Welcome to the Cardiac Rehabilitation Department
... • First degree • Second degree • Third degree or complete heart block (this type requires a pacemaker) ...
... • First degree • Second degree • Third degree or complete heart block (this type requires a pacemaker) ...
Introduction to cardiac conditions
... volume- the amount of blood expelled by the left ventricle with each contraction) • Preload- The stretch on the heart before it contracts • Afterload- It refers to the resistance against which the ventricles must work against to eject their blood volume • Contractility- Refers to the strength and ef ...
... volume- the amount of blood expelled by the left ventricle with each contraction) • Preload- The stretch on the heart before it contracts • Afterload- It refers to the resistance against which the ventricles must work against to eject their blood volume • Contractility- Refers to the strength and ef ...
atrial_standstill
... • Signs of congestive heart failure may develop, and weakness and sluggishness (lethargy) may persist even after heart rate and rhythm are corrected with the pacemaker; CHF signs include cough, difficulty breathing (dyspnea), bluish discoloration of the skin and moist tissues (mucous membranes) of t ...
... • Signs of congestive heart failure may develop, and weakness and sluggishness (lethargy) may persist even after heart rate and rhythm are corrected with the pacemaker; CHF signs include cough, difficulty breathing (dyspnea), bluish discoloration of the skin and moist tissues (mucous membranes) of t ...
Heart Defect Closure Without Surgery
... will be required for closure of ASD or PFO. This is done by passing a probe down your throat. Suitability is assessed by looking at the size and the position of the defect, as well as if there are any other associated congenital abnormalities in your heart. Once the defect is found suitable for clos ...
... will be required for closure of ASD or PFO. This is done by passing a probe down your throat. Suitability is assessed by looking at the size and the position of the defect, as well as if there are any other associated congenital abnormalities in your heart. Once the defect is found suitable for clos ...
Cardiovascular Disease PP
... chambers of the heart there are valves that prevent the blood from flowing in the wrong direction. The valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle is the mitral valve. The valve between the right atrium and right ventricle is the tricuspid. There are two other valves within the heart where ...
... chambers of the heart there are valves that prevent the blood from flowing in the wrong direction. The valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle is the mitral valve. The valve between the right atrium and right ventricle is the tricuspid. There are two other valves within the heart where ...
Atrial Standstill - Milliken Animal Clinic
... • Signs of congestive heart failure may develop, and weakness and sluggishness (lethargy) may persist even after heart rate and rhythm are corrected with the pacemaker; CHF signs include cough, difficulty breathing (dyspnea), bluish discoloration of the skin and moist tissues (mucous membranes) of t ...
... • Signs of congestive heart failure may develop, and weakness and sluggishness (lethargy) may persist even after heart rate and rhythm are corrected with the pacemaker; CHF signs include cough, difficulty breathing (dyspnea), bluish discoloration of the skin and moist tissues (mucous membranes) of t ...
Ventricular Septal Defect - Echo ED: Diagnostic Medical
... the hemoglobin in the blood; this is normal during exercise but when resting this is quite dangerous. Second, when the heart beats too rapidly, it may pump blood less efficiently as there is less time for the myocardium to relax between contractions. Third, the faster the heart beats, the more oxyge ...
... the hemoglobin in the blood; this is normal during exercise but when resting this is quite dangerous. Second, when the heart beats too rapidly, it may pump blood less efficiently as there is less time for the myocardium to relax between contractions. Third, the faster the heart beats, the more oxyge ...
Document
... the needle electrodes… the artificial pacemaker started to work and the ventricular complexes [sped up] to about 76 bpm. However, when we stopped the pacemaker, the ventricular idiopathic rate went back down to the 20’s.” Unpublished proceedings of a conference held on February 16, 1942 by the Brook ...
... the needle electrodes… the artificial pacemaker started to work and the ventricular complexes [sped up] to about 76 bpm. However, when we stopped the pacemaker, the ventricular idiopathic rate went back down to the 20’s.” Unpublished proceedings of a conference held on February 16, 1942 by the Brook ...
File - Sheffield Peer Teaching Society
... Image from: http://hyperphysics.phy-‐astr.gsu.edu/hbase/Biology/ecg.html ...
... Image from: http://hyperphysics.phy-‐astr.gsu.edu/hbase/Biology/ecg.html ...
History of fall
... in older people who fall whilst living independently. They may be effective in those living in institutional care who are at high risk of hip fracture but acceptance and adherence is poor as they are uncomfortable and difficult to get on and off quickly. NICE recommends that all people at risk of ...
