Layers of the Earth Power Point
... crust and core. • The mantle is the layer under the crust. • It is up to 2,897 kilometers(1,800 miles -from here to Arizona) thick. • The mantle is made up of rocks such as silicon, aluminum, iron, and magnesium. • Top layer - hot solid rock 1590 degrees Fahrenheit • Bottom layer - hot liquid rock 3 ...
... crust and core. • The mantle is the layer under the crust. • It is up to 2,897 kilometers(1,800 miles -from here to Arizona) thick. • The mantle is made up of rocks such as silicon, aluminum, iron, and magnesium. • Top layer - hot solid rock 1590 degrees Fahrenheit • Bottom layer - hot liquid rock 3 ...
FINAL PROJECT
... An earthquake is the vibration, sometimes violent, of the Earth's surface that follows a release of energy in the Earth's crust. This energy can be generated by a sudden dislocation of segments of the crust, by a volcanic eruption, or event by manmade explosions. Most destructive quakes, however, ar ...
... An earthquake is the vibration, sometimes violent, of the Earth's surface that follows a release of energy in the Earth's crust. This energy can be generated by a sudden dislocation of segments of the crust, by a volcanic eruption, or event by manmade explosions. Most destructive quakes, however, ar ...
Plate Tectonics, Tectonic Plates Information, Facts, News, Photos
... of the majors are named for the continents embedded within them, such as the North American, African, and Antarctic plates. Though smaller in size, the minors are no less important when it comes to shaping the Earth. The tiny Juan de Fuca plate is largely responsible for the volcanoes that dot the P ...
... of the majors are named for the continents embedded within them, such as the North American, African, and Antarctic plates. Though smaller in size, the minors are no less important when it comes to shaping the Earth. The tiny Juan de Fuca plate is largely responsible for the volcanoes that dot the P ...
Word format
... C. lithosphere, asthenosphere, lower mantle, outer core, inner core D. inner core, mantle, lithosphere, asthenosphere E. inner core, outer core, lower mantle, upper mantle, lithosphere ...
... C. lithosphere, asthenosphere, lower mantle, outer core, inner core D. inner core, mantle, lithosphere, asthenosphere E. inner core, outer core, lower mantle, upper mantle, lithosphere ...
Chapter 2: The Earth - IWA Social Studies Ms. LaMarche
... years ago, the planet probably would not have looked at all like it does today. Many scientists believe that most of the landmasses forming our present-day continents were once part of one gigantic supercontinent called Pangaea (pan•JEE•uh). Over millions of years, this supercontinent has broken apa ...
... years ago, the planet probably would not have looked at all like it does today. Many scientists believe that most of the landmasses forming our present-day continents were once part of one gigantic supercontinent called Pangaea (pan•JEE•uh). Over millions of years, this supercontinent has broken apa ...
Geothermal Energy: Natural heat energy produced by the Earth
... A solid inner core followed by liquid outer core, with the mantle by semi-molten Temp at base of crust about 1000o C, increasing slowly into the core. Hot spots located 2 to 3 km form the surface ...
... A solid inner core followed by liquid outer core, with the mantle by semi-molten Temp at base of crust about 1000o C, increasing slowly into the core. Hot spots located 2 to 3 km form the surface ...
Chapter 4
... Weather v. Climate • Weather a. short-term conditions b. temperature, humidity, precipitation • Climate a. average weather that occurs in a certain region over a period of time b. based on temperature and precipitation ...
... Weather v. Climate • Weather a. short-term conditions b. temperature, humidity, precipitation • Climate a. average weather that occurs in a certain region over a period of time b. based on temperature and precipitation ...
Global Climates and Biomes
... Weather v. Climate • Weather a. short-term conditions b. temperature, humidity, precipitation • Climate a. average weather that occurs in a certain region over a period of time b. based on temperature and precipitation ...
... Weather v. Climate • Weather a. short-term conditions b. temperature, humidity, precipitation • Climate a. average weather that occurs in a certain region over a period of time b. based on temperature and precipitation ...
Global Climates and Biomes
... Weather v. Climate • Weather a. short-term conditions b. temperature, humidity, precipitation • Climate a. average weather that occurs in a certain region over a period of time b. based on temperature and precipitation ...
... Weather v. Climate • Weather a. short-term conditions b. temperature, humidity, precipitation • Climate a. average weather that occurs in a certain region over a period of time b. based on temperature and precipitation ...
Geothermal Energy: Natural heat energy produced by the Earth
... A solid inner core followed by liquid outer core, with the mantle by semi-molten Temp at base of crust about 1000o C, increasing slowly into the core. Hot spots located 2 to 3 km form the surface ...
... A solid inner core followed by liquid outer core, with the mantle by semi-molten Temp at base of crust about 1000o C, increasing slowly into the core. Hot spots located 2 to 3 km form the surface ...
