POD week 16 Problem 1
... o First I decided to find the area of the semi circle in the heart. (∏r²) but since this is only half of a circle my formula was (to find area of 1/2∏r² (using pi as 3.14) full circle.) o The diameter of the semi-circle is 4 ½ so I divided that by 2 to get the radius (2.25) o 2.25²*3.14*1/2~7.9 o So ...
... o First I decided to find the area of the semi circle in the heart. (∏r²) but since this is only half of a circle my formula was (to find area of 1/2∏r² (using pi as 3.14) full circle.) o The diameter of the semi-circle is 4 ½ so I divided that by 2 to get the radius (2.25) o 2.25²*3.14*1/2~7.9 o So ...
Slide ()
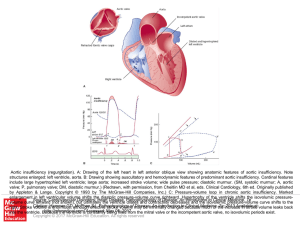
... by Appleton & Lange. Copyright © 1993 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.) C: Pressure-volume loop in chronic aortic insufficiency. Marked enlargement in left ventricular volume shifts the diastolic pressure-volume curve rightward. Hypertrophy of the ventricle shifts the isovolumic pressureSource: Ca ...
... by Appleton & Lange. Copyright © 1993 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.) C: Pressure-volume loop in chronic aortic insufficiency. Marked enlargement in left ventricular volume shifts the diastolic pressure-volume curve rightward. Hypertrophy of the ventricle shifts the isovolumic pressureSource: Ca ...
cardiac rehab fact sheet 2013 Final
... have a heart attack and more than 30% will have a second and potentially fatal event.1 Cardiac rehabilitation (CR) reduces the risk of a future cardiac event by stabilizing, slowing or even reversing the progression of cardiovascular disease (CVD).2 Patients with other cardiovascular diseases such a ...
... have a heart attack and more than 30% will have a second and potentially fatal event.1 Cardiac rehabilitation (CR) reduces the risk of a future cardiac event by stabilizing, slowing or even reversing the progression of cardiovascular disease (CVD).2 Patients with other cardiovascular diseases such a ...
Jeopardy!
... Explain the anatomical difference between the left and right ventricles. L larger and wall thicker Incorrect ...
... Explain the anatomical difference between the left and right ventricles. L larger and wall thicker Incorrect ...
Pacers, ablation, cardioversion, telemetry, Intro to ACLS
... heart pumps out to body in 1 min. NORMAL: 5 to 8 L • CO= HR x SV (CO can be changed by altering heart rate, stroke vol. or both) • Stroke Volume = the amount of blood that the ...
... heart pumps out to body in 1 min. NORMAL: 5 to 8 L • CO= HR x SV (CO can be changed by altering heart rate, stroke vol. or both) • Stroke Volume = the amount of blood that the ...
1. Describe the cardiac conduction system and an ECG. Tell how an
... there, the signal travels to the AV node, through the bundle of HIS, down the bundle branches, and through the Purkinje fibers, causing the ventricles to contract. This signal creates an electrical current that can be seen on a graph called an Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG). Doctors use an ECG to mo ...
... there, the signal travels to the AV node, through the bundle of HIS, down the bundle branches, and through the Purkinje fibers, causing the ventricles to contract. This signal creates an electrical current that can be seen on a graph called an Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG). Doctors use an ECG to mo ...
(Un)Healthy Hearts
... How does oxygen get to the heart muscle? Coronary arteries Blockage of coronary arteries means the heart does not get the oxygen it needs Ischemia: inadequate blood supply to a region Infarction: obstruction of blood supply to a region causing death of tissue ...
... How does oxygen get to the heart muscle? Coronary arteries Blockage of coronary arteries means the heart does not get the oxygen it needs Ischemia: inadequate blood supply to a region Infarction: obstruction of blood supply to a region causing death of tissue ...
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
... 17. Which of the following sequences is they correct pathway of electrical conduction in the heart? a) AV node, SA node, bundle of His, Purkinje system b) SA node, AV node, Purkinje system, bundle of His c) SA node, AV node, bundle of His, Purkinje system d) Sa node, bundle of His, AV node, Purkinje ...
... 17. Which of the following sequences is they correct pathway of electrical conduction in the heart? a) AV node, SA node, bundle of His, Purkinje system b) SA node, AV node, Purkinje system, bundle of His c) SA node, AV node, bundle of His, Purkinje system d) Sa node, bundle of His, AV node, Purkinje ...
sudden loss of consciousness (syncope)
... When a cardiac condition is suspected, medical evaluation is of utmost importance to prevent sudden cardiac death. A careful history and physical examination will eliminate many of other causes of syncope. The principle test required is the electrocardiogram (ECG, EKG), and specific observations for ...
