Anomalous origin of the right pulmonary artery from the ascending
... There are other cardiovascular anomalies that occur frequently in this condition, such as the following: patent ductus arteriosus (75%), ventricular septal defects, aortopulmonary window, aortic coarctation, aortic arch interruption, atrial septal defect and contralateral pulmonary veins stenosis. C ...
... There are other cardiovascular anomalies that occur frequently in this condition, such as the following: patent ductus arteriosus (75%), ventricular septal defects, aortopulmonary window, aortic coarctation, aortic arch interruption, atrial septal defect and contralateral pulmonary veins stenosis. C ...
this PDF file
... Peter S. ECG features of ARVD/C A very good option is describe arrhyhmogenic cardiomyopathy by ECG is the appearance of so-called epsilon waves[2,7]. Epsilon waves are major criteria in the definition of arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy very well characterising conduction delay of the right ventricle. ...
... Peter S. ECG features of ARVD/C A very good option is describe arrhyhmogenic cardiomyopathy by ECG is the appearance of so-called epsilon waves[2,7]. Epsilon waves are major criteria in the definition of arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy very well characterising conduction delay of the right ventricle. ...
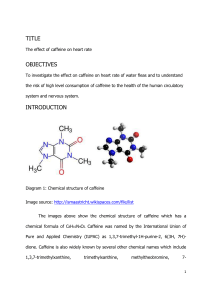
TITLE The effect of caffeine on heart rate OBJECTIVES To
... Caffeine is now a common ingredient of soft drinks such as cola, originally prepared from kola nuts. Research which was carried out shows that soft drinks typically contain about 10 to 15 milligrams of caffeine per serving. Besides, chocolate bars have a high percentage of caffeine content especial ...
... Caffeine is now a common ingredient of soft drinks such as cola, originally prepared from kola nuts. Research which was carried out shows that soft drinks typically contain about 10 to 15 milligrams of caffeine per serving. Besides, chocolate bars have a high percentage of caffeine content especial ...
Heart Rate Variability for Clinicians
... Association is not causation o Endurance athletes have high HRV. o Does exercise training cause increased HRV, or are people with high HRV more suited to endurance exercise? HRV can be exaggerated by increased randomness, which is not a truly normal sinus rhythm despite the normal appearance of ...
... Association is not causation o Endurance athletes have high HRV. o Does exercise training cause increased HRV, or are people with high HRV more suited to endurance exercise? HRV can be exaggerated by increased randomness, which is not a truly normal sinus rhythm despite the normal appearance of ...
A Comprehensive look At heart structure, function, and health
... C–reactive protein ― used as an indicator for heart disease, C-reactive protein is a test that measures the concentration of a protein in serum that indicates acute inflammation. defibrillator ― medical device used in the defibrillation of the heart. It consists of a central unit and a set of ...
... C–reactive protein ― used as an indicator for heart disease, C-reactive protein is a test that measures the concentration of a protein in serum that indicates acute inflammation. defibrillator ― medical device used in the defibrillation of the heart. It consists of a central unit and a set of ...
PDF
... Conceptually, defibrillation can be considered to be a two-step process. First, the applied shock drives currents that traverse the myocardium and cause complex polarization changes in Vm distribution,24 i.e. VEP. Secondly, post-shock active membrane reactions are invoked that eventually result eith ...
... Conceptually, defibrillation can be considered to be a two-step process. First, the applied shock drives currents that traverse the myocardium and cause complex polarization changes in Vm distribution,24 i.e. VEP. Secondly, post-shock active membrane reactions are invoked that eventually result eith ...
Heart Children - Heart Kids NZ
... 1. From the left atrium, the blood moves down into the left ventricle. 2. The ventricle pumps it into the aorta, which is the main artery of the body. 3. From branches in the aorta the blood passes through other arteries, and then through tiny vessels (capillaries), to supply all the organs and t ...
... 1. From the left atrium, the blood moves down into the left ventricle. 2. The ventricle pumps it into the aorta, which is the main artery of the body. 3. From branches in the aorta the blood passes through other arteries, and then through tiny vessels (capillaries), to supply all the organs and t ...
