basic cooking principles 1
... differs with thickness of liquid. Once the heat is carried to the food; it is then distributed by ...
... differs with thickness of liquid. Once the heat is carried to the food; it is then distributed by ...
CHM 122 Chapter 8 -Thermochemistry: Chemical Energy
... Heat transfer occurs by way of collisions between randomly moving particles of matter. The particles with higher thermal energy are moving more quickly, when they collide with slower moving particles, some of their energy is transferred to the slower particle as heat energy increasing its speed Not ...
... Heat transfer occurs by way of collisions between randomly moving particles of matter. The particles with higher thermal energy are moving more quickly, when they collide with slower moving particles, some of their energy is transferred to the slower particle as heat energy increasing its speed Not ...
Thermal Chem Review and Key
... 15. What equation is used to calculate the energy involved in a phase change? Does this equation pertain to the diagonal or plateau sections on your heating and cooling curve? 16. What equation is used to calculate the energy involved in increasing or decreasing the temperature of a substance? Does ...
... 15. What equation is used to calculate the energy involved in a phase change? Does this equation pertain to the diagonal or plateau sections on your heating and cooling curve? 16. What equation is used to calculate the energy involved in increasing or decreasing the temperature of a substance? Does ...
Unit 3 state of matter particle motion and heat transfer
... in thermal energy does not affect temperature ...
... in thermal energy does not affect temperature ...
Unit 4: Themodynamics
... The overall heat of a reaction (ΔH ) is the sum of the ΔHs of each step in the process Can obtain “heat of formation” (ΔH) data for compounds from tables Formation of 1 mole of compounds from their elements ...
... The overall heat of a reaction (ΔH ) is the sum of the ΔHs of each step in the process Can obtain “heat of formation” (ΔH) data for compounds from tables Formation of 1 mole of compounds from their elements ...
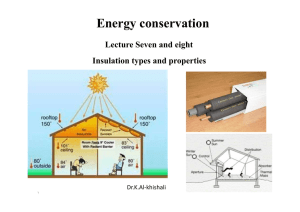
Why insulate?
... •Very high levels of insulation (typically Rip40 walls and Rip60 roof, corresponding to SI Uvalues of 0.15 and 0.1 W/(m²·K) respectively) •Details to ensure insulation continuity where walls meet roofs, foundations, and other walls •Airtight construction, especially around doors and windows •a Heat ...
... •Very high levels of insulation (typically Rip40 walls and Rip60 roof, corresponding to SI Uvalues of 0.15 and 0.1 W/(m²·K) respectively) •Details to ensure insulation continuity where walls meet roofs, foundations, and other walls •Airtight construction, especially around doors and windows •a Heat ...
Practice sheet #8: thermodynamics.
... Use average bond enthalpies to estimate the enthalpy change in this reaction, for one mole of methanol reacting. Use data from Appendix 2A of your textbook to calculate the actual enthalpy change in this reaction, assuming it to be the same at 65°C as at 25°C. Calculate the heat released when 1.00 K ...
... Use average bond enthalpies to estimate the enthalpy change in this reaction, for one mole of methanol reacting. Use data from Appendix 2A of your textbook to calculate the actual enthalpy change in this reaction, assuming it to be the same at 65°C as at 25°C. Calculate the heat released when 1.00 K ...
vaulted ceilings
... Vaulted ceilings can be created by either the inclusion of profiled cutouts within a traditional flat slab soffit or the construction of arched structural elements. Both methods are viable for precast and insitu concrete construction solutions. It is the latter, arched structural elements, which cre ...
... Vaulted ceilings can be created by either the inclusion of profiled cutouts within a traditional flat slab soffit or the construction of arched structural elements. Both methods are viable for precast and insitu concrete construction solutions. It is the latter, arched structural elements, which cre ...
Energy and Entropy
... Example- 100mL of boiling water has the same temperature as 1000mL of boiling water, but the 1000mL of boiling water would have more thermal energy ...
... Example- 100mL of boiling water has the same temperature as 1000mL of boiling water, but the 1000mL of boiling water would have more thermal energy ...
Unit 1: Energy Changes in Chemical Reactions
... when heat is transferred (1st Law of Thermodynamics) → closed vs open system → we can’t tell how much energy is in something until it is released ...
... when heat is transferred (1st Law of Thermodynamics) → closed vs open system → we can’t tell how much energy is in something until it is released ...
Greenhouse versus living room model
... In [2], it is reasoned that the curve-‐fitting of the registered worldwide energy consumption, as shown in fig. 5 in [2] (copied in fig. 1 below), most likely corresponds to the actual consumption. ...
... In [2], it is reasoned that the curve-‐fitting of the registered worldwide energy consumption, as shown in fig. 5 in [2] (copied in fig. 1 below), most likely corresponds to the actual consumption. ...
CHAPTER 1-b - cpas --- center of planning and architecture studies
... - - ) Energy Crisis • Despite of all the previous recommendations and experience forced by the pioneers and their students concerning bioclimatic architecture, the modern move completely ignored the human needs inside the building, turning its back to the nature and depending completely on mechanica ...
