Heat
... boiling points, they become vapors. Molar Heat of Vaporization (Hvap) the amount of heat necessary to vaporize one mole of a given liquid. ...
... boiling points, they become vapors. Molar Heat of Vaporization (Hvap) the amount of heat necessary to vaporize one mole of a given liquid. ...
Heat Transfer Enhancement in Latent Heat Thermal Energy Storage
... the inner multiple pipes and PCM is filled in the annular space of the storage system. There are 7 tubes with 800 mm length through which HTF is flowing as shown in figure 2. A eutectic mixture of LiNO3 (58.1 by vol %) and KCl (41.9 by vol %) is used as PCM, HTF is chosen as Hytherm 600. As the PCM ...
... the inner multiple pipes and PCM is filled in the annular space of the storage system. There are 7 tubes with 800 mm length through which HTF is flowing as shown in figure 2. A eutectic mixture of LiNO3 (58.1 by vol %) and KCl (41.9 by vol %) is used as PCM, HTF is chosen as Hytherm 600. As the PCM ...
Cooling Efficiency Study of Hydrogen Batch Annealing Process
... shown in Table 1. The results of Table 1 show that the average values of pH, conductivity, calcium hardness, alkalinity and RSI are 7.6, 2.4 ms/cm, 813 ppm, 41 ppm, and 5.4, respectively. After October, 2007, the calcium hardness was maintained below 800 ppm, which meant that the Utility Section had ...
... shown in Table 1. The results of Table 1 show that the average values of pH, conductivity, calcium hardness, alkalinity and RSI are 7.6, 2.4 ms/cm, 813 ppm, 41 ppm, and 5.4, respectively. After October, 2007, the calcium hardness was maintained below 800 ppm, which meant that the Utility Section had ...
Paper Title (use style: paper title)
... After computing the values of various thermal resistances, as shown in figure 5, the heat gained by water (qw) and the outlet temperature of water can be computed with the help of Efficiency Factor (F’) – actual heat gain rate per pipe per unit length to the gain, which would occur if the roof were ...
... After computing the values of various thermal resistances, as shown in figure 5, the heat gained by water (qw) and the outlet temperature of water can be computed with the help of Efficiency Factor (F’) – actual heat gain rate per pipe per unit length to the gain, which would occur if the roof were ...
AP Chemistry 2015-2016 Name: Chapter 5: Thermodynamics Date
... c) The system releases 57.5 kJ of heat while doing 13.5 kJ of work on the surroundings. 6) Calculate ∆E for each of the following cases: a) q = + 51 kJ, w = - 15 kJ b) q = + 100. kJ, w = - 65 kJ c) q = - 65 kJ, w = - 20 kJ d) In which of these cases does the system do work on the surroundings? 7) Ca ...
... c) The system releases 57.5 kJ of heat while doing 13.5 kJ of work on the surroundings. 6) Calculate ∆E for each of the following cases: a) q = + 51 kJ, w = - 15 kJ b) q = + 100. kJ, w = - 65 kJ c) q = - 65 kJ, w = - 20 kJ d) In which of these cases does the system do work on the surroundings? 7) Ca ...
Fundamentals of the Heat Transfer Theory
... - to construct a mathematical description of the heat transfer process the first law of thermodynamics, the conservation law of substance and the conservation law of momentum are used. Fourier’s law and Fick’s law are adopted to set up a closed system of differential equations. In deriving the energ ...
... - to construct a mathematical description of the heat transfer process the first law of thermodynamics, the conservation law of substance and the conservation law of momentum are used. Fourier’s law and Fick’s law are adopted to set up a closed system of differential equations. In deriving the energ ...
Chapter 10-11 review [Physics]
... d. isovolumetric process 27. Which of the following is a thermodynamic process during which work is done on or by the system but no energy is transferred to or from the system as heat? a. adiabatic process c. isovolumetric process b. isothermal process d. isobaric process 28. Which of the following ...
... d. isovolumetric process 27. Which of the following is a thermodynamic process during which work is done on or by the system but no energy is transferred to or from the system as heat? a. adiabatic process c. isovolumetric process b. isothermal process d. isobaric process 28. Which of the following ...
