Experiment 5
... where L is the latent heat of transformation appropriate for the type of phase change taking place. In using eq. 2, the sign must be chosen appropriately according to the sign convention discussed above. As an example, if the object is melting, heat is being added so that the plus sign is correct. T ...
... where L is the latent heat of transformation appropriate for the type of phase change taking place. In using eq. 2, the sign must be chosen appropriately according to the sign convention discussed above. As an example, if the object is melting, heat is being added so that the plus sign is correct. T ...
Chapter_03_Thermal_comfort_and_Heat_stess.pdf
... All terms in Eq. (3-38) have dimensions of energy per unit time, i.e. power. Each of these heat transfer terms is considered separately below. Conduction: Conduction heat transfer is by direct contact with solid surfaces, such as chairs, the floor, etc. Since the surface area in such contact is smal ...
... All terms in Eq. (3-38) have dimensions of energy per unit time, i.e. power. Each of these heat transfer terms is considered separately below. Conduction: Conduction heat transfer is by direct contact with solid surfaces, such as chairs, the floor, etc. Since the surface area in such contact is smal ...
Heat Transfer/ Specific Heat Problems Worksheet
... 2. How much heat is lost when a 64 g piece of copper cools from 375 oC, to 26 oC? (The specific heat of copper is 0.38452 J/g x oC). Place your answer in kJ. 3. The specific heat of iron is 0.4494 J/g x oC. How much heat is transferred when a 4.7 kg piece of iron is cooled from 180 oC to 13 oC? Reme ...
... 2. How much heat is lost when a 64 g piece of copper cools from 375 oC, to 26 oC? (The specific heat of copper is 0.38452 J/g x oC). Place your answer in kJ. 3. The specific heat of iron is 0.4494 J/g x oC. How much heat is transferred when a 4.7 kg piece of iron is cooled from 180 oC to 13 oC? Reme ...
ch1010 heat transfer unit i heat conduction
... temperature varies on a regular basis, eg., the variation of temperature of the surface of the earth during a twenty four hour period.. In the non periodic type, the temperature at any point within the system varies non linearly with time. 1.10.1. Systems with negligible internal resistance – Lumped ...
... temperature varies on a regular basis, eg., the variation of temperature of the surface of the earth during a twenty four hour period.. In the non periodic type, the temperature at any point within the system varies non linearly with time. 1.10.1. Systems with negligible internal resistance – Lumped ...
Calorimetry Lab
... 3) Show the calculation for preparing 250 mL of a 1.00 M solution of sodium hydroxide starting with the solid reagent. 4) The master equation for calculating enthalpies of reaction in a calorimeter experiment is q = m C T . What are the units for each of these terms? 5) What is the numerical value ...
... 3) Show the calculation for preparing 250 mL of a 1.00 M solution of sodium hydroxide starting with the solid reagent. 4) The master equation for calculating enthalpies of reaction in a calorimeter experiment is q = m C T . What are the units for each of these terms? 5) What is the numerical value ...
Calorimetry Lab
... 3) Show the calculation for preparing 250 mL of a 1.00 M solution of sodium hydroxide starting with the solid reagent. 4) The master equation for calculating enthalpies of reaction in a calorimeter experiment is q = m C T . What are the units for each of these terms? 5) What is the numerical value ...
... 3) Show the calculation for preparing 250 mL of a 1.00 M solution of sodium hydroxide starting with the solid reagent. 4) The master equation for calculating enthalpies of reaction in a calorimeter experiment is q = m C T . What are the units for each of these terms? 5) What is the numerical value ...
presentation
... • To model the development of metamorphic zones around a dyke that is emplaced at the surface • Develop the discretised 2D heat equation by varying the model’s thermal properties and implementing progressive metamorphism • Show how different rock types affect the degree of metamorphism • I have two ...
... • To model the development of metamorphic zones around a dyke that is emplaced at the surface • Develop the discretised 2D heat equation by varying the model’s thermal properties and implementing progressive metamorphism • Show how different rock types affect the degree of metamorphism • I have two ...
doc heat conversion
... substance becomes hotter. Similarly, when heat energy if withdrawn from a substance the particles move slower and becomes colder. The Relationship between Heat and Temperature When a substance is heated, its temperature rises. Heat decreases or increases the temperature of a body. For instance, when ...
... substance becomes hotter. Similarly, when heat energy if withdrawn from a substance the particles move slower and becomes colder. The Relationship between Heat and Temperature When a substance is heated, its temperature rises. Heat decreases or increases the temperature of a body. For instance, when ...