... When a cardiac condition is suspected, medical evaluation is of utmost importance to prevent sudden cardiac death. A careful history and physical examination will eliminate many of other causes of syncope. The principle test required is the electrocardiogram (ECG, EKG), and specific observations for ...
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSRJCE)
... given before the filtering stage, the noise signals would also have been amplified, which would have led to further trouble! Also, a common emitter amplifier is to be designed with a gain of 100, which will have an adequate frequency response. Increasing the gain by changing the design parameters ma ...
... given before the filtering stage, the noise signals would also have been amplified, which would have led to further trouble! Also, a common emitter amplifier is to be designed with a gain of 100, which will have an adequate frequency response. Increasing the gain by changing the design parameters ma ...
Atrial Fibrillation - Anticoagulation Europe
... If you are healthy and your heart is working normally you are likely to have a regular resting heart rate of around 60 to 90 beats per minute. If you are experiencing atrial fibrillation (AF), however, you may notice your heartbeat becoming irregular and speeding up for no apparent reason. These fee ...
... If you are healthy and your heart is working normally you are likely to have a regular resting heart rate of around 60 to 90 beats per minute. If you are experiencing atrial fibrillation (AF), however, you may notice your heartbeat becoming irregular and speeding up for no apparent reason. These fee ...
Editorials Original Articles Advances in Arrhythmia and
... in Circulation: Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology can be obtained via RightsLink, a service of the Copyright Clearance Center, not the Editorial Office. Once the online version of the published article for which permission is being requested is located, click Request Permissions in the middle column ...
... in Circulation: Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology can be obtained via RightsLink, a service of the Copyright Clearance Center, not the Editorial Office. Once the online version of the published article for which permission is being requested is located, click Request Permissions in the middle column ...
Heart rate and speed dynamics in maratho
... marathon was presented in an attempt to unveil the scaling law behaviour using the Wavelet Transform Modulus Maxima (WTMM) method proposed by Arneodo et al. [9], which estimates the spectrum of singularities of the Hölder exponents using multifractal formalism [74]. This work previously undertaken b ...
... marathon was presented in an attempt to unveil the scaling law behaviour using the Wavelet Transform Modulus Maxima (WTMM) method proposed by Arneodo et al. [9], which estimates the spectrum of singularities of the Hölder exponents using multifractal formalism [74]. This work previously undertaken b ...
maternity and myocardial failure in african women
... failure linked with maternity are described. We appraise the nature of this link. Priority in describing a syndrome of heart failure connected with childbearing may be given to the independent reports of Gouley et al., and of Hull and Hafkesbring, both in 1937, despite the claims made for Virchow (1 ...
... failure linked with maternity are described. We appraise the nature of this link. Priority in describing a syndrome of heart failure connected with childbearing may be given to the independent reports of Gouley et al., and of Hull and Hafkesbring, both in 1937, despite the claims made for Virchow (1 ...
Health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well
... about the roles your heart valves play in healthy circulation. ...
... about the roles your heart valves play in healthy circulation. ...
Treatment of heart failure with preserved Karen Hogg, John J.V. McMurray*
... increase cytosolic calcium concentrations which, if not rapidly reversed, should impair myocardial relaxation. It is possible, however, that the sympatho-inhibitory, pro-parasympathetic and renin–angiotensin–aldosteronesuppressing actions of digoxin are beneficial in HF 38 . The Digitalis Investigat ...
... increase cytosolic calcium concentrations which, if not rapidly reversed, should impair myocardial relaxation. It is possible, however, that the sympatho-inhibitory, pro-parasympathetic and renin–angiotensin–aldosteronesuppressing actions of digoxin are beneficial in HF 38 . The Digitalis Investigat ...
CPR Facts and Statistics
... Approximately 335,000 of all annual adult coronary heart disease deaths in the U.S. are due to sudden cardiac arrest, suffered outside the hospital setting and in hospital emergency departments. About 900 Americans die every day due to sudden cardiac arrest. ...
... Approximately 335,000 of all annual adult coronary heart disease deaths in the U.S. are due to sudden cardiac arrest, suffered outside the hospital setting and in hospital emergency departments. About 900 Americans die every day due to sudden cardiac arrest. ...
Development of the Heart
... The human heart is the rst functional organ to develop. It begins beating and pumping blood around day 21 or 22, a mere three weeks after fertilization. This emphasizes the critical nature of the heart in distributing blood through the vessels and the vital exchange of nutrients, oxygen, and wastes ...