Introduction to Earthquakes EASA
... Earth is cooling over time because it is much warmer than the surrounding vacuum of space. (2)Heat generally “moves” from hotter objects or regions to cooler objects or regions. (3)The “movement” of heat is generally called ...
... Earth is cooling over time because it is much warmer than the surrounding vacuum of space. (2)Heat generally “moves” from hotter objects or regions to cooler objects or regions. (3)The “movement” of heat is generally called ...
Science Grade 8 Daily PACT Review Questions
... fish and reptiles still survived As reptiles, early birds and mammals thrived during the Mesozoic Era, it too came to an end with mass extinctions, including the dinosaur species; possibly due to a world-wide impact catastrophe and climate change eras are divided into periods; periods can be further ...
... fish and reptiles still survived As reptiles, early birds and mammals thrived during the Mesozoic Era, it too came to an end with mass extinctions, including the dinosaur species; possibly due to a world-wide impact catastrophe and climate change eras are divided into periods; periods can be further ...
Energy in the Earth System - HCIPS
... Conversion of Gravitational Energy Gravity is the force of attraction between two bodies. The force of gravity acts between the Sun, Earth, and Moon to create tidal forces, which cause the Earth to bulge in the direction of the Moon. This bulging is kinetic energy, which is converted to heat in the ...
... Conversion of Gravitational Energy Gravity is the force of attraction between two bodies. The force of gravity acts between the Sun, Earth, and Moon to create tidal forces, which cause the Earth to bulge in the direction of the Moon. This bulging is kinetic energy, which is converted to heat in the ...
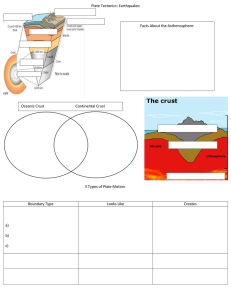
1-3 Notes: Divergent Boundaries Think About… • What causes
... No one knows why magnetic reversals occur. Note: the _______________________ North and South poles never change-just the magnetic field. Evidence of Earth’s magnetic reversals can be found on the seafloor. As molten rock cools in the ocean, its _______________________ line up with Earth’s ma ...
... No one knows why magnetic reversals occur. Note: the _______________________ North and South poles never change-just the magnetic field. Evidence of Earth’s magnetic reversals can be found on the seafloor. As molten rock cools in the ocean, its _______________________ line up with Earth’s ma ...
DATASHEETforHANDOUTBWITHANSWERS
... 1. What happened to the frosting between the squares of chewing gum? Because the chewing gum is dense, it will sink as the plates sink into the asthenosphere and thus push up the frosting where the chewing pieces separate. This is analogous to the magma that comes to the surface where two real plate ...
... 1. What happened to the frosting between the squares of chewing gum? Because the chewing gum is dense, it will sink as the plates sink into the asthenosphere and thus push up the frosting where the chewing pieces separate. This is analogous to the magma that comes to the surface where two real plate ...
Mapping the Ocean Floor
... the rift valley, a deep V-shaped notch. From this valley, new oceanic crust is constantly being extruded from Earth's mantle by processes not yet fully understood. In the case of the Mid-Atlantic rift valley, one sheet flows east and the other west, each moving at about half an inch per year. ...
... the rift valley, a deep V-shaped notch. From this valley, new oceanic crust is constantly being extruded from Earth's mantle by processes not yet fully understood. In the case of the Mid-Atlantic rift valley, one sheet flows east and the other west, each moving at about half an inch per year. ...
Chapter 10 study guide
... Geologists discovered layers of debris from ancient glaciers in southern Africa and South America. Today these areas have climates that are too warm for glaciers to form. Other evidence from fossils showed that tropical or subtropical swamps now have much colder climates. ...
... Geologists discovered layers of debris from ancient glaciers in southern Africa and South America. Today these areas have climates that are too warm for glaciers to form. Other evidence from fossils showed that tropical or subtropical swamps now have much colder climates. ...
HERE
... Elastic Rebound Theory • When the force trying to make the edges slip overcomes the friction making them stick, there is an earthquake. • The bending and “springing back” of the rock is called elastic rebound. • Elastic Rebound Animation- Click HERE Rock breaks and releases energy. ...
... Elastic Rebound Theory • When the force trying to make the edges slip overcomes the friction making them stick, there is an earthquake. • The bending and “springing back” of the rock is called elastic rebound. • Elastic Rebound Animation- Click HERE Rock breaks and releases energy. ...
Plate Tectonics - BSHYear7Geography
... became accepted by the scientific community. Some continents fit together almost perfectly, e.g. South America and Africa. Similar fossils can be found on different continents. This shows these regions were once very close or joined together. ...
... became accepted by the scientific community. Some continents fit together almost perfectly, e.g. South America and Africa. Similar fossils can be found on different continents. This shows these regions were once very close or joined together. ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.