... at peak hours. Solar peak hours can be defined as the period when radiation would be the dominant source of heating (Memon et al., 2009). As shown in different construction materials, granite showed the highest difference between surface and ambient temperature while the solar radiation depicted at ...
Molar Heat of VaporizationREV
... solidifies (or freezes) to a solid q = mol x Hsolid. (no temperature change) ...
... solidifies (or freezes) to a solid q = mol x Hsolid. (no temperature change) ...
3 insulators/conductors
... INSULATORS • materials that do not allow heat to travel through it • poor conductor of heat • materials that prevent heat loss ...
... INSULATORS • materials that do not allow heat to travel through it • poor conductor of heat • materials that prevent heat loss ...
ME 3210 Mechatronics – Thermal Systems
... There are only two elements with thermal systems, thermal capacitance, and thermal resistance. Thermal capacitors store temperature and resistors dissipate energy. There is no element that can store heat flow. There is no such thing as thermal inertia. The consequence of this is that there are only ...
... There are only two elements with thermal systems, thermal capacitance, and thermal resistance. Thermal capacitors store temperature and resistors dissipate energy. There is no element that can store heat flow. There is no such thing as thermal inertia. The consequence of this is that there are only ...
SPECIFIC HEAT
... CALORIMETRY & SPECIFIC HEAT THEORY Heat energy is defined as energy that flows from hot objects to cold objects. It can be measured in calories, kilocalories, or joules of energy. One calorie is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 C. One calorie i ...
... CALORIMETRY & SPECIFIC HEAT THEORY Heat energy is defined as energy that flows from hot objects to cold objects. It can be measured in calories, kilocalories, or joules of energy. One calorie is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 C. One calorie i ...
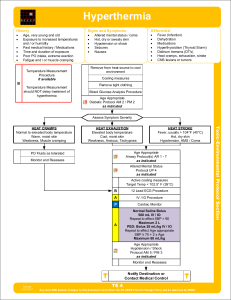
Hyperthermia
... Consists of dehydration, tachycardia, hypotension, temperature 104°F (40°C), and an altered mental status. Sweating generally disappears as body temperature rises above 104°F (40°C). The young and elderly are more prone to be dry with no sweating. Exertional Heat Stroke: In exertional heat stroke (a ...
... Consists of dehydration, tachycardia, hypotension, temperature 104°F (40°C), and an altered mental status. Sweating generally disappears as body temperature rises above 104°F (40°C). The young and elderly are more prone to be dry with no sweating. Exertional Heat Stroke: In exertional heat stroke (a ...
Laboratories at Building Materials, Lund University, Sweden
... Building Materials at Lund University has for many years been specialists in material properties related to water and water vapor, for example diffusion coefficient and sorption isotherms. We have during the last five years complemented this with a thermal properties laboratory, as both thermal and ...
... Building Materials at Lund University has for many years been specialists in material properties related to water and water vapor, for example diffusion coefficient and sorption isotherms. We have during the last five years complemented this with a thermal properties laboratory, as both thermal and ...
Tutorial 3
... layer (B) was 40 ºC. After an additional layer of insulation of thickness of 0.02 m and thermal conductivity 0.2 W/m K, was added to the outer surface of layer (B) the pipe temperature was found to be 500 ºC, the outer surface of layer (B) 180 ºC, and the outer surface of the new insulation 30 ºC. W ...
... layer (B) was 40 ºC. After an additional layer of insulation of thickness of 0.02 m and thermal conductivity 0.2 W/m K, was added to the outer surface of layer (B) the pipe temperature was found to be 500 ºC, the outer surface of layer (B) 180 ºC, and the outer surface of the new insulation 30 ºC. W ...
Buffet_geoneutrino - University of Hawaii Physics and Astronomy
... Power Requirements for Dynamo ...
... Power Requirements for Dynamo ...
Heat Transfer LAB
... particle to another through direct contact. This heat transfer always moves from the faster moving particle (hot) to the slower moving particle (cool). Conductors are substances that permit the flow of heat or electricity easily, while insulators are substances that do not permit the flow of heat or ...
... particle to another through direct contact. This heat transfer always moves from the faster moving particle (hot) to the slower moving particle (cool). Conductors are substances that permit the flow of heat or electricity easily, while insulators are substances that do not permit the flow of heat or ...