... The human heart is the rst functional organ to develop. It begins beating and pumping blood around day 21 or 22, a mere three weeks after fertilization. This emphasizes the critical nature of the heart in distributing blood through the vessels and the vital exchange of nutrients, oxygen, and wastes ...
CARDAIC OUTPUT AND ITS REGULATION
... determined by left ventricular end diastolic volume • Afterload pressure against which ventricles pump blood determined by total peripheral resistance ...
... determined by left ventricular end diastolic volume • Afterload pressure against which ventricles pump blood determined by total peripheral resistance ...
... is the first reported case with heart failure associated both with chylothorax and chylous ascites. It is important to consider heart failure among the causes of both disorders. Case report An 84 year old white woman was admitted following development of progresive dyspnoea, orthopnoea, abdominal di ...
Anatomy of the Cardiovascular System
... Occlude coronary artery heart tissue deprived of oxygen cell death – S/S: ...
... Occlude coronary artery heart tissue deprived of oxygen cell death – S/S: ...
Intraventricular Pressure Gradients in Heart Failure
... The present study showed that diastolic IVPGs, a marker of normal ventricular filling, and systolic IVPGs, a marker of normal ventricular emptying, are abolished in failing hearts. Previously, we demonstrated that diastolic and systolic IVPGs are modulated by physiological nonuniformity between basa ...
... The present study showed that diastolic IVPGs, a marker of normal ventricular filling, and systolic IVPGs, a marker of normal ventricular emptying, are abolished in failing hearts. Previously, we demonstrated that diastolic and systolic IVPGs are modulated by physiological nonuniformity between basa ...
Aortic Regurgitation - Cormedicalgroup.com
... Aortic regurgitation Aortic regurgitation is leakage from the aortic valve. This valve separates the aorta, the largest blood vessel from the left ventricle, the heart's primary pumping chamber. The aorta receives blood from the heart and distributes it to the body. Regurgitation means that the valv ...
... Aortic regurgitation Aortic regurgitation is leakage from the aortic valve. This valve separates the aorta, the largest blood vessel from the left ventricle, the heart's primary pumping chamber. The aorta receives blood from the heart and distributes it to the body. Regurgitation means that the valv ...
Heart failure

Heart failure (HF), often referred to as congestive heart failure (CHF), occurs when the heart is unable to pump sufficiently to maintain blood flow to meet the body's needs. The terms chronic heart failure (CHF) or congestive cardiac failure (CCF) are often used interchangeably with congestive heart failure. Signs and symptoms commonly include shortness of breath, excessive tiredness, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath is usually worse with exercise, while lying down, and may wake the person at night. A limited ability to exercise is also a common feature.Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease including a previous myocardial infarction (heart attack), high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excess alcohol use, infection, and cardiomyopathy of an unknown cause. These cause heart failure by changing either the structure or the functioning of the heart. There are two main types of heart failure: heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure with normal ejection fraction depending on if the ability of the left ventricle to contract is affected, or the heart's ability to relax. The severity of disease is usually graded by the degree of problems with exercise. Heart failure is not the same as myocardial infarction (in which part of the heart muscle dies) or cardiac arrest (in which blood flow stops altogether). Other diseases that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver problems, anemia and thyroid disease.The condition is diagnosed based on the history of the symptoms and a physical examination with confirmation by echocardiography. Blood tests, electrocardiography, and chest radiography may be useful to determine the underlying cause. Treatment depends on the severity and cause of the disease. In people with chronic stable mild heart failure, treatment commonly consists of lifestyle modifications such as stopping smoking, physical exercise, and dietary changes, as well as medications. In those with heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers along with beta blockers are recommended. For those with severe disease, aldosterone antagonists, or hydralazine plus a nitrate may be used. Diuretics are useful for preventing fluid retention. Sometimes, depending on the cause, an implanted device such as a pacemaker or an implantable cardiac defibrillator may be recommended. In some moderate or severe cases cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) may be suggested or cardiac contractility modulation may be of benefit. A ventricular assist device or occasionally a heart transplant may be recommended in those with severe disease despite all other measures.Heart failure is a common, costly, and potentially fatal condition. In developed countries, around 2% of adults have heart failure and in those over the age of 65, this increases to 6–10%. In the year after diagnosis the risk of death is about 35% after which it decreases to below 10% each year. This is similar to the risks with a number of types of cancer. In the United Kingdom the disease is the reason for 5% of emergency hospital admissions. Heart failure has been known since ancient times with the Ebers papyrus commenting on it around 1550 BCE.