
Analysis of Heat Transfer in Rectangular
... θ = Temperature difference, [k] Subscripts conv = convection ch = channel sp = single phase bot = bottom ƒ = fluid i = inlet o =outlet Micro-channel Heat transfer has the very potential of wide applications in cooling high power density microchips in the CPU system, the micro power systems and even ...
... θ = Temperature difference, [k] Subscripts conv = convection ch = channel sp = single phase bot = bottom ƒ = fluid i = inlet o =outlet Micro-channel Heat transfer has the very potential of wide applications in cooling high power density microchips in the CPU system, the micro power systems and even ...
Table S1: Properties of Antigorite as a Model
... wedge flow introduced in exactly the same way as described in Peacock and Wang (1999). This initial temperature field is used also for the no-slab-window scenario but after being modified by assigning a uniform "filling" temperature (1100°C or 1400°C for the model) to all nodes below the slab. Time ...
... wedge flow introduced in exactly the same way as described in Peacock and Wang (1999). This initial temperature field is used also for the no-slab-window scenario but after being modified by assigning a uniform "filling" temperature (1100°C or 1400°C for the model) to all nodes below the slab. Time ...
Exercises - Madison County Schools
... b. In the long run, the entropy will always increase. c. In all but a few cases, entropy in the long run will decrease. d. All natural systems have constant levels of entropy. 48. Circle the letter of each example of increasing entropy. a. gas molecules escaping from a bottle b. an unattended house ...
... b. In the long run, the entropy will always increase. c. In all but a few cases, entropy in the long run will decrease. d. All natural systems have constant levels of entropy. 48. Circle the letter of each example of increasing entropy. a. gas molecules escaping from a bottle b. an unattended house ...
A comprehensive review of solar facades. Transparent
... the investigation was to determine the time and local averaged overall heat transfer coefficients for solar radiation augmented turbulent mixed convection flows in transparent vertical channels. Detailed parameter analysis for a box-window of typical geometry (Height of the box window, H=2.4 m, Dist ...
... the investigation was to determine the time and local averaged overall heat transfer coefficients for solar radiation augmented turbulent mixed convection flows in transparent vertical channels. Detailed parameter analysis for a box-window of typical geometry (Height of the box window, H=2.4 m, Dist ...
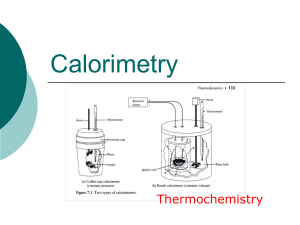
Thermochemistry - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... one another (insulation), then filled with a specific quantity of water and covered with another cup as a cover. A chemical reaction or phase change takes place inside and a thermometer is placed within to measure any change in temperature that occurs to the system. ...
... one another (insulation), then filled with a specific quantity of water and covered with another cup as a cover. A chemical reaction or phase change takes place inside and a thermometer is placed within to measure any change in temperature that occurs to the system. ...
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-ISSN: 2278-1684
... Mixed convection heat transfer from longitudinal fins in a horizontal channel with a uniform heat flux boundary condition at the bottom surface has been studied experimentally by M. Dogan et al.. Experimental results for bottom heated fin arrays have been presented for different fin spacings, fin he ...
... Mixed convection heat transfer from longitudinal fins in a horizontal channel with a uniform heat flux boundary condition at the bottom surface has been studied experimentally by M. Dogan et al.. Experimental results for bottom heated fin arrays have been presented for different fin spacings, fin he ...
Second review [Compatibility Mode]
... When 0.0300 mol of Na was added to 100.0 g of water, the temperature of the resulting solution rose from 25.0 oC to 37.9 oC. If the specific heat of the solution was 4.18 J g-1 K-1, calculate ? H, in kJ, for the reaction as written. ...
... When 0.0300 mol of Na was added to 100.0 g of water, the temperature of the resulting solution rose from 25.0 oC to 37.9 oC. If the specific heat of the solution was 4.18 J g-1 K-1, calculate ? H, in kJ, for the reaction as written. ...
Chapter 10-11 review [Physics]
... 25. According to the first law of thermodynamics, the difference between energy transferred to or from a system as heat and energy transferred to or from a system by work is equivalent to which of the following? a. entropy change c. temperature change b. internal energy change d. specific heat 26. S ...
... 25. According to the first law of thermodynamics, the difference between energy transferred to or from a system as heat and energy transferred to or from a system by work is equivalent to which of the following? a. entropy change c. temperature change b. internal energy change d. specific heat 26. S ...