1 HRV - DANTEST Introduction http://www.dantest.com/ Heart Rate
... mortality, particularly in patients at risk after MI or with CHF. This article reviews the mechanism, the parameters and the use of HRV as a marker reflecting the activity of the sympathetic and vagal components of the ANS on the sinus node, and as a clinical tool for screening and identifying patie ...
... mortality, particularly in patients at risk after MI or with CHF. This article reviews the mechanism, the parameters and the use of HRV as a marker reflecting the activity of the sympathetic and vagal components of the ANS on the sinus node, and as a clinical tool for screening and identifying patie ...
Full-Text PDF
... Molecularly, the cardiac muscle cells in drosophila and mammalian species show a striking degree of similarity. Transcription factor tinman, the drosophila homologue of Nkx2.5, is the determining factor underlying cardiomyocyte differentiation [32,37,38]. Its expression is observed in all cardiac ce ...
... Molecularly, the cardiac muscle cells in drosophila and mammalian species show a striking degree of similarity. Transcription factor tinman, the drosophila homologue of Nkx2.5, is the determining factor underlying cardiomyocyte differentiation [32,37,38]. Its expression is observed in all cardiac ce ...
Taurine depletion caused by knocking out the taurine transporter
... [12–14]. Maintenance of Ca2+ homeostasis is of paramount importance in the heart because either reductions in [Ca2+]i or impaired Ca2+ sensitivity of the myofibrils can lead to the development of heart failure. Second, it possesses antioxidant [11–13] and anti-apoptotic activity [15,16], which would ...
... [12–14]. Maintenance of Ca2+ homeostasis is of paramount importance in the heart because either reductions in [Ca2+]i or impaired Ca2+ sensitivity of the myofibrils can lead to the development of heart failure. Second, it possesses antioxidant [11–13] and anti-apoptotic activity [15,16], which would ...
ACC/AHA Guidelines for the Evaluation and Management of
... the traditional clinical diagnosis of HF for diagnostic or coding purposes. This classification recognizes that there are established risk factors and structural prerequisites for the development of HF and that therapeutic interventions performed even before the appearance of left ventricular dysfun ...
... the traditional clinical diagnosis of HF for diagnostic or coding purposes. This classification recognizes that there are established risk factors and structural prerequisites for the development of HF and that therapeutic interventions performed even before the appearance of left ventricular dysfun ...
2012 EHRA/HRS expert consensus statement on cardiac
... symptoms, quality of life, improvement in LV function, hospitalization, and mortality rates in patients with systolic dysfunction, QRS delay, and heart failure. With the increase in operator experience and advancement in implant tools, a successful CRT implant is now achieved in ⬎90% of cases. This ...
... symptoms, quality of life, improvement in LV function, hospitalization, and mortality rates in patients with systolic dysfunction, QRS delay, and heart failure. With the increase in operator experience and advancement in implant tools, a successful CRT implant is now achieved in ⬎90% of cases. This ...
Percentage of Left Ventricular
... were calculated. The aortic valve area is not listed in five instances, since no temporal relationship existed between pressure-pulse records and measurements of cardiac output. Mean systolic gradients ranged from 11 to 105 mm Hg, aortic valve areas ranged from 1.9 to 0.3 cm2 or 1.3 to 0.2 cm2/m,2) ...
... were calculated. The aortic valve area is not listed in five instances, since no temporal relationship existed between pressure-pulse records and measurements of cardiac output. Mean systolic gradients ranged from 11 to 105 mm Hg, aortic valve areas ranged from 1.9 to 0.3 cm2 or 1.3 to 0.2 cm2/m,2) ...
PowerPoint - Electrocardiography
... when a wavefront spreads toward an electrode, the largest possible deflection will occur When a wavefront spreads perpendicular to a lead, the smallest or no deflection occurs ECG shows the sum of all wavefronts relative to the lead being used to measure (MEA) ...
... when a wavefront spreads toward an electrode, the largest possible deflection will occur When a wavefront spreads perpendicular to a lead, the smallest or no deflection occurs ECG shows the sum of all wavefronts relative to the lead being used to measure (MEA) ...
