Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity
... • Batholiths are large masses of igneous rock that formed when magma intruded at depth, became crystallized, and subsequently was exposed by erosion. • An intrusive igneous body must have a surface exposure greater than 100 square kilometers to be considered a batholith. ...
... • Batholiths are large masses of igneous rock that formed when magma intruded at depth, became crystallized, and subsequently was exposed by erosion. • An intrusive igneous body must have a surface exposure greater than 100 square kilometers to be considered a batholith. ...
Chapter 10
... became crystallized, and subsequently was exposed by erosion. • An intrusive igneous body must have a surface exposure greater than 100 square kilometers to be considered a batholith. ...
... became crystallized, and subsequently was exposed by erosion. • An intrusive igneous body must have a surface exposure greater than 100 square kilometers to be considered a batholith. ...
Ch 3 Homework Answers
... whether or not the field became very weak for a while). 43. As magma (molten rock) flows out along a divergent boundary, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, the new rock cools and becomes magnetized in the direction of the Earth’s magnetic field at that time. So seafloor near the divergent boundary will ...
... whether or not the field became very weak for a while). 43. As magma (molten rock) flows out along a divergent boundary, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, the new rock cools and becomes magnetized in the direction of the Earth’s magnetic field at that time. So seafloor near the divergent boundary will ...
CRCT Review - Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics.
... _____ 10. What hypothesis by Alfred Wegener explains why continents seem to fit together? a. continental spreading c. Wegener’s puzzle b. plate tectonics d. continental drift _____ 11. What did Wegener hypothesize happened to the continents? a. They broke up and re-formed. b. They drifted together t ...
... _____ 10. What hypothesis by Alfred Wegener explains why continents seem to fit together? a. continental spreading c. Wegener’s puzzle b. plate tectonics d. continental drift _____ 11. What did Wegener hypothesize happened to the continents? a. They broke up and re-formed. b. They drifted together t ...
Reflexes and the Nervous System
... chain of rubber bands attached to it. Have a child slowly pull on the rubber bands (at arms length on the floor to avoid eye injuries etc). After increasing the tension (slowly!!) in smaller 3 cm intervals or so, notice there is very little, if any movement of the block. However, after a certain poi ...
... chain of rubber bands attached to it. Have a child slowly pull on the rubber bands (at arms length on the floor to avoid eye injuries etc). After increasing the tension (slowly!!) in smaller 3 cm intervals or so, notice there is very little, if any movement of the block. However, after a certain poi ...
Convergent boundaries
... 15. What are two bad things that can happen as a result of plate tectonics, how did plate tectonics cause these events? The mountains were formed by the motion of the plates and they could produce earthquakes, volcanoes, tsunamis.... The convection currents cause that plate tectonics can separate be ...
... 15. What are two bad things that can happen as a result of plate tectonics, how did plate tectonics cause these events? The mountains were formed by the motion of the plates and they could produce earthquakes, volcanoes, tsunamis.... The convection currents cause that plate tectonics can separate be ...
Continental drift
... • Mountains can also be formed when one plate over another plate • The Earth’s plates are constantly moving even today • The movement of plates sometimes shakes the Earth’s surface causing an earthquake • Earthquakes are common around faults • Fault – is a break in the Earth’s crust where movement o ...
... • Mountains can also be formed when one plate over another plate • The Earth’s plates are constantly moving even today • The movement of plates sometimes shakes the Earth’s surface causing an earthquake • Earthquakes are common around faults • Fault – is a break in the Earth’s crust where movement o ...
Big Bang Theory (Scientific View)
... This allowed the denser materials to sink to the Earth’s center (due to gravitational forces) and the lighter materials to float upwards. This process is often referred to as differentiation or segregation. This sorting of material by density, early in Earth’s history, is still occurring today; howe ...
... This allowed the denser materials to sink to the Earth’s center (due to gravitational forces) and the lighter materials to float upwards. This process is often referred to as differentiation or segregation. This sorting of material by density, early in Earth’s history, is still occurring today; howe ...
Free preview of PowerPoint and Teacher Notes
... hanging wall to go up, or “fold”. 3 examples are the Appalachians, Himalayas, and Alps ...
... hanging wall to go up, or “fold”. 3 examples are the Appalachians, Himalayas, and Alps ...
WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF TECTONIC HAZARDS? 1 Structure of
... Find/draw a labelled cross section through the earth showing the different layers (asthenosphere, etc) Find/draw a diagram and write a paragraph to show how convection currents work. 2 Theory of plate tectonics Write about Alfred Wegener’s idea of continental drift What evidence is there tha ...
... Find/draw a labelled cross section through the earth showing the different layers (asthenosphere, etc) Find/draw a diagram and write a paragraph to show how convection currents work. 2 Theory of plate tectonics Write about Alfred Wegener’s idea of continental drift What evidence is there tha ...
Plate Tectonics
... • The Earth’s crust is divided into 12 major plates which are moved in various directions. • This plate motion causes them to collide, pull apart, or scrape against each other. • Each type of interaction causes a characteristic set of Earth structures or “tectonic” features. • The word, tectonic, re ...
... • The Earth’s crust is divided into 12 major plates which are moved in various directions. • This plate motion causes them to collide, pull apart, or scrape against each other. • Each type of interaction causes a characteristic set of Earth structures or “tectonic” features. • The word, tectonic, re ...
Lesson 1 - Humanities.Com
... core. A liquid layer, also made up of iron and nickel. Still extremely hot, temperatures similar to inner core. Mantle - widest section of the Earth. Diameter of approximately 2900km. Made up of semi-molten rock called magma. In the upper parts of the mantle the rock is hard, but lower down the rock ...