Environmental control of cultural institutions Part 4
... popularising this approach. However, it is better not to rely on screening conventional openings from the sun by the use of such 'brise-soleil' type grids, because they act to store the solar radiation and effectively transfer it to ventilating air passing over them on the way to the interior. If th ...
... popularising this approach. However, it is better not to rely on screening conventional openings from the sun by the use of such 'brise-soleil' type grids, because they act to store the solar radiation and effectively transfer it to ventilating air passing over them on the way to the interior. If th ...
Analysis of Heat Transfer in Rectangular
... Micro-channel Heat transfer has the very potential of wide applications in cooling high power density microchips in the CPU system, the micro power systems and even many other large scale thermal systems requiring effective cooling capacity. This is a result of the micro size of the cooling system w ...
... Micro-channel Heat transfer has the very potential of wide applications in cooling high power density microchips in the CPU system, the micro power systems and even many other large scale thermal systems requiring effective cooling capacity. This is a result of the micro size of the cooling system w ...
Physics 202 Homework
... ∆Q = cm∆T = (2000)(m1 )(10) = (20000)(m1 ) Then melt the ice: ∆Q = mLf = (m1 )(335000) Then raise the temperature of the liquid ice: ∆Q = cm∆T = (4186)(m1 )(50) = (209300)(m1 ) Adding these together yields the total heat required: ∆Q = (20000)(m1 ) + (335000)(m1 ) + (209300)(m1 ) = (564300)(m1 ) Thi ...
... ∆Q = cm∆T = (2000)(m1 )(10) = (20000)(m1 ) Then melt the ice: ∆Q = mLf = (m1 )(335000) Then raise the temperature of the liquid ice: ∆Q = cm∆T = (4186)(m1 )(50) = (209300)(m1 ) Adding these together yields the total heat required: ∆Q = (20000)(m1 ) + (335000)(m1 ) + (209300)(m1 ) = (564300)(m1 ) Thi ...
Appendix A – Heat transfer coefficients
... gas phase since, in both cases, the heat exchange conditions are the same: natural convection on a vertical plate. For the heat exchange between the rabble arms and the gas phase, the Nusselt number is calculated with the same equation A.14 on the hearths 1 to 6. In the hearths 7 and 8, the Nusselt ...
... gas phase since, in both cases, the heat exchange conditions are the same: natural convection on a vertical plate. For the heat exchange between the rabble arms and the gas phase, the Nusselt number is calculated with the same equation A.14 on the hearths 1 to 6. In the hearths 7 and 8, the Nusselt ...
Industrial Extraction
... given to the quantity of heat which is forming at production acid and equal 3.25 k.J per day. Looses for a heating in surroundings are equal 0.40 k.J per day. The heat to warm up the constructive materials of the device is 1.15 k.J per day ...
... given to the quantity of heat which is forming at production acid and equal 3.25 k.J per day. Looses for a heating in surroundings are equal 0.40 k.J per day. The heat to warm up the constructive materials of the device is 1.15 k.J per day ...
21.7 The High Specific Heat Capacity of Water
... What happens when a warmer substance comes in contact with a cooler substance? • Heat flows between two objects of different temperature until they have the same temperature. • The loss of thermal energy from the warmer object equals the gain of thermal energy for the cooler object ...
... What happens when a warmer substance comes in contact with a cooler substance? • Heat flows between two objects of different temperature until they have the same temperature. • The loss of thermal energy from the warmer object equals the gain of thermal energy for the cooler object ...
Temperature Differences in the Beam Screen
... kept under the necessary limit without any additional actions • Some Possibilities to decrease the temperature difference: o Increase cross section area of BS between the dipoles o Different material or composition of materials o Separate cooling ...
... kept under the necessary limit without any additional actions • Some Possibilities to decrease the temperature difference: o Increase cross section area of BS between the dipoles o Different material or composition of materials o Separate cooling ...
EQ: How can heat be transferred from one place to another?
... transfers to another object/form of matter. Heat transfer occurs only in one direction. ...
... transfers to another object/form of matter. Heat transfer occurs only in one direction. ...
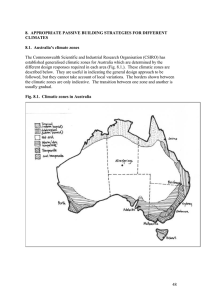
Solar passive design – combining orientation, thermal mass and
... of thermal mass, but many cannot store large quantities of heat (e.g. wood, plasterboard), while others re-radiate heat rapidly rather than retaining it (e.g. metals). Water has the highest thermal mass of any common material on Earth, but we cannot build with water, so the best thermal mass for bui ...
