How to Survive a Heart Attack Be Lean
... STENOSIS) which allows sufficient time for the growing collaterals to preserve myocardial viability. Thus, repeated effort – related but stable angina or recurrent ‘silent’ ischemia is associated with adequate developing CCC. With or without diabetes, ‘silent’ ischemia can be normalized by CCC. [Int ...
... STENOSIS) which allows sufficient time for the growing collaterals to preserve myocardial viability. Thus, repeated effort – related but stable angina or recurrent ‘silent’ ischemia is associated with adequate developing CCC. With or without diabetes, ‘silent’ ischemia can be normalized by CCC. [Int ...
Hypotension and shock: The truth about blood pressure : Nursing2016
... Many clinicians consider diuretics such as furosemide as BP-lowering drugs. But a patient’s BP response to furosemide depends on his location on the Frank-Starling curve: When patients are hypovolemic (understretched myocardium) or even euvolemic (optimally stretched myocardium), furosemide will gen ...
... Many clinicians consider diuretics such as furosemide as BP-lowering drugs. But a patient’s BP response to furosemide depends on his location on the Frank-Starling curve: When patients are hypovolemic (understretched myocardium) or even euvolemic (optimally stretched myocardium), furosemide will gen ...
Intro to Cardiovascular System
... Differences in Right and Left Ventricles Left ventricle is visibly more muscular It is responsible for pushing the blood out of the heart and into the vessel systems that carry blood to the entire body ...
... Differences in Right and Left Ventricles Left ventricle is visibly more muscular It is responsible for pushing the blood out of the heart and into the vessel systems that carry blood to the entire body ...
Effects of Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy on the First Heart Sound...
... reduces the risk of adverse outcomes in well selected patients, is cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) using an implantable pacemaker for biventricular pacing [3]. However, the benefit of CRT treatment varies greatly among patients. Between 25-40% of treated patients see no benefit [2], and the ...
... reduces the risk of adverse outcomes in well selected patients, is cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) using an implantable pacemaker for biventricular pacing [3]. However, the benefit of CRT treatment varies greatly among patients. Between 25-40% of treated patients see no benefit [2], and the ...
rhytmcen
... has highest success rate and quickest action, but can cause dysrhythmias after single dose) Chronic AF usually with cardiomyopathy: rate control, anticoagulation for 3 weeks (or TEE) followed by electrical cardioversion ...
... has highest success rate and quickest action, but can cause dysrhythmias after single dose) Chronic AF usually with cardiomyopathy: rate control, anticoagulation for 3 weeks (or TEE) followed by electrical cardioversion ...
Homogeneity out of heterogeneity.
... turbulence. This remarkable adaptation of form to function becomes apparent when disease alters the patterns of blood flow through the heart. For example, a narrowed valve or a defect in the interventricular septum creates turbulence that dissipates the energy of cardiac contraction and is readily d ...
... turbulence. This remarkable adaptation of form to function becomes apparent when disease alters the patterns of blood flow through the heart. For example, a narrowed valve or a defect in the interventricular septum creates turbulence that dissipates the energy of cardiac contraction and is readily d ...
Angina Pectoris - RadiologyInfo.org
... like exercise. The second time will be at rest. Performing the evaluation both with stress and rest helps determine if the decreased blood flow only occurs with exercise. The coronary arteries (blood vessels that supply blood and oxygen to the heart) can also be imaged similar to CT angiography to l ...
... like exercise. The second time will be at rest. Performing the evaluation both with stress and rest helps determine if the decreased blood flow only occurs with exercise. The coronary arteries (blood vessels that supply blood and oxygen to the heart) can also be imaged similar to CT angiography to l ...
Serial ECG Analysis after Myocardial Infarction: When Heart Failure
... process. After MI, patients have a strongly increased risk of developing HF. HF is known to be accompanied by cardiac enlargement, hypertrophy and fibrosis; all these are factors that corrupt conduction and increase action potential durations in affected areas, thus having a detrimental influence on ...
... process. After MI, patients have a strongly increased risk of developing HF. HF is known to be accompanied by cardiac enlargement, hypertrophy and fibrosis; all these are factors that corrupt conduction and increase action potential durations in affected areas, thus having a detrimental influence on ...
Diastolic Heart Failure - Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center
... fied in patients with a normal ejection fraction,23 but the predominant abnormality in this condition is in diastole. The left ventricular size and ejection fraction are normal, and the left ventricle has a limited capacity to fill at a normal left atrial pressure.4 Patients with diastolic dysfuncti ...
... fied in patients with a normal ejection fraction,23 but the predominant abnormality in this condition is in diastole. The left ventricular size and ejection fraction are normal, and the left ventricle has a limited capacity to fill at a normal left atrial pressure.4 Patients with diastolic dysfuncti ...
Heart Functions: the MEA and the Frank Starling Law of the heart 2/14
... • The mean electrical axis is the average direction of depolarization in the heart. • Einthoven’s Triangle: represents an equilateral triangle at the center of chest. (remember the heart is shifted slight to left side) • Dead heart tissue does not depolarize • ECG Changes: Large R-wave becomes a sma ...
