Course ME 32200 – Heat Transfer Laboratory Type of Course
... H. I Abu-Mulaweh, Heat Transfer Laboratory Manual, current edition. ...
... H. I Abu-Mulaweh, Heat Transfer Laboratory Manual, current edition. ...
11-Heat Energy
... Heat Capacity Heat Capacity is a measure of how much heat energy must be added to raise the temperature of an object. A large heat capacity means that a lot of heat must be added transferred to raise the temperature of the object by a given amount. A bigger object of the same material has a bigger ...
... Heat Capacity Heat Capacity is a measure of how much heat energy must be added to raise the temperature of an object. A large heat capacity means that a lot of heat must be added transferred to raise the temperature of the object by a given amount. A bigger object of the same material has a bigger ...
Specific Heat
... Duluth, next to Lake Superior, stays cool in the summer and relatively warm in the winter. Why? Substance copper granite lead ice water ...
... Duluth, next to Lake Superior, stays cool in the summer and relatively warm in the winter. Why? Substance copper granite lead ice water ...
Thermal Energy Day 1 Matter Unit
... waves directly transport energy through space (ex. sunlight). ...
... waves directly transport energy through space (ex. sunlight). ...
~therm= heat,temperature
... • An organism that has adapted to living in very high temperatures or heat, such as bacteria or algae ...
... • An organism that has adapted to living in very high temperatures or heat, such as bacteria or algae ...
Silicone Heat Transfer Compound
... providing an extremely efficient and exceptionally thermally conductive compound which will operate over a wide temperature range. Electrolube Heat Transfer Compound is recommended where the efficient and reliable thermal coupling of electrical and electronic components is required or between any su ...
... providing an extremely efficient and exceptionally thermally conductive compound which will operate over a wide temperature range. Electrolube Heat Transfer Compound is recommended where the efficient and reliable thermal coupling of electrical and electronic components is required or between any su ...
Chapter 15 – Section 2 Heat
... Heat and Thermal Energy • Heat is the transfer of thermal energy from one object to another when the objects are at different temperatures. • The amount of heat that is transferred when two objects are brought into contact depends on the difference in temperature between the objects. ...
... Heat and Thermal Energy • Heat is the transfer of thermal energy from one object to another when the objects are at different temperatures. • The amount of heat that is transferred when two objects are brought into contact depends on the difference in temperature between the objects. ...
Heat and the Umpire
... weakness” to pull yourself out of a game or ask for help. Often times this is one of the biggest hurdles to overcome. This “macho” approach occurs in all facets of sports whether we are talking about broken bones, sprains or concussions, no one wants to come out of the game or be seen as weak. Its n ...
... weakness” to pull yourself out of a game or ask for help. Often times this is one of the biggest hurdles to overcome. This “macho” approach occurs in all facets of sports whether we are talking about broken bones, sprains or concussions, no one wants to come out of the game or be seen as weak. Its n ...
doc - University of Colorado Boulder
... plant hormone), can have large effects on plant growth and have to be controlled. This can be accomplished using a ______________. At night, low light, or during germination, plants produce _____ (gas) and need ______ (gas) for their metabolism. In order to not exceed toxic levels of this gas in the ...
... plant hormone), can have large effects on plant growth and have to be controlled. This can be accomplished using a ______________. At night, low light, or during germination, plants produce _____ (gas) and need ______ (gas) for their metabolism. In order to not exceed toxic levels of this gas in the ...
specific heat
... How much energy would be needed to heat 450 g of copper metal from 25.0 ºC to 75.0 ºC? The specific heat of copper at 25.0 ºC is 0.385 J/g ºC. ...
... How much energy would be needed to heat 450 g of copper metal from 25.0 ºC to 75.0 ºC? The specific heat of copper at 25.0 ºC is 0.385 J/g ºC. ...
2 Pieces - cloudfront.net
... If two objects have different temperatures, which direction does the heat move? ...
... If two objects have different temperatures, which direction does the heat move? ...
Heat Transfer Comparison in Coaxial Tube in Tube Heat Exchanger
... Department of Thermodynamics, Thermal and Processing Technology University of Zagreb ...
... Department of Thermodynamics, Thermal and Processing Technology University of Zagreb ...
CHE311 HEAT TRANSFER 2016-17 Fall Semester Prof.Dr.Serpil
... 1. A 50-cm-diameter pipeline in the Arctic carries hot oil at 30◦C and is exposed to a surrounding temperature of−20◦C. A special powder insulation 5 cm thick surrounds the pipe and has a thermal conductivity of 7 mW/m◦ C. The convection heat-transfer coefficient on the outside of the pipe is 9 W/m2 ...