... of thermal mass, but many cannot store large quantities of heat (e.g. wood, plasterboard), while others re-radiate heat rapidly rather than retaining it (e.g. metals). Water has the highest thermal mass of any common material on Earth, but we cannot build with water, so the best thermal mass for bui ...
Radiant Cooling: Thermally Active Floors
... heat gain directly from the slab. With a lower limit on the temperature of the floor surface of 68°F (20°C), and a room temperature of 76°F (24°C), the maximum cooling capacity of a floor can be less than 10 Btu/ft2·h (31 W/m2·h). European comfort standards allow a maximum air temperature of 79°F (2 ...
... heat gain directly from the slab. With a lower limit on the temperature of the floor surface of 68°F (20°C), and a room temperature of 76°F (24°C), the maximum cooling capacity of a floor can be less than 10 Btu/ft2·h (31 W/m2·h). European comfort standards allow a maximum air temperature of 79°F (2 ...
Science 9th grade LEARNING OBJECT How is heat transferred
... 2. Solar panel: The heat reaches the panel from the Sun through radiation. If an object is placed on top of the panel, the heat will be transferred by conduction. (Figure 7) 3. Microwave oven: Electrons located in higher energetic levels inside the atom fall to lower levels, releasing electromagneti ...
... 2. Solar panel: The heat reaches the panel from the Sun through radiation. If an object is placed on top of the panel, the heat will be transferred by conduction. (Figure 7) 3. Microwave oven: Electrons located in higher energetic levels inside the atom fall to lower levels, releasing electromagneti ...
Heat
... 1. Work the problems suggested on last week’s calendar. 2. Complete the short answer first. This section is worth 54.5 points. Spend no more than one hour on this section. 3. There are NO calculations in the multiple choice section. The 13 questions are conceptbased, and they count 3.5 points each. ...
... 1. Work the problems suggested on last week’s calendar. 2. Complete the short answer first. This section is worth 54.5 points. Spend no more than one hour on this section. 3. There are NO calculations in the multiple choice section. The 13 questions are conceptbased, and they count 3.5 points each. ...
Total-Precast Solution Provides Sturdy Data Center
... where small louvers and exhaust vents were needed, making those less obtrusive.” The louvers are on the second level, placing the medallions high in a visible location. Windows were used on the first floor around office spaces. “The medallions were a key design challenge in terms of placing them and ...
... where small louvers and exhaust vents were needed, making those less obtrusive.” The louvers are on the second level, placing the medallions high in a visible location. Windows were used on the first floor around office spaces. “The medallions were a key design challenge in terms of placing them and ...
Summary
... you think the rate of heat transfer from the surface has increased or decreased as a result of addition of fins? 5. Fins are normally meant to enhance heat transfer. Under what circumstances the addition of fins may actually decrease heat transfer? 6. Hot water is to be cooled as it flows through th ...
... you think the rate of heat transfer from the surface has increased or decreased as a result of addition of fins? 5. Fins are normally meant to enhance heat transfer. Under what circumstances the addition of fins may actually decrease heat transfer? 6. Hot water is to be cooled as it flows through th ...
AGU Fall Meeting 08 - Global Heat Flow Database
... tested the reliability of the computations using different half-spreading rates and different node spacings and verified that the models yield equivalent results at equivalent times and depths. The model result agrees closely with the GDH1, HSC, and PSM models for ages less than 5 ma and shows sligh ...
... tested the reliability of the computations using different half-spreading rates and different node spacings and verified that the models yield equivalent results at equivalent times and depths. The model result agrees closely with the GDH1, HSC, and PSM models for ages less than 5 ma and shows sligh ...
Building insulation materials

Building insulation materials are the building materials which form the thermal envelope of a building or otherwise reduce heat transfer.Insulation may be categorized by its composition (natural or synthetic materials), form (batts, blankets, loose-fill, spray foam, and panels), structural contribution (insulating concrete forms, structured panels, and straw bales), functional mode (conductive, radiative, convective), resistance to heat transfer, environmental impacts, and more. Sometimes a thermally reflective surface called a radiant barrier is added to a material to reduce the transfer of heat through radiation as well as conduction. The choice of which material or combination of materials is used depends on a wide variety of factors. Some insulation materials have health risks, some so significant the materials are no longer allowed to be used but remain in use in some older buildings such as asbestos fibers and urea