Star Birth - Sierra College Astronomy Home Page
... fragments • These fragments can coalesce into one or they can form into two stars which orbit each other – a binary star system • Stars that end up within 0.1 AU of each other are called a close binary system. © Sierra College Astronomy Department ...
... fragments • These fragments can coalesce into one or they can form into two stars which orbit each other – a binary star system • Stars that end up within 0.1 AU of each other are called a close binary system. © Sierra College Astronomy Department ...
IND 6 - 1 Stars and Stellar Evolution In order to better understand
... A low mass star (less than 8 times the mass of our Sun ( < 8 Msun)) eventually ejects its outer layers to produce a planetary nebula. The now naked stellar core remaining is called a white dwarf (because it is very hot but dim). In contrast, a high-mass star, more than 8 times the mass of our Su ...
... A low mass star (less than 8 times the mass of our Sun ( < 8 Msun)) eventually ejects its outer layers to produce a planetary nebula. The now naked stellar core remaining is called a white dwarf (because it is very hot but dim). In contrast, a high-mass star, more than 8 times the mass of our Su ...
Gravitational redshifts
... synthetic line profiles) are shorter than laboratory values due to convective blueshift. Curves before and after mid-transit (µ = 0.21, 0.59, 0.87) are not exact mirror images due to intrinsic stellar line asymmetries. This simulation from a CO5BOLD model predicts the behavior of an Fe I line ( 620 ...
... synthetic line profiles) are shorter than laboratory values due to convective blueshift. Curves before and after mid-transit (µ = 0.21, 0.59, 0.87) are not exact mirror images due to intrinsic stellar line asymmetries. This simulation from a CO5BOLD model predicts the behavior of an Fe I line ( 620 ...
gravitational collapse to black holes
... However, whereas the TOV equations are a system of ODEs, rotating models result in a system of PDEs and need to be solved for using sophisticated numerical techniques ...
... However, whereas the TOV equations are a system of ODEs, rotating models result in a system of PDEs and need to be solved for using sophisticated numerical techniques ...
Iron does not burn.
... have a spin in the same direction as the proton's spin (i.e., parallel) or spin in the direct opposite direction as the proton's spin (i.e., anti-parallel). The energy state of an electron spinning anti-parallel is slightly lower than the energy state of a parallel-spin electron. Remember that the a ...
... have a spin in the same direction as the proton's spin (i.e., parallel) or spin in the direct opposite direction as the proton's spin (i.e., anti-parallel). The energy state of an electron spinning anti-parallel is slightly lower than the energy state of a parallel-spin electron. Remember that the a ...
The Cosmic Perspective Star Stuff
... cool and dim after their initial formation. c) Nuclear fission would be impossible and elements heavier than iron would not exist. d) Stars would continue burning heavier and heavier elements and the universe would have far more lead and uranium. e) Stars would be much less dense, and therefore l ...
... cool and dim after their initial formation. c) Nuclear fission would be impossible and elements heavier than iron would not exist. d) Stars would continue burning heavier and heavier elements and the universe would have far more lead and uranium. e) Stars would be much less dense, and therefore l ...
The Helium Flash - Stages 10 to 11
... As the helium depletes, the star will basically reproduce it’s the path that took it to stage 9. The helium will burn out at the center of the core, and helium burning as well as hydrogen burning will continue is the outer shells. The star will expand to a red giant once again, this time with shells ...
... As the helium depletes, the star will basically reproduce it’s the path that took it to stage 9. The helium will burn out at the center of the core, and helium burning as well as hydrogen burning will continue is the outer shells. The star will expand to a red giant once again, this time with shells ...
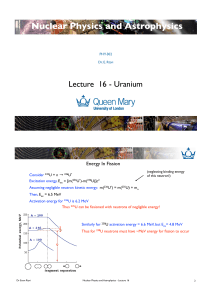
Lecture 16 - QMUL physics
... Consider N thermal neutrons in first generation Each fission produces ν neutrons We will not get νN fast neutrons immediately Some thermal n0s will be absorbed eg. (n,γ) reactions Define η: mean number of fission (i.e fast) neutrons per original thermal neutron Not all thermal neutrons will cause fi ...
... Consider N thermal neutrons in first generation Each fission produces ν neutrons We will not get νN fast neutrons immediately Some thermal n0s will be absorbed eg. (n,γ) reactions Define η: mean number of fission (i.e fast) neutrons per original thermal neutron Not all thermal neutrons will cause fi ...