... • The mean electrical axis is the average direction of depolarization in the heart. • Einthoven’s Triangle: represents an equilateral triangle at the center of chest. (remember the heart is shifted slight to left side) • Dead heart tissue does not depolarize • ECG Changes: Large R-wave becomes a sma ...
Trying to succeed when the right ventricle fails
... patients with systolic and diastolic heart failure and are associated with poor survival. Simple echocardiographic and MRI indices of right ventricular function relate to prognosis and may also be useful in following response to therapy. Management of acute and chronic right ventricular failure is l ...
... patients with systolic and diastolic heart failure and are associated with poor survival. Simple echocardiographic and MRI indices of right ventricular function relate to prognosis and may also be useful in following response to therapy. Management of acute and chronic right ventricular failure is l ...
Diastolic Heart Failure - Ether
... fied in patients with a normal ejection fraction,23 but the predominant abnormality in this condition is in diastole. The left ventricular size and ejection fraction are normal, and the left ventricle has a limited capacity to fill at a normal left atrial pressure.4 Patients with diastolic dysfuncti ...
... fied in patients with a normal ejection fraction,23 but the predominant abnormality in this condition is in diastole. The left ventricular size and ejection fraction are normal, and the left ventricle has a limited capacity to fill at a normal left atrial pressure.4 Patients with diastolic dysfuncti ...
MATERIALS AND METHODS
... water at 0.1 M concentration and stored separately. Stock solution of T.T.C was prepared in distilled water approximately as a 2% solution. At the time of incubation the phosphate solutions were mixed to give a pH of 8.0. Then an equal amount of the T.T.C. solution was added. The addition of the T.T ...
... water at 0.1 M concentration and stored separately. Stock solution of T.T.C was prepared in distilled water approximately as a 2% solution. At the time of incubation the phosphate solutions were mixed to give a pH of 8.0. Then an equal amount of the T.T.C. solution was added. The addition of the T.T ...
cardiovascular a&p
... dilates the coronary arteries • May take up to 3 (5 minutes apart) then call 911 • NTG may cause severe headache and hypotension ...
... dilates the coronary arteries • May take up to 3 (5 minutes apart) then call 911 • NTG may cause severe headache and hypotension ...
Successful Treatment of Idiopathic Dilated
... Therefore, triple diuretic therapy was initiated 2 weeks after the addition of lisinopril and the increase in furosemide to better control his CHF to better control his CHF, with the goal of stabilizing him clinically in order to perform a complete cardiac evaluation. Hydrochlorthiazide, a thiazide ...
... Therefore, triple diuretic therapy was initiated 2 weeks after the addition of lisinopril and the increase in furosemide to better control his CHF to better control his CHF, with the goal of stabilizing him clinically in order to perform a complete cardiac evaluation. Hydrochlorthiazide, a thiazide ...
Catheter Ablation - Heart Rhythm Society
... Parkinson White (WPW) Syndrome • Atrial Tachycardia ...
... Parkinson White (WPW) Syndrome • Atrial Tachycardia ...
Impact of preload changes on positive and negative left ventricular
... The present study shows that the acoustic cardiography parameter EMAT reflects the changes in LV maximum dP/dt associated with acute increases in LV volume. The positive and negative LV maximum dP/dt correlated significantly, both before and after LV angiography. This relationship may result from th ...
... The present study shows that the acoustic cardiography parameter EMAT reflects the changes in LV maximum dP/dt associated with acute increases in LV volume. The positive and negative LV maximum dP/dt correlated significantly, both before and after LV angiography. This relationship may result from th ...
Valvular Heart Disease
... Valvular leaflets enlarge and prolapse into left atrium during systole Usually benign, but may progress to mitral regurgitation Affects 5%-10% of the population (most common in women 14-30). ...
... Valvular leaflets enlarge and prolapse into left atrium during systole Usually benign, but may progress to mitral regurgitation Affects 5%-10% of the population (most common in women 14-30). ...
The Human Heart - SeniorScienceKGS
... cardiac muscle cells can contract all by themselves. However, if left to their own devices, cardiac muscle cells in different areas of your heart would beat at different rates. Muscle cells in your ventricles would beat more slowly than those in your atria. Without some kind of unifying function, yo ...
... cardiac muscle cells can contract all by themselves. However, if left to their own devices, cardiac muscle cells in different areas of your heart would beat at different rates. Muscle cells in your ventricles would beat more slowly than those in your atria. Without some kind of unifying function, yo ...
Cardiac Conditions for the Learner
... Know Your Ranges—See the chart below for the ranges outlined by the American Heart Association. Be sure you also know your employer’s ranges. They may vary slightly. Medications—Diuretics (sometimes called “water pills”) help flush out extra fluid and sodium from the body. Clients on diuretics go to ...