... core. A liquid layer, also made up of iron and nickel. Still extremely hot, temperatures similar to inner core. Mantle - widest section of the Earth. Diameter of approximately 2900km. Made up of semi-molten rock called magma. In the upper parts of the mantle the rock is hard, but lower down the rock ...
The Earth-Moon System - Academic Computer Center
... Formation of Maria and Highlands • As the Moon formed, denser material sank towards the core while lighter material floated to the surface. • The Highlands were formed after the Moon’s crust cooled. • This surface was constantly being impacted during the early years of the solar system. • Much late ...
... Formation of Maria and Highlands • As the Moon formed, denser material sank towards the core while lighter material floated to the surface. • The Highlands were formed after the Moon’s crust cooled. • This surface was constantly being impacted during the early years of the solar system. • Much late ...
Deformation
... plate sinks into the mantle. This is due to plates being rich in silicon and aluminium (sial) that are less dense than the material below so they float of the surface of the mantle. Rocks on both sides are folded and uplifted. Example Himalayas ...
... plate sinks into the mantle. This is due to plates being rich in silicon and aluminium (sial) that are less dense than the material below so they float of the surface of the mantle. Rocks on both sides are folded and uplifted. Example Himalayas ...
Chapter 5 Plate Tectonics: A Scientific Theory Unfolds
... Lithosphere and Asthenosphere • Earth’s crust and upper most mantle are solid and compose the lithosphere – Stresses cause brittle and elastic deformation ...
... Lithosphere and Asthenosphere • Earth’s crust and upper most mantle are solid and compose the lithosphere – Stresses cause brittle and elastic deformation ...
Metamorphic Rocks
... 1. Contact metamorphism – due heat from adjacent rocks 2. Hydrothermal metamorphism – chemical alterations from hot, ion-rich water 3. Regional metamorphism -- Occurs in the cores of mountain belts and subduction zones (Converging Margins) . Makes great volumes of metamorphic rock. ...
... 1. Contact metamorphism – due heat from adjacent rocks 2. Hydrothermal metamorphism – chemical alterations from hot, ion-rich water 3. Regional metamorphism -- Occurs in the cores of mountain belts and subduction zones (Converging Margins) . Makes great volumes of metamorphic rock. ...
Plate Tectonics Short Study Guide
... ____ 9. Crust is neither destroyed nor formed along which of the following boundaries? a. convergent c. transform b. divergent d. magnetic ____ 10. The driving forces of tectonic plates are related to convection currents in Earth’s ____. a. crust c. inner core b. mantle d. outer core Completion Comp ...
... ____ 9. Crust is neither destroyed nor formed along which of the following boundaries? a. convergent c. transform b. divergent d. magnetic ____ 10. The driving forces of tectonic plates are related to convection currents in Earth’s ____. a. crust c. inner core b. mantle d. outer core Completion Comp ...
Plate Tectonics 07ppt
... • Subduction - process which one plate slides under the other (subducts) • Volcanic arc islands are formed ...
... • Subduction - process which one plate slides under the other (subducts) • Volcanic arc islands are formed ...
The Earth and its Moon - Mid
... same material at the beginning of the Solar System. Problem: Moon has different density and composition. 3) "Capture": The Moon was a stray body captured into orbit around Earth. Problem: an extremely unlikely event. ...
... same material at the beginning of the Solar System. Problem: Moon has different density and composition. 3) "Capture": The Moon was a stray body captured into orbit around Earth. Problem: an extremely unlikely event. ...
Name:
... d. subduction 25. The volcanoes in Africa form on a plate boundary where two land plates pull apart from one another. These volcanoes form by … a. Rifting b. Sea floor spreading c. hot spot d. subduction 26. An underwater volcano is called a: ________________________. Matching: Volcanic features tha ...
... d. subduction 25. The volcanoes in Africa form on a plate boundary where two land plates pull apart from one another. These volcanoes form by … a. Rifting b. Sea floor spreading c. hot spot d. subduction 26. An underwater volcano is called a: ________________________. Matching: Volcanic features tha ...
8_Plate_Tectonics
... The Andes Mountains run the length of the West Coast of South America, rising in the north in Colombia and finishing in Chile and Argentina in the south. They are the world's longest mountain range running for over 7,000 km and covering 6 countries. The mountains have been formed as a result of the ...
... The Andes Mountains run the length of the West Coast of South America, rising in the north in Colombia and finishing in Chile and Argentina in the south. They are the world's longest mountain range running for over 7,000 km and covering 6 countries. The mountains have been formed as a result of the ...
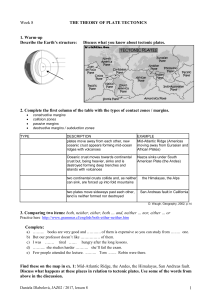
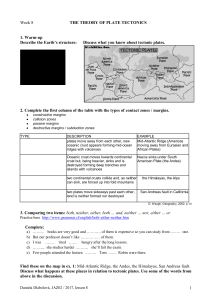
1 Week 8 THE THEORY OF PLATE TECTONICS 1. Warm
... The Andes Mountains run the length of the West Coast of South America, rising in the north in Colombia and finishing in Chile and Argentina in the south. They are the world's longest mountain range running for over 7,000 km and covering 6 countries. The mountains have been formed as a result of the ...
... The Andes Mountains run the length of the West Coast of South America, rising in the north in Colombia and finishing in Chile and Argentina in the south. They are the world's longest mountain range running for over 7,000 km and covering 6 countries. The mountains have been formed as a result of the ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.