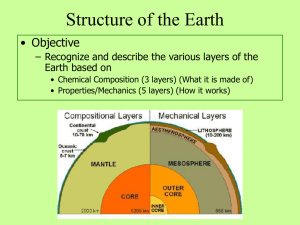
Structure of the Ear..
... How might the Earth’s surface be different if the Asthenosphere was solid? a. The Earth’s mountains would be much taller b. There would be more earthquakes c. The Earth’s mountain ranges would be more numerous d. There would be no mountains or earthquakes ...
... How might the Earth’s surface be different if the Asthenosphere was solid? a. The Earth’s mountains would be much taller b. There would be more earthquakes c. The Earth’s mountain ranges would be more numerous d. There would be no mountains or earthquakes ...
Name: _________________________ Period: ______ Date
... The oceanic and continental plates are colliding and the more dense oceanic plate is being subducted underneath the continental plate. B. Why are volcanoes and earthquakes found along these type of plate boundaries? Volcanoes- As one plate slides under another, hot rock material in the upper mantle ...
... The oceanic and continental plates are colliding and the more dense oceanic plate is being subducted underneath the continental plate. B. Why are volcanoes and earthquakes found along these type of plate boundaries? Volcanoes- As one plate slides under another, hot rock material in the upper mantle ...
6th Grade Earth Science
... • A mineral can also be identified by the ______ shape of its crystals. • _______ Cleavage - minerals show particular patterns when they are broken along flat planes. ...
... • A mineral can also be identified by the ______ shape of its crystals. • _______ Cleavage - minerals show particular patterns when they are broken along flat planes. ...
common formative assessment planning template
... explains the formation, movement and seduction of Earth’s plates. 2. Most volcanoes and earthquakes are located at tectonic plate boundaries where plates come together or move apart from each other. Volcanic activity and the folding and faulting of rock layers during the shifting of the Earth’s crus ...
... explains the formation, movement and seduction of Earth’s plates. 2. Most volcanoes and earthquakes are located at tectonic plate boundaries where plates come together or move apart from each other. Volcanic activity and the folding and faulting of rock layers during the shifting of the Earth’s crus ...
processes that shape the earth
... Some earthquakes can happen below oceans. If strong enough, it causes a giant wave called a tsunami. Seismograph ~ scientist study earthquakes using this instrument. It detects and records seismic waves caused by earthquakes. Seismic waves are vibrations caused by earthquakes. 2. Volcanoes ~ ...
... Some earthquakes can happen below oceans. If strong enough, it causes a giant wave called a tsunami. Seismograph ~ scientist study earthquakes using this instrument. It detects and records seismic waves caused by earthquakes. Seismic waves are vibrations caused by earthquakes. 2. Volcanoes ~ ...
anddestructiveforces_powerpoint
... land itself is totally changed. You can see scars across the landscape. Those scars appear when one block of land has moved compared to another. Roads often change their placement. They either become uneven or just crack. Streams can also change course. Sometimes rocks can fall and block the stream. ...
... land itself is totally changed. You can see scars across the landscape. Those scars appear when one block of land has moved compared to another. Roads often change their placement. They either become uneven or just crack. Streams can also change course. Sometimes rocks can fall and block the stream. ...
File - Pi Beta Philes!
... C. the development of one or more working hypotheses or models to explain facts D. development of observations and experiments to test the hypotheses 12) ________ rocks form by crystallization and consolidation of molten magma. A. Sedimentary B. Indigenous C. Primary D. Igneous 13) ________ rocks a ...
... C. the development of one or more working hypotheses or models to explain facts D. development of observations and experiments to test the hypotheses 12) ________ rocks form by crystallization and consolidation of molten magma. A. Sedimentary B. Indigenous C. Primary D. Igneous 13) ________ rocks a ...
Social Studies
... Inner Core 2. Pangaea a. The name given to Earth’s landmasses when it formed one huge supercontinent. 3. Continental Drift Theory a. Forces within earth caused Pangaea to break apart into continental plates and drift apart. 4. Mountain formation a. tectonic plates push together b. two plates collide ...
... Inner Core 2. Pangaea a. The name given to Earth’s landmasses when it formed one huge supercontinent. 3. Continental Drift Theory a. Forces within earth caused Pangaea to break apart into continental plates and drift apart. 4. Mountain formation a. tectonic plates push together b. two plates collide ...
Inside the Earth
... Physical Structure of the Earth (5 Layers) • Lithosphere- rigid outer layer (crust) • Asthenosphere- solid rock that flows slowly (like hot asphalt) • Mesosphere- middle layer • Outer Core- liquid layer • Inner Core- solid, very dense ...
... Physical Structure of the Earth (5 Layers) • Lithosphere- rigid outer layer (crust) • Asthenosphere- solid rock that flows slowly (like hot asphalt) • Mesosphere- middle layer • Outer Core- liquid layer • Inner Core- solid, very dense ...
Vocabulary for Earth`s Structure and Note Cards Crust – the
... Mantle – The layer of the Earth between the crust and the outer core Core – the Earth’s layer that extends from below the mantle to the center of the Earth. Outer core – liquid part of the core, made of molten iron and nickel Inner core – solid part of the core, mostly made of solid iron and nickel ...