... in older people who fall whilst living independently. They may be effective in those living in institutional care who are at high risk of hip fracture but acceptance and adherence is poor as they are uncomfortable and difficult to get on and off quickly. NICE recommends that all people at risk of ...
ePapyrus PDF Document
... Department of Pediatrics, Cardiac and Vascular Center, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea ...
... Department of Pediatrics, Cardiac and Vascular Center, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea ...
It Takes a Lickin`, but Keeps on Tickin`….
... push real hard on this artery because it could cause them to pass out if after a short time.) Have students take their pulse for one minute counting each beat and then record that number on a scratch piece of paper. While students are taking their pulse, FAST FORWARD the video to the video picture o ...
... push real hard on this artery because it could cause them to pass out if after a short time.) Have students take their pulse for one minute counting each beat and then record that number on a scratch piece of paper. While students are taking their pulse, FAST FORWARD the video to the video picture o ...
Right ventricular failure in congenital heart disease
... includes hypertrophy2). Although some reports state that hyper trophy itself is beneficial for overcoming the increased backward pressure, it is well accepted that a persistent increase in the pressure of the right ventricle causes a loss of contractile force that is required for pumping out the bl ...
... includes hypertrophy2). Although some reports state that hyper trophy itself is beneficial for overcoming the increased backward pressure, it is well accepted that a persistent increase in the pressure of the right ventricle causes a loss of contractile force that is required for pumping out the bl ...
PDF - the Houpt Lab
... into the lungs and systemic circulation Diastolic pressure (bottom number) arterial pressure when ventricle is relaxed Systolic pressure (top number) arterial pressure when ventricle contracts and pumps ...
... into the lungs and systemic circulation Diastolic pressure (bottom number) arterial pressure when ventricle is relaxed Systolic pressure (top number) arterial pressure when ventricle contracts and pumps ...
Ventricular Tachycardia
... by other heart problems such as coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, an enlarged heart (cardiomyopathy) or heart valve disease. It also can develop after a heart attack (myocardial infarction) or after heart surgery because of scar tissue that forms on the heart. Ventricular tachycardia can ...
... by other heart problems such as coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, an enlarged heart (cardiomyopathy) or heart valve disease. It also can develop after a heart attack (myocardial infarction) or after heart surgery because of scar tissue that forms on the heart. Ventricular tachycardia can ...
IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS)
... with congestive heart failure with age, sex, educational status, occupation, marital status, type of work, habits, dietary pattern. Planned nursing interventions were effective and individualized care is given which reduced length of hospital ...
... with congestive heart failure with age, sex, educational status, occupation, marital status, type of work, habits, dietary pattern. Planned nursing interventions were effective and individualized care is given which reduced length of hospital ...
makassed islamic charitable hospital
... d. Most cases of mitral valve stenosis are due to chronic rheumatic valve disease. ...
... d. Most cases of mitral valve stenosis are due to chronic rheumatic valve disease. ...
Heart Rate - Vernon Hills High School
... When the heart contracts and blood flows to the rest of the body, it does so at a certain pressure. ...
... When the heart contracts and blood flows to the rest of the body, it does so at a certain pressure. ...
Tetrology of fallot
... reproduced results displayed with certain cardiac malformations. This anomaly accounts for 10% of all congenital heart disease and has an estimated prevalence of 1 in 2000 births ...
... reproduced results displayed with certain cardiac malformations. This anomaly accounts for 10% of all congenital heart disease and has an estimated prevalence of 1 in 2000 births ...
Final manuscript for IC - Imperial Spiral
... Activity of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is elevated in patients with heart failure and it has deleterious effects on the heart, peripheral vasculature, kidneys and skeletal muscle.2-7 The majority of this evidence relates to heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF).7 In patients ...
... Activity of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is elevated in patients with heart failure and it has deleterious effects on the heart, peripheral vasculature, kidneys and skeletal muscle.2-7 The majority of this evidence relates to heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF).7 In patients ...
11 Heart - bloodhounds Incorporated
... After Diastole occurs the ventricles begin to contract from the apex towards the base of the heart The deoxygenated blood on the right side of the heart is pushed through the pulmonary trunk after opening the semi-lunar valve to the pulmonary arteries into the lungs to become oxygenated. The oxygena ...
... After Diastole occurs the ventricles begin to contract from the apex towards the base of the heart The deoxygenated blood on the right side of the heart is pushed through the pulmonary trunk after opening the semi-lunar valve to the pulmonary arteries into the lungs to become oxygenated. The oxygena ...
Who Discovered the Frank-Starling Mechanism?
... isolated frog heart was connected to an artificial circulation. A side arm was inserted to enable pressure measurements with a manometer. It was a working heart preparation with recirculation. The primary aim was to study the effect of temperature on the frequency and contraction of the heart. It wa ...
