's needs. The terms chronic heart failure (CHF) or congestive cardiac failure (CCF) are often used interchangeably with congestive heart failure. Signs and symptoms commonly include shortness of breath, excessive tiredness, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath is usually worse with exercise, while lying down, and may wake the person at night. A limited ability to exercise is also a common feature.Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease including a previous myocardial infarction (heart attack), high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excess alcohol use, infection, and cardiomyopathy of an unknown cause. These cause heart failure by changing either the structure or the functioning of the heart. There are two main types of heart failure: heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure with normal ejection fraction depending on if the ability of the left ventricle to contract is affected, or the heart's ability to relax. The severity of disease is usually graded by the degree of problems with exercise. Heart failure is not the same as myocardial infarction (in which part of the heart muscle dies) or cardiac arrest (in which blood flow stops altogether). Other diseases that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver problems, anemia and thyroid disease.The condition is diagnosed based on the history of the symptoms and a physical examination with confirmation by echocardiography. Blood tests, electrocardiography, and chest radiography may be useful to determine the underlying cause. Treatment depends on the severity and cause of the disease. In people with chronic stable mild heart failure, treatment commonly consists of lifestyle modifications such as stopping smoking, physical exercise, and dietary changes, as well as medications. In those with heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers along with beta blockers are recommended. For those with severe disease, aldosterone antagonists, or hydralazine plus a nitrate may be used. Diuretics are useful for preventing fluid retention. Sometimes, depending on the cause, an implanted device such as a pacemaker or an implantable cardiac defibrillator may be recommended. In some moderate or severe cases cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) may be suggested or cardiac contractility modulation may be of benefit. A ventricular assist device or occasionally a heart transplant may be recommended in those with severe disease despite all other measures.Heart failure is a common, costly, and potentially fatal condition. In developed countries, around 2% of adults have heart failure and in those over the age of 65, this increases to 6–10%. In the year after diagnosis the risk of death is about 35% after which it decreases to below 10% each year. This is similar to the risks with a number of types of cancer. In the United Kingdom the disease is the reason for 5% of emergency hospital admissions. Heart failure has been known since ancient times with the Ebers papyrus commenting on it around 1550 BCE.