1 - Dorman High School
... A reaction cannot be exothermic overall if activation energy is required. B) A system is the most stable when it is at its lowest energy state. C) Energy can be defined as whatever is required to oppose a natural tendency. D) Energy transferred into a system can also be transferred out of the system ...
... A reaction cannot be exothermic overall if activation energy is required. B) A system is the most stable when it is at its lowest energy state. C) Energy can be defined as whatever is required to oppose a natural tendency. D) Energy transferred into a system can also be transferred out of the system ...
Date:
... Today’s Goal: Students will be able to determine the best metal to use for reclaiming copper from waste solution. Focus: Which metal is best at reclaiming copper from the used copper chloride solution? ...
... Today’s Goal: Students will be able to determine the best metal to use for reclaiming copper from waste solution. Focus: Which metal is best at reclaiming copper from the used copper chloride solution? ...
Name: Date:_____ Period:______ Weather According to Buddy the
... 14. The scary radiator causes Buddy to call his father in fear. What heat transfer is represented by the scary radiator? Describe this heat transfer and provide TWO other examples. (4 points) ...
... 14. The scary radiator causes Buddy to call his father in fear. What heat transfer is represented by the scary radiator? Describe this heat transfer and provide TWO other examples. (4 points) ...
05Thermal_PhysicsALT
... • Isolated system: No matter or energy is exchanged with the environment. (ex: thermos) • Closed system (or “control mass”): no matter is exchanged with the environment. (ex: gas in a cylinder with a piston.) • Open system (or “control volume”): Allows exchange of both matter and energy with the env ...
... • Isolated system: No matter or energy is exchanged with the environment. (ex: thermos) • Closed system (or “control mass”): no matter is exchanged with the environment. (ex: gas in a cylinder with a piston.) • Open system (or “control volume”): Allows exchange of both matter and energy with the env ...
8. Temperature and Heat - City, University of London
... Heat (Q) is the energy transferred due to temperature differences and its units are Joules It takes 4186J of heat to raise the temperature of 1kg of water by 1°C The heat required for a 1°C increase varies from one substance to another, e.g. it takes only 129J of heat to increase the temperature of ...
... Heat (Q) is the energy transferred due to temperature differences and its units are Joules It takes 4186J of heat to raise the temperature of 1kg of water by 1°C The heat required for a 1°C increase varies from one substance to another, e.g. it takes only 129J of heat to increase the temperature of ...
File
... ethanol. Given that the specific heat capacity of ethanol is 2.4 kJ/kg. oC, and that the temperature changed from 21.05oC to 19.39oC, what is the molar heat of fusion for the benzene? Note: Ethanol is the surroundings, not water and benzene dissolves in the ethanol. ...
... ethanol. Given that the specific heat capacity of ethanol is 2.4 kJ/kg. oC, and that the temperature changed from 21.05oC to 19.39oC, what is the molar heat of fusion for the benzene? Note: Ethanol is the surroundings, not water and benzene dissolves in the ethanol. ...
An Upper Bound for the Critical Boiling Heat Flux
... through a 1-mm thickness of pure silver. At higher pressures it therefore becomes impossible to supply a heater surface with these heat fluxes (at steady state) by any known means. Gambill et al. (1960, 1961), for example, encountered the wall AT limit in a few of their early swirl-flow tests at q > ...
... through a 1-mm thickness of pure silver. At higher pressures it therefore becomes impossible to supply a heater surface with these heat fluxes (at steady state) by any known means. Gambill et al. (1960, 1961), for example, encountered the wall AT limit in a few of their early swirl-flow tests at q > ...
2521/103 ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND DRAWING Oct/Nov.2010
... (d) Ice at 00c is added to 300 g of water at initial temperature of 800C in a vacuum flask. When 120 g of ice has been added and all melted the temperature of the flask and its contents is 400C. When a further 100 g of ice has been added the final temperature becomes 100C. The specific capacity of w ...
... (d) Ice at 00c is added to 300 g of water at initial temperature of 800C in a vacuum flask. When 120 g of ice has been added and all melted the temperature of the flask and its contents is 400C. When a further 100 g of ice has been added the final temperature becomes 100C. The specific capacity of w ...