Chapter 10 Power Point
... Hot liquids and gases expand and rise while the cooler liquid or gas falls (all caused by a difference in densities!) ...
... Hot liquids and gases expand and rise while the cooler liquid or gas falls (all caused by a difference in densities!) ...
Flat Plate Boundary Layer
... A radiator is a type of heat exchanger. It is designed to transfer heat from the hot coolant that flows through it to the air blown through it by the fan. Most modern cars use aluminum radiators. These radiators are made by brazing thin aluminum fins to flattened aluminum tubes. The coolant flows fr ...
... A radiator is a type of heat exchanger. It is designed to transfer heat from the hot coolant that flows through it to the air blown through it by the fan. Most modern cars use aluminum radiators. These radiators are made by brazing thin aluminum fins to flattened aluminum tubes. The coolant flows fr ...
Page 1 of 2 Gerbing`s Heated Clothing // How it Works 02/11/2009
... further tune how the heat is delivered. More, when using the ribbon matrix, we could refine the heat delivery to an even greater degree by altering the number of wires in the ribbon (from 2 up to 6). It is this “tunability” to each garment application that is one of the major advantages of Microwire ...
... further tune how the heat is delivered. More, when using the ribbon matrix, we could refine the heat delivery to an even greater degree by altering the number of wires in the ribbon (from 2 up to 6). It is this “tunability” to each garment application that is one of the major advantages of Microwire ...
Neonatal Thermoregulation
... Allen, K. (2011) Neonatal thermal care: A discussion of two incubator modes for optimising thermoregulation. A care study. Journal of Neonatal Nursing. 17, 2; 43-48 Aylott, M. (2006a) The Neonatal energy triangle part 1; Metabolic adaptation. Paediatric Nursing. 18, ...
... Allen, K. (2011) Neonatal thermal care: A discussion of two incubator modes for optimising thermoregulation. A care study. Journal of Neonatal Nursing. 17, 2; 43-48 Aylott, M. (2006a) The Neonatal energy triangle part 1; Metabolic adaptation. Paediatric Nursing. 18, ...
Heat Transfer There are three mechanisms for the transfer of heat
... Question: in the absence of internal heat production, how does the geotherm look like? If there’s nonzero net heat flow per unit area out of the slab, this heat must be generated internally in the slab. In that case: d2 t q(y + δy) − q(y) = δy(−k 2 ) = δyρH, dy where: H is the heat production rate ...
... Question: in the absence of internal heat production, how does the geotherm look like? If there’s nonzero net heat flow per unit area out of the slab, this heat must be generated internally in the slab. In that case: d2 t q(y + δy) − q(y) = δy(−k 2 ) = δyρH, dy where: H is the heat production rate ...
Table S1: Properties of Antigorite as a Model
... For the stalled-slab scenario, the initial temperature field is calculated for a much larger model domain assuming a 10-Ma old slab subducting at 4 cm/yr at the steady state, with boundary conditions and mantle wedge flow introduced in exactly the same way as described in Peacock and Wang (1999). Th ...
... For the stalled-slab scenario, the initial temperature field is calculated for a much larger model domain assuming a 10-Ma old slab subducting at 4 cm/yr at the steady state, with boundary conditions and mantle wedge flow introduced in exactly the same way as described in Peacock and Wang (1999). Th ...
Discovery Education Science Connection
... Evaporative cooling is when wind causes moisture on the skin to turn into vapor, taking heat away from the body in the process. Standing in direct sunlight can make the heat index increase by 15° F. On a particular day, the heat index may be 95° F. The temperature will feel much hotter to a person w ...
... Evaporative cooling is when wind causes moisture on the skin to turn into vapor, taking heat away from the body in the process. Standing in direct sunlight can make the heat index increase by 15° F. On a particular day, the heat index may be 95° F. The temperature will feel much hotter to a person w ...
21.3 Administering Heat/Cold Applications
... Used most often with patients that have Chronic joint disease, such as arthritis, or sometimes prior to ROM exercises Paraffin Wax is mixed with Mineral Oil and melted The body part is dipped in the wax four to five times creating a sealing of heat and left in place for 20-30 minutes ...
