Chapter 4 [PDF only] - Princeton University Press
... The equations of pressure, opacity, and nuclear power density all depend sensitively on the abundances. Indeed, at some point, the hydrogen fuel in the core will be largely used up, and the star will lose the energy source that produces pressure, the gradient of which supports the star against gravi ...
... The equations of pressure, opacity, and nuclear power density all depend sensitively on the abundances. Indeed, at some point, the hydrogen fuel in the core will be largely used up, and the star will lose the energy source that produces pressure, the gradient of which supports the star against gravi ...
Unified Description of Neutrino-Nucleus Interactions within Nuclear
... Figure 4 shows Rosenbluth separation results performed in the 1970’s as the ratio GEp /GD , where GD is the dipole FF given below by Eq. 14; it is noteworthy that these results strongly suggest a decrease of GEp with increasing Q2 , a fact noted in all four references [Ber71, Pri71, Bar73, Han73]. ...
... Figure 4 shows Rosenbluth separation results performed in the 1970’s as the ratio GEp /GD , where GD is the dipole FF given below by Eq. 14; it is noteworthy that these results strongly suggest a decrease of GEp with increasing Q2 , a fact noted in all four references [Ber71, Pri71, Bar73, Han73]. ...
White dwarf binaries
... constraints on the basic physical properties of accretion disks which can then be applied in many other fields. The typical luminosity and range of temperatures produced in CVs can be estimated in the following way. If material is being accreted by the white dwarf at a rate Ṁ then the release of gr ...
... constraints on the basic physical properties of accretion disks which can then be applied in many other fields. The typical luminosity and range of temperatures produced in CVs can be estimated in the following way. If material is being accreted by the white dwarf at a rate Ṁ then the release of gr ...
kd - The HST Treasury Program on Eta Carinae
... Detection of the secondary star is highly desirable because that would eliminate single-star models. Unfortunately, as we explained in sections 2—4 above, there is no proof that any emission seen with FUSE came from a second star. It’s not hard to imagine a single-star model. The equatorial photosph ...
... Detection of the secondary star is highly desirable because that would eliminate single-star models. Unfortunately, as we explained in sections 2—4 above, there is no proof that any emission seen with FUSE came from a second star. It’s not hard to imagine a single-star model. The equatorial photosph ...
Observations of V838 Mon light echo
... In classical novae, hydrogen explosion happens in a layer on a white dwarf surface. A small amount of matter located above being ejected into space has a mass of 1/1000 or 1/10000 solar masses. When the ejected gas expands, its density decreases rapidly, it passes into the optically thin state and g ...
... In classical novae, hydrogen explosion happens in a layer on a white dwarf surface. A small amount of matter located above being ejected into space has a mass of 1/1000 or 1/10000 solar masses. When the ejected gas expands, its density decreases rapidly, it passes into the optically thin state and g ...
Presentation - Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics
... be defined in cool star coronas. (Sanz-Forcada et al. 2003) ...
... be defined in cool star coronas. (Sanz-Forcada et al. 2003) ...
Planck Era
... 'Big Bang' theory. However when astronomer Sir Fred Hoyle first coined the phrase 'Big Bang' he did so in order to mock the theory. Hoyle was a firm believer in the alternative steady state theory which gives the universe no start or end. However the name stuck and the term Big Bang is now widely us ...
... 'Big Bang' theory. However when astronomer Sir Fred Hoyle first coined the phrase 'Big Bang' he did so in order to mock the theory. Hoyle was a firm believer in the alternative steady state theory which gives the universe no start or end. However the name stuck and the term Big Bang is now widely us ...
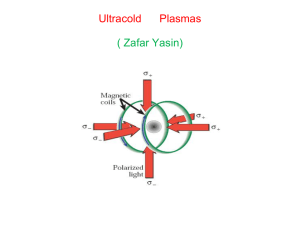
Ultracold Plasmas
... - Laser cool atoms to slightly above sub-milikelvin temperatures. - Trap the laser-cooled atoms using Magneto Optical trap. - Photoionize , using laser light near the ionization threshold. - Diagnostics with applied electric fields. ...
... - Laser cool atoms to slightly above sub-milikelvin temperatures. - Trap the laser-cooled atoms using Magneto Optical trap. - Photoionize , using laser light near the ionization threshold. - Diagnostics with applied electric fields. ...
n - Indico
... • A. Best, A. Di Leva, G. Imbriani, | Università di Napoli and INFN Napoli, Italy • G. Gervino | Università di Torino and INFN Torino, Italy • M. Aliotta, C. Bruno, T. Davinson | University of Edinburgh, United Kingdom • G. D’Erasmo, E.M. Fiore, V. Mossa, F. Pantaleo, V. Paticchio, R. Perrino*, L. S ...
... • A. Best, A. Di Leva, G. Imbriani, | Università di Napoli and INFN Napoli, Italy • G. Gervino | Università di Torino and INFN Torino, Italy • M. Aliotta, C. Bruno, T. Davinson | University of Edinburgh, United Kingdom • G. D’Erasmo, E.M. Fiore, V. Mossa, F. Pantaleo, V. Paticchio, R. Perrino*, L. S ...