Thermodynamics and the aims of statistical mechanics
... The totality of all possible positions qi for all of the particles i ∈ {1, 2, . . . N } constitutes a 3N -dimensional space called configuration space, Q. Any history of the N particles will be represented by a trajectory γ : R → Q through this space. At any given time t, the trajectory passes throu ...
... The totality of all possible positions qi for all of the particles i ∈ {1, 2, . . . N } constitutes a 3N -dimensional space called configuration space, Q. Any history of the N particles will be represented by a trajectory γ : R → Q through this space. At any given time t, the trajectory passes throu ...
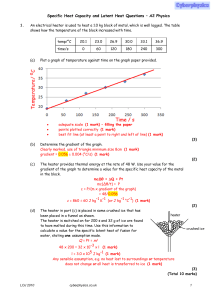
Specific Heat Capacity and Latent Heat Questions
... The student in part (a) continues to heat the water so that it boils for 105 s. When the mass ofthe beaker and water is measured again, it is found that it has decreased by 94 g. (i) Calculate a value for the specific latent heat of vaporisation of water. Q = ml = Pt 94 × 10−3 x l = 2000 × 105 (1 ma ...
... The student in part (a) continues to heat the water so that it boils for 105 s. When the mass ofthe beaker and water is measured again, it is found that it has decreased by 94 g. (i) Calculate a value for the specific latent heat of vaporisation of water. Q = ml = Pt 94 × 10−3 x l = 2000 × 105 (1 ma ...
Physics Trail - Queensland Museum
... • Summarise the various heat exchange systems that apply to locomotive engines of different types. • Relate the factors that influence heat exchange efficiency to the heat exchange system. For example, colour strongly relates to radiation efficiency. Some factors may relate to more than one system. ...
... • Summarise the various heat exchange systems that apply to locomotive engines of different types. • Relate the factors that influence heat exchange efficiency to the heat exchange system. For example, colour strongly relates to radiation efficiency. Some factors may relate to more than one system. ...
Inducing Hypothermia in Neonates on Extracorporeal Membrane
... hypothermia in extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) cases where neurological impairment occurs in a significant portion of the population [5]. In ECMO cases, neurological damage maybe due to alteration of cerebral blood flow, reoxygenation injury, thromboemboli and ischemia, and loss of puslat ...
... hypothermia in extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) cases where neurological impairment occurs in a significant portion of the population [5]. In ECMO cases, neurological damage maybe due to alteration of cerebral blood flow, reoxygenation injury, thromboemboli and ischemia, and loss of puslat ...
International Heat Flow Commission Global Heat Flow Database
... vertical and heat flow calculated from the gradient is vertical heat flow. ...
... vertical and heat flow calculated from the gradient is vertical heat flow. ...
Thermal Applications
... dynamic conduction and ventilation heat transfer is accounted for. Glazing solar transmission properties are treated using an analysis based on the Fresnel equations. At the user’s option the effects of ventilation air exchanges and external solar shading, as calculated by SunCast, may be incorporat ...
... dynamic conduction and ventilation heat transfer is accounted for. Glazing solar transmission properties are treated using an analysis based on the Fresnel equations. At the user’s option the effects of ventilation air exchanges and external solar shading, as calculated by SunCast, may be incorporat ...
HCC Learning Web
... (q) required to raise the temperature of a given quantity (m) of the substance by one degree Celsius. ...
... (q) required to raise the temperature of a given quantity (m) of the substance by one degree Celsius. ...
Laws of Thermodynamics
... thermodynamics was becoming a more formal subject, it was realized that there was no consistent definition of temperature. A zeroth law of thermodynamics was added to rectify this. Later still, a third law of thermodynamics was added to summarize the observed properties of matter at extremely low te ...
... thermodynamics was becoming a more formal subject, it was realized that there was no consistent definition of temperature. A zeroth law of thermodynamics was added to rectify this. Later still, a third law of thermodynamics was added to summarize the observed properties of matter at extremely low te ...





![Chapter 10-11 review [Physics]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006569087_1-016d8ea7c10ac000ca8ef396184a0e82-300x300.png)