... Used most often with patients that have Chronic joint disease, such as arthritis, or sometimes prior to ROM exercises Paraffin Wax is mixed with Mineral Oil and melted The body part is dipped in the wax four to five times creating a sealing of heat and left in place for 20-30 minutes ...
Heat on the move
... Heat can move from one place to another – heat Put the three spoons into the container of hot is transferred. It always moves from somewhere water. Feel the ends of the spoons. Which of the or something hot to a place or object that’s cooler. ends became hot? Can you think of some examples? When hea ...
... Heat can move from one place to another – heat Put the three spoons into the container of hot is transferred. It always moves from somewhere water. Feel the ends of the spoons. Which of the or something hot to a place or object that’s cooler. ends became hot? Can you think of some examples? When hea ...
Lesson Plan: What Makes Something Feel Warm? Modeling Energy
... energy changes. In this session we will explore changes in thermal energy, such as how we feel when we forget to put on a sweater during cold weather, or when we wear too many clothes when it’s hot outside. Students’ understanding of heat, temperature and chemical systems needs to be carefully const ...
... energy changes. In this session we will explore changes in thermal energy, such as how we feel when we forget to put on a sweater during cold weather, or when we wear too many clothes when it’s hot outside. Students’ understanding of heat, temperature and chemical systems needs to be carefully const ...
Heat transfer in heated industrial premises with using radiant
... economically justified. Expedient use of infrared gas radiators for optimal thermal regime in certain areas large space for production purposes. Introduction in practice of heat radiation heating systems until recently, severely limited by including in connection with the lack of science-based techn ...
... economically justified. Expedient use of infrared gas radiators for optimal thermal regime in certain areas large space for production purposes. Introduction in practice of heat radiation heating systems until recently, severely limited by including in connection with the lack of science-based techn ...
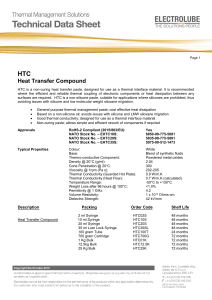
Product Code: HTC
... There are many methods of measuring thermal conductivity, resulting in large variances in results. Electrolube utilise a heat flow method which takes into account the surface resistance of the test substrate, thus offering highly accurate results of true thermal conductivity. Some alternative method ...
... There are many methods of measuring thermal conductivity, resulting in large variances in results. Electrolube utilise a heat flow method which takes into account the surface resistance of the test substrate, thus offering highly accurate results of true thermal conductivity. Some alternative method ...
3-1C (a) If the lateral surfaces of the rod are insulated, the heat
... 3-10C Once the rate of heat transfer Q& is known, the temperature drop across any layer can be determined ...
... 3-10C Once the rate of heat transfer Q& is known, the temperature drop across any layer can be determined ...
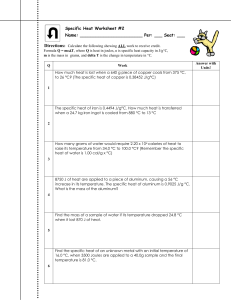
Specific Heat WS #2 - My Chemistry Class
... 8750 J of heat are applied to a piece of aluminum, causing a 56 °C increase in its temperature. The specific heat of aluminum is 0.9025 J/g °C. What is the mass of the aluminum? ...
... 8750 J of heat are applied to a piece of aluminum, causing a 56 °C increase in its temperature. The specific heat of aluminum is 0.9025 J/g °C. What is the mass of the aluminum? ...
HTC Heat Transfer Compound
... There are many methods of measuring thermal conductivity, resulting in large variances in results. Electrolube utilise a heat flow method which takes into account the surface resistance of the test substrate, thus offering highly accurate results of true thermal conductivity. Some alternative method ...
... There are many methods of measuring thermal conductivity, resulting in large variances in results. Electrolube utilise a heat flow method which takes into account the surface resistance of the test substrate, thus offering highly accurate results of true thermal conductivity. Some alternative method ...
Space Shuttle thermal protection system

The Space Shuttle thermal protection system (TPS) is the barrier that protected the Space Shuttle Orbiter during the searing 1,650 °C (3,000 °F) heat of atmospheric reentry. A secondary goal was to protect from the heat and cold of space while on orbit.