... Mantle – The layer of the Earth between the crust and the outer core Core – the Earth’s layer that extends from below the mantle to the center of the Earth. Outer core – liquid part of the core, made of molten iron and nickel Inner core – solid part of the core, mostly made of solid iron and nickel ...
landforms!!!!!!!
... pushes up towards the surface of the Earth’s crust. If the magma does not break through but rises a section of the crust and creates a plateau. Another way plateaus are formed is when lava breaks through the Earth’s crust and builds on itself over and over to form a raised area of land. Plateaus are ...
... pushes up towards the surface of the Earth’s crust. If the magma does not break through but rises a section of the crust and creates a plateau. Another way plateaus are formed is when lava breaks through the Earth’s crust and builds on itself over and over to form a raised area of land. Plateaus are ...
The Appalachian Story sheet
... 13. Generally the sediments are approximately _________ million years old in this region, formed in the ancient ocean called "__________________________". 14. The breccia was originally formed by underwater _________________________, and contains critical information. 15. At Greenpoint, a dozen of f ...
... 13. Generally the sediments are approximately _________ million years old in this region, formed in the ancient ocean called "__________________________". 14. The breccia was originally formed by underwater _________________________, and contains critical information. 15. At Greenpoint, a dozen of f ...
Dynamic Earth Review Sheet
... Layers of the Earth o Be able to use the chart on page 10 to determine the different properties of the layers of the Earth. o Describe the major differences between continental and oceanic crust? ...
... Layers of the Earth o Be able to use the chart on page 10 to determine the different properties of the layers of the Earth. o Describe the major differences between continental and oceanic crust? ...
Early Earth Quiz Prep
... 1. The continents are made of lighter rocks than the plates, so ____________ _____________________________________________________________ 2. When the Americas bump into Asia in a few hundred million years _____________________________________________________________ 3. True or false (circle) – Cont ...
... 1. The continents are made of lighter rocks than the plates, so ____________ _____________________________________________________________ 2. When the Americas bump into Asia in a few hundred million years _____________________________________________________________ 3. True or false (circle) – Cont ...
Mountains, Volcanoes and Earthquakes
... earthquake’s strength is called its magnitude and is measured on the Richter scale. Like volcanoes, earthquakes mostly occur along plate boundaries. ...
... earthquake’s strength is called its magnitude and is measured on the Richter scale. Like volcanoes, earthquakes mostly occur along plate boundaries. ...
Dynamic Earth Review Sheet Plate Tectonics Be able to use the
... Layers of the Earth o Be able to use the chart on page 10 to determine the different properties of the layers of the Earth. o Describe the major differences between continental and oceanic crust? ...
... Layers of the Earth o Be able to use the chart on page 10 to determine the different properties of the layers of the Earth. o Describe the major differences between continental and oceanic crust? ...
The Big Picture
... ment, thus creating a landscape of different appearance. of magma occured in pulses over a period of time, crystalizing between 50 and 55 million years ago. The last dinosaurs were What if the magma intrusion in Texas Canyon had extinct 10 million years before these rocks were formed. The risen to t ...
... ment, thus creating a landscape of different appearance. of magma occured in pulses over a period of time, crystalizing between 50 and 55 million years ago. The last dinosaurs were What if the magma intrusion in Texas Canyon had extinct 10 million years before these rocks were formed. The risen to t ...
Plate Tectonics Earth`s Layers Boundaries Earthquakes Wild Card
... The deep interior of the earth can be mapped using… ...
... The deep interior of the earth can be mapped using… ...
GEO Team Practice Test Question Stems
... ____ 14. A rock that forms from cooling lava is classified as an ____. ____ 15. When large masses of magma solidify far below Earth’s surface, they form igneous rocks that have a ____. ____ 16. Lava that cools so quickly that ions do not have time to arrange themselves into crystals will form igneou ...
... ____ 14. A rock that forms from cooling lava is classified as an ____. ____ 15. When large masses of magma solidify far below Earth’s surface, they form igneous rocks that have a ____. ____ 16. Lava that cools so quickly that ions do not have time to arrange themselves into crystals will form igneou ...
Earth`s Interior
... – The forces that make and shape planet Earth. – The chemical and physical characteristics of rock. – The processes that create Earth’s features and search for clues about Earth’s history. ...
... – The forces that make and shape planet Earth. – The chemical and physical characteristics of rock. – The processes that create Earth’s features and search for clues about Earth’s history. ...
The Interior of Earth
... o Earth was molten o More dense materials sunk below (iron and nickel – became core) o Silicate rocks were buoyed up (floated) o This process when material is separated called differentiation All planets are differentiated Mars has a lot of iron on its surface and it rusted (that’s why Mars is red) ...
... o Earth was molten o More dense materials sunk below (iron and nickel – became core) o Silicate rocks were buoyed up (floated) o This process when material is separated called differentiation All planets are differentiated Mars has a lot of iron on its surface and it rusted (that’s why Mars is red) ...
Plate Tectonics Journey to the center of the Earth
... 41. The theory of plate tectonics EXPLAINS: a. _________________ b. Movement c. _________________ of Earth’s plates 42. What are some examples of changes that occur because of the movement of Earth’s plates? ...
... 41. The theory of plate tectonics EXPLAINS: a. _________________ b. Movement c. _________________ of Earth’s plates 42. What are some examples of changes that occur because of the movement of Earth’s plates? ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.