“Missing” Local Group Satellites
... • Leo T: a unique (?) laboratory – a very low mass, relatively isolated system with gas and recent star formation • Hα (Gemini) and UV (pointed GALEX + Swift/UVOT) observations to study recent star formation: no detected H II regions no ongoing SF… or no O stars? • LG dwarfs may still have g ...
... • Leo T: a unique (?) laboratory – a very low mass, relatively isolated system with gas and recent star formation • Hα (Gemini) and UV (pointed GALEX + Swift/UVOT) observations to study recent star formation: no detected H II regions no ongoing SF… or no O stars? • LG dwarfs may still have g ...
My power point presentation on spectroscopy of stars (ppt file)
... • I take spectra of distant stars and then try to discover what they are telling us about those stars • I do this by modelling the spectra, using a computer programme that computes what the spectrum would look like for a “model star” • The parameters of the model are changed until good agreement is ...
... • I take spectra of distant stars and then try to discover what they are telling us about those stars • I do this by modelling the spectra, using a computer programme that computes what the spectrum would look like for a “model star” • The parameters of the model are changed until good agreement is ...
The masses of stars
... mass stars are thought to be much more common than those of high mass. The lower limit of about 8% of a Solar mass comes about because objects of lesser mass never achieve a high enough core temperature for nuclear fusion to begin. Low mass objects are thought to commonly form in the same way as, an ...
... mass stars are thought to be much more common than those of high mass. The lower limit of about 8% of a Solar mass comes about because objects of lesser mass never achieve a high enough core temperature for nuclear fusion to begin. Low mass objects are thought to commonly form in the same way as, an ...
Stellar Evolution
... A star of more than 8 solar masses can fuse elements far beyond carbon in its core, leading to a very different fate. Its path across the H–R diagram is essentially a straight line – it stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off. Eventually the star dies in a violent explosion called a ...
... A star of more than 8 solar masses can fuse elements far beyond carbon in its core, leading to a very different fate. Its path across the H–R diagram is essentially a straight line – it stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off. Eventually the star dies in a violent explosion called a ...
Chapter 12
... The experiment here referred to is fetched directly from student literature of atomic physics. Let’s examine it in detail in aim to later on using it for calculating the proton radius: Some types of nucleus cores have such a Property that they can be transformed to another type of core, where the ne ...
... The experiment here referred to is fetched directly from student literature of atomic physics. Let’s examine it in detail in aim to later on using it for calculating the proton radius: Some types of nucleus cores have such a Property that they can be transformed to another type of core, where the ne ...
Agenda - Relativity Group
... a. Yes, all stars create heavier elements than carbon when they become a supernova. b. Yes, but there would be far fewer heavier elements because high-mass stars form elements like iron far more prolifically than low-mass stars. c. No, the core temperatures of low-mass stars are too low to fuse othe ...
... a. Yes, all stars create heavier elements than carbon when they become a supernova. b. Yes, but there would be far fewer heavier elements because high-mass stars form elements like iron far more prolifically than low-mass stars. c. No, the core temperatures of low-mass stars are too low to fuse othe ...
The Chemical Composition of the Local Interstellar Dust
... abundance reference: Sun, local F & G stars, B stars Sun: + star that can be studied best + independent abundances from different indicators - 4.56 Gyr old, representative for present-day ISM? F&G stars: + differential abundances relative to Sun + increased number statistics - difficult age determin ...
... abundance reference: Sun, local F & G stars, B stars Sun: + star that can be studied best + independent abundances from different indicators - 4.56 Gyr old, representative for present-day ISM? F&G stars: + differential abundances relative to Sun + increased number statistics - difficult age determin ...
Particle Astrophysics Lecture 5 Gamma-ray Astronomy
... amount of EBL. However it is difficult tp distinguish between an intrinsic softening of blazar spectra and a softening caused by the interaction with low energy EBL photons. ...
... amount of EBL. However it is difficult tp distinguish between an intrinsic softening of blazar spectra and a softening caused by the interaction with low energy EBL photons. ...
HI in Local Group Dwarf Galaxies
... to our detection limits, and these upper limits are lower than the HI mass of any known dwarf which has HI. • Dwarf galaxies at smaller galactocentric distances have less HI on average than those at larger distances. • The HI -distance trend supports data from simulations which suggest ram-pressure ...
... to our detection limits, and these upper limits are lower than the HI mass of any known dwarf which has HI. • Dwarf galaxies at smaller galactocentric distances have less HI on average than those at larger distances. • The HI -distance trend supports data from simulations which suggest ram-pressure ...
P-nuclei
p-Nuclei (p stands for proton-rich) are certain proton-rich, naturally occurring isotopes of some elements between selenium and mercury which cannot be produced in either s- or r-process.