Chapter 22 Neutron Stars and Black Holes
... According to models for stellar explosions: After a carbon detonation supernova (white dwarf in binary), little or nothing remains of the original star. After a core collapse supernova, part of the core may survive. It is very dense—as dense as an atomic nucleus—and is called a neutron star. [Recall ...
... According to models for stellar explosions: After a carbon detonation supernova (white dwarf in binary), little or nothing remains of the original star. After a core collapse supernova, part of the core may survive. It is very dense—as dense as an atomic nucleus—and is called a neutron star. [Recall ...
Neutrino Physics M. SPURIO University of Bologna and INFN
... Once the core of the star becomes constituted primarily of iron, further compression of the core does not ignite nuclear fusion and the star is unable to thermodynamically support its outer envelope. As the surrounding matter falls inward under gravity, the temperature of the core rises and iron ...
... Once the core of the star becomes constituted primarily of iron, further compression of the core does not ignite nuclear fusion and the star is unable to thermodynamically support its outer envelope. As the surrounding matter falls inward under gravity, the temperature of the core rises and iron ...
(a) Because the core of heavy-mass star never reaches high enough
... (c) When core temperature increases, pressure decreases. Lower pressure contracts the system which then cools the core. (d) When core temperature increases, pressure decreases. Lower pressure expands the system which further heats up the core. (e) When core temperature decreases, pressure decreases. ...
... (c) When core temperature increases, pressure decreases. Lower pressure contracts the system which then cools the core. (d) When core temperature increases, pressure decreases. Lower pressure expands the system which further heats up the core. (e) When core temperature decreases, pressure decreases. ...
answers2006_07_BC
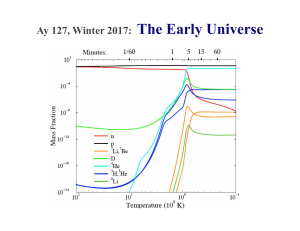
... near-uniformity over the whole sky this is surprising because different “sides” of the sky should never have exchanged photons, and therefore do not know each other’s temperature – it is one of the key pieces of evidence for inflation very small temperature fluctuations (1 in 100000) by studying the ...
... near-uniformity over the whole sky this is surprising because different “sides” of the sky should never have exchanged photons, and therefore do not know each other’s temperature – it is one of the key pieces of evidence for inflation very small temperature fluctuations (1 in 100000) by studying the ...
Cosmology Fact Sheet
... However, if you measure the distance to a certain type of star using parallax and see how bright it is, then you have the beginning of a “standard candle”. If you can recognize this same type of star, only much further away (using chemical composition found by spectral lines, or some other method), ...
... However, if you measure the distance to a certain type of star using parallax and see how bright it is, then you have the beginning of a “standard candle”. If you can recognize this same type of star, only much further away (using chemical composition found by spectral lines, or some other method), ...
Developing an Efficient Low-Temperature Nuclear Fusion Reactor
... known as Bloch state. Bloch states will cause the waves of different deuterons to overlap and when the kinetic energy of the vibration becomes greater than the potential energy of the Coulomb barrier, the result is that the deuteron waves would fuse into one another since the Coulomb barrier become ...
... known as Bloch state. Bloch states will cause the waves of different deuterons to overlap and when the kinetic energy of the vibration becomes greater than the potential energy of the Coulomb barrier, the result is that the deuteron waves would fuse into one another since the Coulomb barrier become ...
Nuclear Synthesis
... • Hertzprung-Russell diagram identifiers (main sequence, red giant, white dwarf) • luminosity vs radius vs surface temperature for stars • star clusters and how they are used to study star aging • steps leading from gas cloud to main sequence star • steps leading from Red giant to supernova (or ...
... • Hertzprung-Russell diagram identifiers (main sequence, red giant, white dwarf) • luminosity vs radius vs surface temperature for stars • star clusters and how they are used to study star aging • steps leading from gas cloud to main sequence star • steps leading from Red giant to supernova (or ...
printer-friendly version of benchmark
... value known as the Chandraskhkar Limit. At the end of the star’s life, when stellar fusion ceases suddenly, core masses at or above this limit have so much gravitational attraction that they collapse to very small size and this resulting rebound of energy results in a supernova. It is possible for a ...
... value known as the Chandraskhkar Limit. At the end of the star’s life, when stellar fusion ceases suddenly, core masses at or above this limit have so much gravitational attraction that they collapse to very small size and this resulting rebound of energy results in a supernova. It is possible for a ...
Grade 8: Physical Science
... systems. As a basis for understanding this concept, students know: a. carbon, because of its ability to combine in many ways with itself and other elements, has a central role in the chemistry of living organisms. b. living organisms are made of molecules largely consisting of carbon, hydrogen, nitr ...
... systems. As a basis for understanding this concept, students know: a. carbon, because of its ability to combine in many ways with itself and other elements, has a central role in the chemistry of living organisms. b. living organisms are made of molecules largely consisting of carbon, hydrogen, nitr ...
PoA Examples Sheet 3
... Provide a physical explanation for this scaling. Derive furthermore how the frequency integrated power per unit volume depends on temperature. 5. The photospheric temperature of an optically thick accretion disc varies with radius as T ∝ R−3/4 . Explain why you expect the spectrum of the radiation p ...
... Provide a physical explanation for this scaling. Derive furthermore how the frequency integrated power per unit volume depends on temperature. 5. The photospheric temperature of an optically thick accretion disc varies with radius as T ∝ R−3/4 . Explain why you expect the spectrum of the radiation p ...