Noninvasive single-beat determination of left ventricular end
... upon an accurate assessment of the underlying pathophysiology, accompanied by close patient monitoring and tailored treatment (1–3). Such comprehensive management approaches stabilize acute exacerbations, reduce readmissions, enhance quality of life and improve survival (1–3). However, variability o ...
... upon an accurate assessment of the underlying pathophysiology, accompanied by close patient monitoring and tailored treatment (1–3). Such comprehensive management approaches stabilize acute exacerbations, reduce readmissions, enhance quality of life and improve survival (1–3). However, variability o ...
Left ventricular ejection time, not heart rate, is an independent
... the study population were previously described in the parent studies, which focused on PWV reference values, epidemiological features, pulse wave analysis validation, and PWV impact on outcome, respectively (2, 3, 6 – 8, 14, 17, 37– 40, 44). Subjects from these cohorts who were receiving any cardiov ...
... the study population were previously described in the parent studies, which focused on PWV reference values, epidemiological features, pulse wave analysis validation, and PWV impact on outcome, respectively (2, 3, 6 – 8, 14, 17, 37– 40, 44). Subjects from these cohorts who were receiving any cardiov ...
EXPERIMENTS ON THE CAUSATION AND AMELIORATION
... left auricle. Left ventricular contractions weaker than those of right. 10.54. Both ventricles beat synchronously, following auricles; left ventricle stronger beat than before. No foam in trachea. ll.01..Chambers beat synchronously; good strength. +11.03½. 0.47 cc. of adrenalin, into trachea. 11.04. ...
... left auricle. Left ventricular contractions weaker than those of right. 10.54. Both ventricles beat synchronously, following auricles; left ventricle stronger beat than before. No foam in trachea. ll.01..Chambers beat synchronously; good strength. +11.03½. 0.47 cc. of adrenalin, into trachea. 11.04. ...
Gallop Rhythm of the Heart
... left side of the heart in essential hypertension and aortic stenosis, and on the right side in pulmonary hypertension of varied etiology and in pulmonic stenosis. When atrial gallop is present in essential hypertension, there is invariably evidence of left ventricular hypertrophy, either from physic ...
... left side of the heart in essential hypertension and aortic stenosis, and on the right side in pulmonary hypertension of varied etiology and in pulmonic stenosis. When atrial gallop is present in essential hypertension, there is invariably evidence of left ventricular hypertrophy, either from physic ...
Permanent cardiac pacemaker: an emergency perspective
... Infectious complication is not common but may occasionally be severe and life threatening. Patients with diabetes, malignancy, on steroid or anticoagulant therapy are at higher risk. It is also more common in longer procedures, reoperation and in patients with a temporary pacing lead in situ.10 Infe ...
... Infectious complication is not common but may occasionally be severe and life threatening. Patients with diabetes, malignancy, on steroid or anticoagulant therapy are at higher risk. It is also more common in longer procedures, reoperation and in patients with a temporary pacing lead in situ.10 Infe ...
Comparative Ultrastructural Morphometry Of The Relationship
... amounts of calcium stored in these elements for contraction. This adaptation would also be necessary for the large stroke volume required of the heart of hibernators, even when cardiac output is reduced to 1/60 of normal level in such states [20]. The wider FSR tubules observed in myocytes of hibern ...
... amounts of calcium stored in these elements for contraction. This adaptation would also be necessary for the large stroke volume required of the heart of hibernators, even when cardiac output is reduced to 1/60 of normal level in such states [20]. The wider FSR tubules observed in myocytes of hibern ...
Echocardiographic Assessment of Diastolic Function
... abnormalities, but in approximately one-third of patients, heart failure symptoms are primarily caused by diastolic dysfunction, as LV systolic function is relatively preserved. The pathophysiological basis of diastolic dysfunction is that adequate filling of the ventricles, and, therefore, adequate ...
... abnormalities, but in approximately one-third of patients, heart failure symptoms are primarily caused by diastolic dysfunction, as LV systolic function is relatively preserved. The pathophysiological basis of diastolic dysfunction is that adequate filling of the ventricles, and, therefore, adequate ...