Liquids
... Heat is the amount of energy a chemical has, frequently measured in joules (J). Because we can’t directly measure heat, we have to measure “temperature”, which reflects how much kinetic energy an object has (as measured in °C or Kelvins). In thermodynamics, the term “enthalpy” is used interchangeabl ...
... Heat is the amount of energy a chemical has, frequently measured in joules (J). Because we can’t directly measure heat, we have to measure “temperature”, which reflects how much kinetic energy an object has (as measured in °C or Kelvins). In thermodynamics, the term “enthalpy” is used interchangeabl ...
Thermal comfort - thermal mass: housing in hot dry climates
... may enable easier and faster conditioning (Hassid, 1994). It is also assumed that heavy cooling and heating peak loads are more easily treated in light interiors, where indoor air can easily be conditioned. This may be true under certain conditions and specific building types. Nevertheless, it shoul ...
... may enable easier and faster conditioning (Hassid, 1994). It is also assumed that heavy cooling and heating peak loads are more easily treated in light interiors, where indoor air can easily be conditioned. This may be true under certain conditions and specific building types. Nevertheless, it shoul ...
doc heat conversion
... substance becomes hotter. Similarly, when heat energy if withdrawn from a substance the particles move slower and becomes colder. The Relationship between Heat and Temperature When a substance is heated, its temperature rises. Heat decreases or increases the temperature of a body. For instance, when ...
... substance becomes hotter. Similarly, when heat energy if withdrawn from a substance the particles move slower and becomes colder. The Relationship between Heat and Temperature When a substance is heated, its temperature rises. Heat decreases or increases the temperature of a body. For instance, when ...
Chapter 8 Thermochemistry: Chemical Energy
... System = the object in question Surrounding(s) = everything outside the system When both system and surrounding at same temperature thermal equilibrium When not Heat transfer to surrounding = exothermic (you feel the heat) hot metal!! Heat transfer to system = endothermic (you feel c ...
... System = the object in question Surrounding(s) = everything outside the system When both system and surrounding at same temperature thermal equilibrium When not Heat transfer to surrounding = exothermic (you feel the heat) hot metal!! Heat transfer to system = endothermic (you feel c ...
Nernst`s postulate derived directly from the vanishing heat capacity
... It is worthwhile pointing out that when T is very small, so is −(∆T )S , whereas (∆yi )S need not be small. It may have a finite value which can be varied by controlling the exterior conditions, whether the temperature of the system is high or low [1,2]. In fact, this observation has been used extens ...
... It is worthwhile pointing out that when T is very small, so is −(∆T )S , whereas (∆yi )S need not be small. It may have a finite value which can be varied by controlling the exterior conditions, whether the temperature of the system is high or low [1,2]. In fact, this observation has been used extens ...
Lesson Plans - University High School
... differentiate among the four states of matter in terms of particle distance, particle motion, and definite/indefinite shapes and volumes describe temperature as a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance describe matter at absolute zero (0 K) apply kinetic-molecular theo ...
... differentiate among the four states of matter in terms of particle distance, particle motion, and definite/indefinite shapes and volumes describe temperature as a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance describe matter at absolute zero (0 K) apply kinetic-molecular theo ...
Final Exam Review- no solutions
... 27. During a collision, automobile air bags are inflated by the N2 gas formed by the explosive decomposition of sodium azide, NaN3: 2 NaN3 2 Na + 3 N2 What mass of sodium azide would be needed to inflate a 30.0 L bag to a pressure of 1.40 atm at 25°C? ...
... 27. During a collision, automobile air bags are inflated by the N2 gas formed by the explosive decomposition of sodium azide, NaN3: 2 NaN3 2 Na + 3 N2 What mass of sodium azide would be needed to inflate a 30.0 L bag to a pressure of 1.40 atm at 25°C? ...
Heat Transfer by Conduction
... For glass and most nonporous materials, the thermal conductivities are much lower, from about 0.35 to 3.5. For most liquid k is lower than that for solids, with typical values of about 0.17. k decreases by 3 ~ 4 %t for a 10 ºC rise in temperature, except water. ...
... For glass and most nonporous materials, the thermal conductivities are much lower, from about 0.35 to 3.5. For most liquid k is lower than that for solids, with typical values of about 0.17. k decreases by 3 ~ 4 %t for a 10 ºC rise in temperature, except water. ...
