L 17
... Refrigerators and the 2nd Law • Does this violate the 2nd law? NO, because it is not a spontaneous process • Refrigerators require energy input (work) (electricity) to operate. • Heat does not flow spontaneously from cold to hot, but it can be made to flow backwards if there is an input of WORK. • ...
... Refrigerators and the 2nd Law • Does this violate the 2nd law? NO, because it is not a spontaneous process • Refrigerators require energy input (work) (electricity) to operate. • Heat does not flow spontaneously from cold to hot, but it can be made to flow backwards if there is an input of WORK. • ...
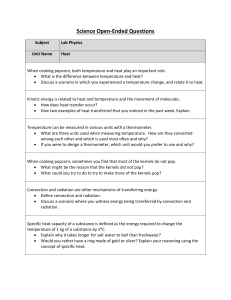
Physics-Heat OEQs
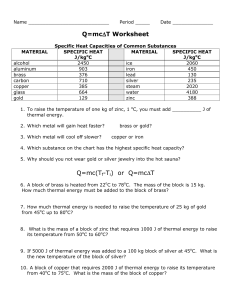
... Specific heat capacity of a substance is defined as the energy required to change the temperature of 1 kg of a substance by 1⁰C. Explain why it takes longer for salt water to boil than freshwater? Would you rather have a ring made of gold or silver? Explain your reasoning using the concept of sp ...
... Specific heat capacity of a substance is defined as the energy required to change the temperature of 1 kg of a substance by 1⁰C. Explain why it takes longer for salt water to boil than freshwater? Would you rather have a ring made of gold or silver? Explain your reasoning using the concept of sp ...
Abrasive: A hard material used to grind, cut or
... Phosphorescence: Luminescence that lasts for more than one second. Photovoltaic cells: A device capable of converting light energy to electricity. Photoconductivity: Electrical conductivity induced by light. Photon: Quantum of electromagnetic energy. Piezoelectric: Material which produces an electri ...
... Phosphorescence: Luminescence that lasts for more than one second. Photovoltaic cells: A device capable of converting light energy to electricity. Photoconductivity: Electrical conductivity induced by light. Photon: Quantum of electromagnetic energy. Piezoelectric: Material which produces an electri ...
HeatTransfer
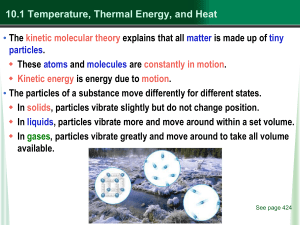
... • The kinetic molecular theory explains that all matter is made up of tiny particles. These atoms and molecules are constantly in motion. Kinetic energy is energy due to motion. • The particles of a substance move differently for different states. In solids, particles vibrate slightly but do n ...
... • The kinetic molecular theory explains that all matter is made up of tiny particles. These atoms and molecules are constantly in motion. Kinetic energy is energy due to motion. • The particles of a substance move differently for different states. In solids, particles vibrate slightly but do n ...
2.2) Conduction - Concord Consortium
... In the building trades, the rate of heat loss is called conductivity (U), which is the same as k, seen on page 31. The most common measure of conductivity is its inverse: resistance to heat flow, called R or R-value. R (thermal resistivity) = 1 / U (thermal conductivity) The greater the value of R, ...
... In the building trades, the rate of heat loss is called conductivity (U), which is the same as k, seen on page 31. The most common measure of conductivity is its inverse: resistance to heat flow, called R or R-value. R (thermal resistivity) = 1 / U (thermal conductivity) The greater the value of R, ...
95HE-4
... 3. Which of the following combinations of properties would be most desirable for a cooking pot A. High specific heat and low thermal conductivity B. Low specific heat and high thermal condcutivity C. High specific heat and high thermal conductivity D. Low specific heat and low thermal conductivity 4 ...
... 3. Which of the following combinations of properties would be most desirable for a cooking pot A. High specific heat and low thermal conductivity B. Low specific heat and high thermal condcutivity C. High specific heat and high thermal conductivity D. Low specific heat and low thermal conductivity 4 ...
Un-Steady State Conduction
... The objective of this experiment is to study unsteady-state conduction and to determine the thermal conductivity of the solid. If all the necessary physical properties of the solid are known, the thermal history within the body may be evaluated for a given set of energy input conditions. A calculate ...
... The objective of this experiment is to study unsteady-state conduction and to determine the thermal conductivity of the solid. If all the necessary physical properties of the solid are known, the thermal history within the body may be evaluated for a given set of energy input conditions. A calculate ...
Workshop National sur l`Hydrogène – Université Kasdi Merbah – Ou
... Radiative transport within the electrode and electrolyte layers, as well as surface-tosurface radiation within the fuel and oxygen flow channels, has the potential to greatly influence temperature fields and overall operating conditions of solid oxide fuel cells (SOFC). Radiation from the stack to t ...
... Radiative transport within the electrode and electrolyte layers, as well as surface-tosurface radiation within the fuel and oxygen flow channels, has the potential to greatly influence temperature fields and overall operating conditions of solid oxide fuel cells (SOFC). Radiation from the stack to t ...
Heat and Thermal Energy Word Problems
... 13. A 500 g block of metal absorbs 5016 J of heat when its temperature changes from 20.0oC to 30.0oC. Calculate the specific heat of the metal. 14. A copper wire has a mass of 165 g. An electric current runs through the wire for a short time and its temperature rises from 21oC to 39oC. What minimum ...
... 13. A 500 g block of metal absorbs 5016 J of heat when its temperature changes from 20.0oC to 30.0oC. Calculate the specific heat of the metal. 14. A copper wire has a mass of 165 g. An electric current runs through the wire for a short time and its temperature rises from 21oC to 39oC. What minimum ...