$doc.title
... The astronomers soon determined that shifting the spectrum of SCP 06F6 similarly aligned it with the others. In the end, it turned out that all six supernovae are siblings, and that they all have ...
... The astronomers soon determined that shifting the spectrum of SCP 06F6 similarly aligned it with the others. In the end, it turned out that all six supernovae are siblings, and that they all have ...
Beta decay is a type of radioactive decay in which a beta
... charge, Z. Therefore the set of allnuclides with the same A can be introduced; these isobaric nuclides may turn into each other via beta decay. A beta-stable nucleus may undergo other kinds of radioactive decay (for example, alpha decay). In nature, most isotopes are beta-stable, but there exist a f ...
... charge, Z. Therefore the set of allnuclides with the same A can be introduced; these isobaric nuclides may turn into each other via beta decay. A beta-stable nucleus may undergo other kinds of radioactive decay (for example, alpha decay). In nature, most isotopes are beta-stable, but there exist a f ...
Marcelo Borges Fernandes1, Michaela Kraus2, Jiri Kubát2
... Abstract: We report on the variation of the rapidly rotating SMC supergiant star LHA 115-S 23 (AzV 172) for which we found a decrease in effective temperature from 11000 K to 9000 K and a simultaneous increase in rotation velocity from 110 km/s to 150 km/s (the latter corresponding to 75% of its cri ...
... Abstract: We report on the variation of the rapidly rotating SMC supergiant star LHA 115-S 23 (AzV 172) for which we found a decrease in effective temperature from 11000 K to 9000 K and a simultaneous increase in rotation velocity from 110 km/s to 150 km/s (the latter corresponding to 75% of its cri ...
A neutron star with a carbon atmosphere in the Cassiopeia A
... data from two studies of Cas A, both using the ACIS-S charge-coupled device which provides spatial and spectral information.11 A series of Chandra observations, totalling 1 megasecond, was performed in 2004 to study the supernova remnant12 ; these are referred to here as the Hwang data. A shorter (7 ...
... data from two studies of Cas A, both using the ACIS-S charge-coupled device which provides spatial and spectral information.11 A series of Chandra observations, totalling 1 megasecond, was performed in 2004 to study the supernova remnant12 ; these are referred to here as the Hwang data. A shorter (7 ...
arXiv:1606.05438v1 [astro-ph.SR] 17 Jun 2016
... systems. The material transferred onto the white dwarf piles up under degenerate conditions, driving a thermonuclear runaway. In those outbursts, about 10−7 − 10−3 M⊙ , enriched in CNO and, sometimes, other intermediate-mass elements (e.g., Ne, Na, Mg, or Al, for ONe novae) are ejected into the inte ...
... systems. The material transferred onto the white dwarf piles up under degenerate conditions, driving a thermonuclear runaway. In those outbursts, about 10−7 − 10−3 M⊙ , enriched in CNO and, sometimes, other intermediate-mass elements (e.g., Ne, Na, Mg, or Al, for ONe novae) are ejected into the inte ...
Discussion Activity #13
... least 10 times as much matter as we see in the Milky Way disk, suggesting that the halo is full of dark matter. B. The orbital speeds of stars far from the galactic center are surprisingly high, suggesting that these stars are feeling gravitational effects from unseen matter in the halo. C. Our view ...
... least 10 times as much matter as we see in the Milky Way disk, suggesting that the halo is full of dark matter. B. The orbital speeds of stars far from the galactic center are surprisingly high, suggesting that these stars are feeling gravitational effects from unseen matter in the halo. C. Our view ...
Physics, Chapter 44: Stable Nuclei
... Investigations with the mass spectrograph have established that there are about 300 different stable isotopes among the 102 known elements. The range of mass numbers runs from 1 to more than 250. The atomic masses of these isotopes differ very little from whole numbers. The number of stable isotopes ...
... Investigations with the mass spectrograph have established that there are about 300 different stable isotopes among the 102 known elements. The range of mass numbers runs from 1 to more than 250. The atomic masses of these isotopes differ very little from whole numbers. The number of stable isotopes ...
Lecture 6: Main Sequence Stars
... of the light trying to pass through the material. It turns-‐out that opacity is a very strong funcCon of temperature. At low temperatures everything is neutral (or even molecular) and the main sour ...
... of the light trying to pass through the material. It turns-‐out that opacity is a very strong funcCon of temperature. At low temperatures everything is neutral (or even molecular) and the main sour ...
Lecture 2: Chapter 16 Electric Charge and Electric Field
... feel the same force. But, since F = ma, and since the proton’s mass is much greater, the proton’s acceleration will be much smaller! ...
... feel the same force. But, since F = ma, and since the proton’s mass is much greater, the proton’s acceleration will be much smaller! ...
The supernova of AD1181 – an update
... a “guest star” (kexing); this is the usual oriental term for a star-like object. Neither of the Japanese records gives any indication of the period of visibility of the star. However, the two independent records from South and North China affirm a lengthy duration. As the supernova was circumpolar, ...
... a “guest star” (kexing); this is the usual oriental term for a star-like object. Neither of the Japanese records gives any indication of the period of visibility of the star. However, the two independent records from South and North China affirm a lengthy duration. As the supernova was circumpolar, ...
P-nuclei
p-Nuclei (p stands for proton-rich) are certain proton-rich, naturally occurring isotopes of some elements between selenium and mercury which cannot be produced in either s- or r-process.
















![arXiv:1606.05438v1 [astro-ph.SR] 17 Jun 2016](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/013048193_1-92364881cbcc0fdb7f47e7990acc1537-300x300.png)