1.49 MB - KFUPM Resources
... practice, it is usual to use a figure for a particular structure, e.g. a brick wall, rather than take the values of the conductivities of its constituent materials. The figure used is called the U-value. It refers to Unit Heat Loss Rate , and its unit is the watt per metre squared per kelvin, W m-2 ...
... practice, it is usual to use a figure for a particular structure, e.g. a brick wall, rather than take the values of the conductivities of its constituent materials. The figure used is called the U-value. It refers to Unit Heat Loss Rate , and its unit is the watt per metre squared per kelvin, W m-2 ...
SIMULATING TALL BUILDINGS USING ENERGYPLUS
... The authors' role in the project was to develop the simulation input for the EnergyPlus model. This involved envelope geometry and constructions, internal gains, schedules, shading surfaces, and the HVAC system. Two EnergyPlus models were developed. One represented the baseline model as prescribed b ...
... The authors' role in the project was to develop the simulation input for the EnergyPlus model. This involved envelope geometry and constructions, internal gains, schedules, shading surfaces, and the HVAC system. Two EnergyPlus models were developed. One represented the baseline model as prescribed b ...
Diapositive 1
... CALICE ECAL: ~ 82.2 M of channels Assuming that the chip power is 25 µW/channel total power to dissipate will be : 2055 W external cooling OK inside each slab : necessity of cooling system but active or passive ? Ex: Pessimist simulation of heat conduction just by the heat shield : λ = 400 W/m/K ( ...
... CALICE ECAL: ~ 82.2 M of channels Assuming that the chip power is 25 µW/channel total power to dissipate will be : 2055 W external cooling OK inside each slab : necessity of cooling system but active or passive ? Ex: Pessimist simulation of heat conduction just by the heat shield : λ = 400 W/m/K ( ...
Lesson
... The major cost comes from the digital thermometers and portable stove. The other items can be bought at supermarkets or borrowed from a chemistry classroom. Learning Goals: After this lesson, students should be able to: Understand heat flows from a hot source to a cold source Recall the equation ...
... The major cost comes from the digital thermometers and portable stove. The other items can be bought at supermarkets or borrowed from a chemistry classroom. Learning Goals: After this lesson, students should be able to: Understand heat flows from a hot source to a cold source Recall the equation ...
AP Chemistry Unit 5
... o + H (water gains energy to change from solid to liquid) 1 g of butane (C4H10) undergoes complete combustion o H (heat is released) What if the system is contained so no heat can be released? Will a piston rise or fall? o 2 C4H10 + 13 O2 8 CO2 + 10 H2O volume of products > volume of reactants o ...
... o + H (water gains energy to change from solid to liquid) 1 g of butane (C4H10) undergoes complete combustion o H (heat is released) What if the system is contained so no heat can be released? Will a piston rise or fall? o 2 C4H10 + 13 O2 8 CO2 + 10 H2O volume of products > volume of reactants o ...
Conductive Thermal Transfer
... • If elevation increased by heating after Laramide, where should it have risen? • And what should it have looked like before flat-slab subduction? ...
... • If elevation increased by heating after Laramide, where should it have risen? • And what should it have looked like before flat-slab subduction? ...
The Islamic University of Gaza
... 3- When a 25.0-g block of aluminum absorbs 10.0 kJ of heat, its temperature will rise how many degrees? The specific heat of Al is 0.900 J/ºC.g a. 444oC ...
... 3- When a 25.0-g block of aluminum absorbs 10.0 kJ of heat, its temperature will rise how many degrees? The specific heat of Al is 0.900 J/ºC.g a. 444oC ...
List 6-10 types of energy and give an example of each. State
... Explain your choice: The sun shines down as an input of radiant (KE), which is then transformed into chemical (PE) as the sunflower produces a sunflower seed. 3. What is heat? How are heat and temperature different? What direction does heat transfer? [Heat & Thermal Energy Part 1: Kinetic Molecular ...
... Explain your choice: The sun shines down as an input of radiant (KE), which is then transformed into chemical (PE) as the sunflower produces a sunflower seed. 3. What is heat? How are heat and temperature different? What direction does heat transfer? [Heat & Thermal Energy Part 1: Kinetic Molecular ...





![Second review [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003692853_1-a578e4717b0c8365c11d7e7f576654ae-300x300.png)
![Chapter 10-11 review [Physics]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006569087_1-016d8ea7c10ac000ca8ef396184a0e82-300x300.png)