Tetralogy of Fallot: from fetus to adult
... A fetal echocardiography is important both for the diagnosis of TOF and for the precise characterization of fetus cardiac anatomy, since the TOF associated anatomical variations have different outcomes. As the four-chamber view usually appears normal, TOF is easily missed in a routine ultrasound. [1 ...
... A fetal echocardiography is important both for the diagnosis of TOF and for the precise characterization of fetus cardiac anatomy, since the TOF associated anatomical variations have different outcomes. As the four-chamber view usually appears normal, TOF is easily missed in a routine ultrasound. [1 ...
Heart Sounds
... murmur noted during the second trimester of pregnancy (her first pregnancy). The patient has no history of cardiac disease and the murmur was not noted during previous exams. She is asymptomatic. Exam shows a mildly displaced apical impulse and lower extremity edema. S1 and S2 are normal and an S3 i ...
... murmur noted during the second trimester of pregnancy (her first pregnancy). The patient has no history of cardiac disease and the murmur was not noted during previous exams. She is asymptomatic. Exam shows a mildly displaced apical impulse and lower extremity edema. S1 and S2 are normal and an S3 i ...
Baroreflex modulation of ventricular rhythm in atrial fibrillation
... plasma levels are not available, In a recent paper we discussed also the action of other drugs such as amiodarone, quinidine and verapamil in atrial fibrillation[21 1. lt can be assumed that at least part of the effect of a drug with an influence on the ventricular rate in at rial fibrillation is me ...
... plasma levels are not available, In a recent paper we discussed also the action of other drugs such as amiodarone, quinidine and verapamil in atrial fibrillation[21 1. lt can be assumed that at least part of the effect of a drug with an influence on the ventricular rate in at rial fibrillation is me ...
Heart failure

Heart failure (HF), often referred to as congestive heart failure (CHF), occurs when the heart is unable to pump sufficiently to maintain blood flow to meet the body's needs. The terms chronic heart failure (CHF) or congestive cardiac failure (CCF) are often used interchangeably with congestive heart failure. Signs and symptoms commonly include shortness of breath, excessive tiredness, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath is usually worse with exercise, while lying down, and may wake the person at night. A limited ability to exercise is also a common feature.Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease including a previous myocardial infarction (heart attack), high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excess alcohol use, infection, and cardiomyopathy of an unknown cause. These cause heart failure by changing either the structure or the functioning of the heart. There are two main types of heart failure: heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure with normal ejection fraction depending on if the ability of the left ventricle to contract is affected, or the heart's ability to relax. The severity of disease is usually graded by the degree of problems with exercise. Heart failure is not the same as myocardial infarction (in which part of the heart muscle dies) or cardiac arrest (in which blood flow stops altogether). Other diseases that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver problems, anemia and thyroid disease.The condition is diagnosed based on the history of the symptoms and a physical examination with confirmation by echocardiography. Blood tests, electrocardiography, and chest radiography may be useful to determine the underlying cause. Treatment depends on the severity and cause of the disease. In people with chronic stable mild heart failure, treatment commonly consists of lifestyle modifications such as stopping smoking, physical exercise, and dietary changes, as well as medications. In those with heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers along with beta blockers are recommended. For those with severe disease, aldosterone antagonists, or hydralazine plus a nitrate may be used. Diuretics are useful for preventing fluid retention. Sometimes, depending on the cause, an implanted device such as a pacemaker or an implantable cardiac defibrillator may be recommended. In some moderate or severe cases cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) may be suggested or cardiac contractility modulation may be of benefit. A ventricular assist device or occasionally a heart transplant may be recommended in those with severe disease despite all other measures.Heart failure is a common, costly, and potentially fatal condition. In developed countries, around 2% of adults have heart failure and in those over the age of 65, this increases to 6–10%. In the year after diagnosis the risk of death is about 35% after which it decreases to below 10% each year. This is similar to the risks with a number of types of cancer. In the United Kingdom the disease is the reason for 5% of emergency hospital admissions. Heart failure has been known since ancient times with the Ebers papyrus commenting on it around 1550 BCE.