... Know Your Ranges—See the chart below for the ranges outlined by the American Heart Association. Be sure you also know your employer’s ranges. They may vary slightly. Medications—Diuretics (sometimes called “water pills”) help flush out extra fluid and sodium from the body. Clients on diuretics go to ...
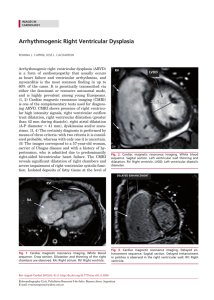
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia
... than 42 mm during diastole), right atrial dilatation (A-P diameter > 41 mm), dyskinesias and/or aneurisms. (3, 4) The certainty diagnosis is performed by means of three criteria: with two criteria it is considered probable, whereas with only one it is uncertain. (5) The images correspond to a 57-yea ...
... than 42 mm during diastole), right atrial dilatation (A-P diameter > 41 mm), dyskinesias and/or aneurisms. (3, 4) The certainty diagnosis is performed by means of three criteria: with two criteria it is considered probable, whereas with only one it is uncertain. (5) The images correspond to a 57-yea ...
PPT - Arne Christensen | Anna Maria College
... The heart is derived from mesoderm and forms in the neck area, moving posterior to the thoracic region as the head elongates. At first, it starts off as a single tube, with the conus arteriosus at the anterior end followed by the atrium, ventricle and ending with the cinus venosus at the posterior. ...
... The heart is derived from mesoderm and forms in the neck area, moving posterior to the thoracic region as the head elongates. At first, it starts off as a single tube, with the conus arteriosus at the anterior end followed by the atrium, ventricle and ending with the cinus venosus at the posterior. ...
Stenosis of the mitral valve
... 30% of all mitral valve failures. According to V.H.Vasilenko it exsists at 500-800 patients on 100000 of population. 30-60% of patients in anamnesis had no obvious attacks and rheumatic disease is without symptoms. This failure is formed in young age at women. There are mild (d – till 0,5 sm), m ...
... 30% of all mitral valve failures. According to V.H.Vasilenko it exsists at 500-800 patients on 100000 of population. 30-60% of patients in anamnesis had no obvious attacks and rheumatic disease is without symptoms. This failure is formed in young age at women. There are mild (d – till 0,5 sm), m ...
Document
... Result: • slower than normal ventricular rate • no coordination between P waves and QRS complexes Treatment: • Use of artificial pacemakers • agonists at ß-adrenoceptors may be useful in the short term but in general drug treatment is of limited use for heart block ...
... Result: • slower than normal ventricular rate • no coordination between P waves and QRS complexes Treatment: • Use of artificial pacemakers • agonists at ß-adrenoceptors may be useful in the short term but in general drug treatment is of limited use for heart block ...
Heart failure

Heart failure (HF), often referred to as congestive heart failure (CHF), occurs when the heart is unable to pump sufficiently to maintain blood flow to meet the body's needs. The terms chronic heart failure (CHF) or congestive cardiac failure (CCF) are often used interchangeably with congestive heart failure. Signs and symptoms commonly include shortness of breath, excessive tiredness, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath is usually worse with exercise, while lying down, and may wake the person at night. A limited ability to exercise is also a common feature.Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease including a previous myocardial infarction (heart attack), high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excess alcohol use, infection, and cardiomyopathy of an unknown cause. These cause heart failure by changing either the structure or the functioning of the heart. There are two main types of heart failure: heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure with normal ejection fraction depending on if the ability of the left ventricle to contract is affected, or the heart's ability to relax. The severity of disease is usually graded by the degree of problems with exercise. Heart failure is not the same as myocardial infarction (in which part of the heart muscle dies) or cardiac arrest (in which blood flow stops altogether). Other diseases that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver problems, anemia and thyroid disease.The condition is diagnosed based on the history of the symptoms and a physical examination with confirmation by echocardiography. Blood tests, electrocardiography, and chest radiography may be useful to determine the underlying cause. Treatment depends on the severity and cause of the disease. In people with chronic stable mild heart failure, treatment commonly consists of lifestyle modifications such as stopping smoking, physical exercise, and dietary changes, as well as medications. In those with heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers along with beta blockers are recommended. For those with severe disease, aldosterone antagonists, or hydralazine plus a nitrate may be used. Diuretics are useful for preventing fluid retention. Sometimes, depending on the cause, an implanted device such as a pacemaker or an implantable cardiac defibrillator may be recommended. In some moderate or severe cases cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) may be suggested or cardiac contractility modulation may be of benefit. A ventricular assist device or occasionally a heart transplant may be recommended in those with severe disease despite all other measures.Heart failure is a common, costly, and potentially fatal condition. In developed countries, around 2% of adults have heart failure and in those over the age of 65, this increases to 6–10%. In the year after diagnosis the risk of death is about 35% after which it decreases to below 10% each year. This is similar to the risks with a number of types of cancer. In the United Kingdom the disease is the reason for 5% of emergency hospital admissions. Heart failure has been known since ancient times with the Ebers papyrus commenting on it around 1550 BCE.