... 1. A 50-cm-diameter pipeline in the Arctic carries hot oil at 30◦C and is exposed to a surrounding temperature of−20◦C. A special powder insulation 5 cm thick surrounds the pipe and has a thermal conductivity of 7 mW/m◦ C. The convection heat-transfer coefficient on the outside of the pipe is 9 W/m2 ...
Heat Flow in a Copper Rod
... Convective and Radiative Heat Loss Adds new term to partial differential equation. h : transfer coefficient for free air ...
... Convective and Radiative Heat Loss Adds new term to partial differential equation. h : transfer coefficient for free air ...
2 - D STEADY STATE HEAT CONDUCTION
... These equations may be solved by spreadsheet iteration 'updating' each temperature 'cell' in sequence . Alternatively an array of simultaneous equations may be set up and solved by Gaussian elimination, either by hand (!) or by computer. BOUNDARY CONDITIONS The above equations apply to interior poin ...
... These equations may be solved by spreadsheet iteration 'updating' each temperature 'cell' in sequence . Alternatively an array of simultaneous equations may be set up and solved by Gaussian elimination, either by hand (!) or by computer. BOUNDARY CONDITIONS The above equations apply to interior poin ...
Chapters 1 and 2
... Temperature is the thing that’s the same for two objects, after they’ve been in contact long enough. Long enough so that the two objects are in thermal equilibrium. Time required to reach thermal equilibrium is the relaxation time. Temperature is usually measured in K, C or F and cannot be expres ...
... Temperature is the thing that’s the same for two objects, after they’ve been in contact long enough. Long enough so that the two objects are in thermal equilibrium. Time required to reach thermal equilibrium is the relaxation time. Temperature is usually measured in K, C or F and cannot be expres ...
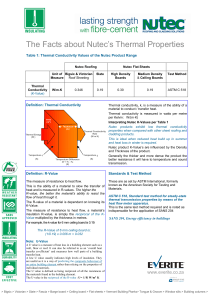
The Facts about Nutec Thermal Properties 11 5 12.pub
... thermal transmission properties by means of the heat flow meter apparatus. This is the same test method required and is noted as indispensable for the application of SANS 204 ...
... thermal transmission properties by means of the heat flow meter apparatus. This is the same test method required and is noted as indispensable for the application of SANS 204 ...
The initial screen level temperature, the relation to surface analysis
... Run the physics 4 timesteps only including surface scheme and vertical diffusion (+ changes in lw-radiation due to different surface temperatures), starting from the analysed values. Perturb the surface temps, (reasonably distributed among the tiles) and calculate the numerical derivative of the T2m ...
... Run the physics 4 timesteps only including surface scheme and vertical diffusion (+ changes in lw-radiation due to different surface temperatures), starting from the analysed values. Perturb the surface temps, (reasonably distributed among the tiles) and calculate the numerical derivative of the T2m ...
TDS template
... Cement Plaster (Mortar) 1.25” thick (29mm) - 1.25 Exterior Gypsum Sheathing 5/8” thick (13mm) - .67 Airspace - .68 Total R Value of all of the above materials = 4.46 NOTE: Portland cement based mortars will have an R-Value similar to concrete. The thickness of the mortar will equal it’s R-Valu ...
... Cement Plaster (Mortar) 1.25” thick (29mm) - 1.25 Exterior Gypsum Sheathing 5/8” thick (13mm) - .67 Airspace - .68 Total R Value of all of the above materials = 4.46 NOTE: Portland cement based mortars will have an R-Value similar to concrete. The thickness of the mortar will equal it’s R-Valu ...
Skills Worksheet
... basement. The hot gases from the combustion of wood or coal rose through the ducts and provided heat for the building. After the fall of the Roman Empire, these heating pipes disappeared. People used open fires and fireplaces. One problem with fireplaces is that 80 percent of the heat escapes up the ...
... basement. The hot gases from the combustion of wood or coal rose through the ducts and provided heat for the building. After the fall of the Roman Empire, these heating pipes disappeared. People used open fires and fireplaces. One problem with fireplaces is that 80 percent of the heat escapes up the ...
Document
... R-Value defined: a numerical measure of resistance to the flow of heat; the higher the R-value, the greater the resistance to heat flow Specific resistance of any material is directly related to it’s thickness ...
... R-Value defined: a numerical measure of resistance to the flow of heat; the higher the R-value, the greater the resistance to heat flow Specific resistance of any material is directly related to it’s thickness ...
Space Shuttle thermal protection system

The Space Shuttle thermal protection system (TPS) is the barrier that protected the Space Shuttle Orbiter during the searing 1,650 °C (3,000 °F) heat of atmospheric reentry. A secondary goal was to protect from the heat and cold of space while on orbit.