... - - ) Energy Crisis • Despite of all the previous recommendations and experience forced by the pioneers and their students concerning bioclimatic architecture, the modern move completely ignored the human needs inside the building, turning its back to the nature and depending completely on mechanica ...
Chapter 6
... • Some energy can be lost as heat (ex: frictional heating), represented by q • Heat vs. Temperature: TEMPERATURE reflects movement of particles. HEAT deals with transfer of energy between two objects due to a temperature difference. • Energy can also be transferred through work (force activing over ...
... • Some energy can be lost as heat (ex: frictional heating), represented by q • Heat vs. Temperature: TEMPERATURE reflects movement of particles. HEAT deals with transfer of energy between two objects due to a temperature difference. • Energy can also be transferred through work (force activing over ...
H 2 SO 4
... N2 molecule is very stable • No significant tropospheric chemical or photochemical reactions of N2 • N2 is the most common energy-absorbing third body, “M”, in atmospheric chemistry Fixation of N from atmospheric N2 is an important environmental phenomenon • Biochemically by specialized bacteria • C ...
... N2 molecule is very stable • No significant tropospheric chemical or photochemical reactions of N2 • N2 is the most common energy-absorbing third body, “M”, in atmospheric chemistry Fixation of N from atmospheric N2 is an important environmental phenomenon • Biochemically by specialized bacteria • C ...
Conceptual Summary/Outline of Topics
... iii. Convection (really a subclass of conduction). 1. Fluid (air, water, magma) in contact with hot surface 2. Heat transfer to interface layer of fluid by conduction, followed by bulk motion carrying heated fluid away. 3. In absence of active device for circulation of fluid, gravity is essential (b ...
... iii. Convection (really a subclass of conduction). 1. Fluid (air, water, magma) in contact with hot surface 2. Heat transfer to interface layer of fluid by conduction, followed by bulk motion carrying heated fluid away. 3. In absence of active device for circulation of fluid, gravity is essential (b ...
Heat Transfer
... The heated radiators, meanwhile, create convection currents in the air. Air around the radiator is warmed first. It expands, rises, and spreads over the ceiling, while colder air from near the floor moves in around the radiator. This cold air is heated in turn and also rises. In this way, convecti ...
... The heated radiators, meanwhile, create convection currents in the air. Air around the radiator is warmed first. It expands, rises, and spreads over the ceiling, while colder air from near the floor moves in around the radiator. This cold air is heated in turn and also rises. In this way, convecti ...
Thermo Powerpoint
... Because there is no way to measure the absolute value of the enthalpy of a substance, must I measure the enthalpy change for every reaction of interest? Standard enthalpy of formation (DH0f) is the heat change that results when one mole of a compound is formed from its elements at a pressure of 1 a ...
... Because there is no way to measure the absolute value of the enthalpy of a substance, must I measure the enthalpy change for every reaction of interest? Standard enthalpy of formation (DH0f) is the heat change that results when one mole of a compound is formed from its elements at a pressure of 1 a ...
How Cooling Towers Function
... temperature control. Cooling water systems control these temperatures by transferring heat from hot process fluids into cooling water. As this happens, the cooling water itself gets hot; before it can be used again it must either be cooled or replaced by a fresh supply of cool water. This makeup wat ...
... temperature control. Cooling water systems control these temperatures by transferring heat from hot process fluids into cooling water. As this happens, the cooling water itself gets hot; before it can be used again it must either be cooled or replaced by a fresh supply of cool water. This makeup wat ...
Chapter 10 Test Form A Chapter 10 Test Form B
... ergy of the molecules increases. The temperature increases because temperature is proportional to kinetic energy of the molecules. 17. The molecules of water have a higher kinetic energy, so there are more particle collisions per time per mass in the water than in the hand. Energy is transferred as ...
... ergy of the molecules increases. The temperature increases because temperature is proportional to kinetic energy of the molecules. 17. The molecules of water have a higher kinetic energy, so there are more particle collisions per time per mass in the water than in the hand. Energy is transferred as ...
Heat Energy - MullisChemistry
... Warm fluid expands and is less dense than surrounding fluid: Warm rises and cool sinks. Convection currents continue to form as long as there is a heat source. ...
... Warm fluid expands and is less dense than surrounding fluid: Warm rises and cool sinks. Convection currents continue to form as long as there is a heat source. ...
Mathematical modelling and analysis of corrugated
... absorber plate with a well insulated parallel bottom plate, forming a rectangular duct profile. The corrugation of the absorber plate is equilateral triangle in shape and the air is made to flow into the corrugation. The theoretical solutions of the thermal performance of the solar flat plate collec ...
... absorber plate with a well insulated parallel bottom plate, forming a rectangular duct profile. The corrugation of the absorber plate is equilateral triangle in shape and the air is made to flow into the corrugation. The theoretical solutions of the thermal performance of the solar flat plate collec ...
P1_student_checklist 2016
... recognise that energy is being transferred when materials melt or boil although there is no change in temperature define specific latent heat. state and use the formula: energy = mass x specific latent heat explain that energy is needed to break intermolecular bonds during changes of state ...
... recognise that energy is being transferred when materials melt or boil although there is no change in temperature define specific latent heat. state and use the formula: energy = mass x specific latent heat explain that energy is needed to break intermolecular bonds during changes of state ...