Round2 - Quizbowl Packet Archive
... ANSWER: Möbius strip
18. It’s not Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, but mutations at codon 178 on the PRNP gene can cause an inherited variant
of this disease. Tasimelteon and ramelteon can be used to treat it by acting on the suprachiasmatic nucleus. A 2012
paper published by Dizon and Cheng establis ...
... ANSWER: Möbius strip
Equation of State of Dense Matter and the Upper Mass Limit for
... The theory of dense matter at nuclear and supranuclear densities has developed over several decades and a multitude of papers have been devoted to this subject. Even though we can extrapolate the theory from fits to nuclear phenomena to a description of nuclear matter, basically the parameters must ...
... The theory of dense matter at nuclear and supranuclear densities has developed over several decades and a multitude of papers have been devoted to this subject. Even though we can extrapolate the theory from fits to nuclear phenomena to a description of nuclear matter, basically the parameters must ...
LENA
... after PSD-analysis this could be suppressed in LENA to ~ 0.25 / y ! (efficiency ~ 70% ) •A 30 kt detector (~ 1034 protons as target) would have a sensitivity of t < a few 1034 years for the K-decay after ~10 years measuring time •The minimal SUSY SU(5) model predicts the K-decay mode to be dominant ...
... after PSD-analysis this could be suppressed in LENA to ~ 0.25 / y ! (efficiency ~ 70% ) •A 30 kt detector (~ 1034 protons as target) would have a sensitivity of t < a few 1034 years for the K-decay after ~10 years measuring time •The minimal SUSY SU(5) model predicts the K-decay mode to be dominant ...
Vortex buoyancy in superfluid and superconducting neutron stars
... an “intermediate” state, while type-II superconductors – into mixed state. Intermediate state of type-I superconductor: consists of alternating domains of superconducting (field-free ) regions and normal regions hosting magnetic field ...
... an “intermediate” state, while type-II superconductors – into mixed state. Intermediate state of type-I superconductor: consists of alternating domains of superconducting (field-free ) regions and normal regions hosting magnetic field ...
Astronomy C - Scioly.org
... 43. What two paths can pre-main sequence stars follow on the HR diagram on their way to the main sequence? [2 pts] 44. What form of heat transport distinguishes the path that is exclusively for stars above 0.5 Msun? 45. What is the primary criterion for determining the habitable zone around a star? ...
... 43. What two paths can pre-main sequence stars follow on the HR diagram on their way to the main sequence? [2 pts] 44. What form of heat transport distinguishes the path that is exclusively for stars above 0.5 Msun? 45. What is the primary criterion for determining the habitable zone around a star? ...
PowerPoint Presentation - 18. The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard
... – what the ancient Greeks & Romans called a star which suddenly appeared! ...
... – what the ancient Greeks & Romans called a star which suddenly appeared! ...
poster
... The imaging program of SNLS is part of the CFHT Legacy Survey (CFHTLS) program, a large multi purpose imaging survey. It will use 202 dark/grey nights of observations over 5 years. As a fundamental complement to these observations, a spectroscopic program is carried out on VLT, Gemini North and Sout ...
... The imaging program of SNLS is part of the CFHT Legacy Survey (CFHTLS) program, a large multi purpose imaging survey. It will use 202 dark/grey nights of observations over 5 years. As a fundamental complement to these observations, a spectroscopic program is carried out on VLT, Gemini North and Sout ...
Review for Astronomy 3 Midterm #2
... Supernovae Type II are formed as a result of the core collapse of a very massive star – in a fraction of a second all the protons and neutrons in the star combine to form neutrons, thus forming a neutron star -- Neutron stars have a radius of about 10 km, a rotation rate of ~ 1 second on average ( ...
... Supernovae Type II are formed as a result of the core collapse of a very massive star – in a fraction of a second all the protons and neutrons in the star combine to form neutrons, thus forming a neutron star -- Neutron stars have a radius of about 10 km, a rotation rate of ~ 1 second on average ( ...
Stellar Evolution – Cosmic Cycles of Formation and Destruction
... collapse in a Type II supernova event, leaving behind a pulsar, neutron star, magnetar or black hole and a supernova remnant. Some hyper-massive stars collapse into back holes without a supernova event, and some undergo a supernova event that leaves no core remnant behind – such as SN2006GY. ...
... collapse in a Type II supernova event, leaving behind a pulsar, neutron star, magnetar or black hole and a supernova remnant. Some hyper-massive stars collapse into back holes without a supernova event, and some undergo a supernova event that leaves no core remnant behind – such as SN2006GY. ...
P-nuclei
p-Nuclei (p stands for proton-rich) are certain proton-rich, naturally occurring isotopes of some elements between selenium and mercury which cannot be produced in either s- or r-process.
![Chapter 4 [PDF only] - Princeton University Press](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016931743_1-7c8ec22374457bf50a0a03f55488ddc7-300x300.png)