... isolated frog heart was connected to an artificial circulation. A side arm was inserted to enable pressure measurements with a manometer. It was a working heart preparation with recirculation. The primary aim was to study the effect of temperature on the frequency and contraction of the heart. It wa ...
Imaging of hypoplastic left heart syndrome –A rare
... aortic orifice and hypoplasia of ascending aorta constitutes Hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS). Ultrasound and fetal cardiac echocardiography play an important role in detecting HLHS prenatally. HLHS can be detected by 18 – 22 weeks of gestation by USG. It is the most common cardiac malformatio ...
... aortic orifice and hypoplasia of ascending aorta constitutes Hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS). Ultrasound and fetal cardiac echocardiography play an important role in detecting HLHS prenatally. HLHS can be detected by 18 – 22 weeks of gestation by USG. It is the most common cardiac malformatio ...
this section does not print
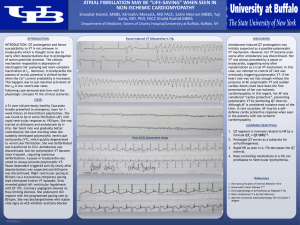
... eventually triggering polymorphic VT. If her heart rate was not fast enough without the presence of AF, polymorphic VT and sudden cardiac death could have been the first presentation of her non-ischemic cardiomyopathy. In this regard, her AF was considered “cardio-protective”, preventing polymorphic ...
... eventually triggering polymorphic VT. If her heart rate was not fast enough without the presence of AF, polymorphic VT and sudden cardiac death could have been the first presentation of her non-ischemic cardiomyopathy. In this regard, her AF was considered “cardio-protective”, preventing polymorphic ...
Anaesthesia for the Patient with Pulmonary Hypertension
... 1. The presence of severe systemic disease in a patient undergoing intermediate risk surgery. Optimisation of the patient’s chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and pulmonary hypertension is warranted pre-operatively. 2. The cardiovascular and respiratory sequelae of pneumoperitoneum, trendelenburg ...
... 1. The presence of severe systemic disease in a patient undergoing intermediate risk surgery. Optimisation of the patient’s chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and pulmonary hypertension is warranted pre-operatively. 2. The cardiovascular and respiratory sequelae of pneumoperitoneum, trendelenburg ...
Heart failure

Heart failure (HF), often referred to as congestive heart failure (CHF), occurs when the heart is unable to pump sufficiently to maintain blood flow to meet the body's needs. The terms chronic heart failure (CHF) or congestive cardiac failure (CCF) are often used interchangeably with congestive heart failure. Signs and symptoms commonly include shortness of breath, excessive tiredness, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath is usually worse with exercise, while lying down, and may wake the person at night. A limited ability to exercise is also a common feature.Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease including a previous myocardial infarction (heart attack), high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excess alcohol use, infection, and cardiomyopathy of an unknown cause. These cause heart failure by changing either the structure or the functioning of the heart. There are two main types of heart failure: heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure with normal ejection fraction depending on if the ability of the left ventricle to contract is affected, or the heart's ability to relax. The severity of disease is usually graded by the degree of problems with exercise. Heart failure is not the same as myocardial infarction (in which part of the heart muscle dies) or cardiac arrest (in which blood flow stops altogether). Other diseases that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver problems, anemia and thyroid disease.The condition is diagnosed based on the history of the symptoms and a physical examination with confirmation by echocardiography. Blood tests, electrocardiography, and chest radiography may be useful to determine the underlying cause. Treatment depends on the severity and cause of the disease. In people with chronic stable mild heart failure, treatment commonly consists of lifestyle modifications such as stopping smoking, physical exercise, and dietary changes, as well as medications. In those with heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers along with beta blockers are recommended. For those with severe disease, aldosterone antagonists, or hydralazine plus a nitrate may be used. Diuretics are useful for preventing fluid retention. Sometimes, depending on the cause, an implanted device such as a pacemaker or an implantable cardiac defibrillator may be recommended. In some moderate or severe cases cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) may be suggested or cardiac contractility modulation may be of benefit. A ventricular assist device or occasionally a heart transplant may be recommended in those with severe disease despite all other measures.Heart failure is a common, costly, and potentially fatal condition. In developed countries, around 2% of adults have heart failure and in those over the age of 65, this increases to 6–10%. In the year after diagnosis the risk of death is about 35% after which it decreases to below 10% each year. This is similar to the risks with a number of types of cancer. In the United Kingdom the disease is the reason for 5% of emergency hospital admissions. Heart failure has been known since ancient times with the Ebers papyrus commenting on it around 1550 BCE.