nuclear physics nuclear physics
... and nuclear medicine. Nuclear physics is divided into nuclear structure physics that studies the properties of nucleus (such as mass and decay) and physics of nuclear reactions that studies the processes in which two or more nuclei interact in various ways to form other nuclei. ...
... and nuclear medicine. Nuclear physics is divided into nuclear structure physics that studies the properties of nucleus (such as mass and decay) and physics of nuclear reactions that studies the processes in which two or more nuclei interact in various ways to form other nuclei. ...
Life Cycle of a Star notes
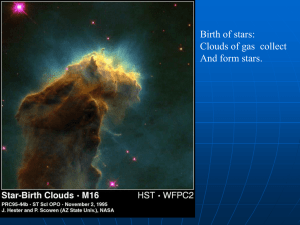
... As the protostar continues to collapse due to gravity, it will attract more atoms and continually increase in mass and density. The increased density and gravity will cause the core temperature to eventually rise. ...
... As the protostar continues to collapse due to gravity, it will attract more atoms and continually increase in mass and density. The increased density and gravity will cause the core temperature to eventually rise. ...
Stellar Interiors - Hydrostatic Equilibrium and Ignition on the Main
... The basis of energy generation by nuclear fusion is that two reactants come together with sufficient collisional energy to get close enough to experience the strong force. This force has a range ~10-13 cm, i.e., about 1/100,000 the size of the hydrogen atom. So two protons need to be no more than 10 ...
... The basis of energy generation by nuclear fusion is that two reactants come together with sufficient collisional energy to get close enough to experience the strong force. This force has a range ~10-13 cm, i.e., about 1/100,000 the size of the hydrogen atom. So two protons need to be no more than 10 ...
Document
... known as the Large Magellanic Cloud that lies just beyond the Milky Way. The star, known in modern times as Sanduleak 69202, was a blue supergiant 25 times more massive than the Sun. Such explosions distribute all the common elements such as Oxygen, Carbon, Nitrogen, Calcium and Iron into interstell ...
... known as the Large Magellanic Cloud that lies just beyond the Milky Way. The star, known in modern times as Sanduleak 69202, was a blue supergiant 25 times more massive than the Sun. Such explosions distribute all the common elements such as Oxygen, Carbon, Nitrogen, Calcium and Iron into interstell ...
Document
... must exist as a mixture of both left-handed and righthanded states. Hence, the neutrino emitted by a neutron has some chance of being a left-handed particle and thus to be reabsorbed by another neutron - and the neutrinoless double beta decay can occur! The probability depends on the mass of the neu ...
... must exist as a mixture of both left-handed and righthanded states. Hence, the neutrino emitted by a neutron has some chance of being a left-handed particle and thus to be reabsorbed by another neutron - and the neutrinoless double beta decay can occur! The probability depends on the mass of the neu ...
THE LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR
... suns for a short time. There are two general types of Supernova:Type I - These occur in binary star systems in which gas from one star falls on to a white dwarf, causing it to explode. Type II - These occur in stars ten times or more as massive as the Sun, which suffer runaway internal nuclear react ...
... suns for a short time. There are two general types of Supernova:Type I - These occur in binary star systems in which gas from one star falls on to a white dwarf, causing it to explode. Type II - These occur in stars ten times or more as massive as the Sun, which suffer runaway internal nuclear react ...
Sample Final Exam
... If two loops of wire are concentric as shown and a current is abruptly turned on in the outer loop, show the direction of the current in the inner one. This is just two circles, one inside the other. Try with both clockwise and counterclockwise, turning on and turning off. ...
... If two loops of wire are concentric as shown and a current is abruptly turned on in the outer loop, show the direction of the current in the inner one. This is just two circles, one inside the other. Try with both clockwise and counterclockwise, turning on and turning off. ...
Einstein
... • …are the leftover cores from supernova explosions. • If the core < 3 M, it will stop collapsing and be held up by neutron degeneracy pressure. • Neutron stars are very dense (1012 g/cm3 ) – 1.5 M with a diameter of 10 to 20 km ...
... • …are the leftover cores from supernova explosions. • If the core < 3 M, it will stop collapsing and be held up by neutron degeneracy pressure. • Neutron stars are very dense (1012 g/cm3 ) – 1.5 M with a diameter of 10 to 20 km ...
References - becquerel
... energy range, the pattern of the relativistic fragmentation loses sensitivity either to the collision energy or to the particular properties of a target nucleus. As an illustration, a 3.65 A GeV/c 28Si fragmentation in emulsion is shown in fig. 1. The tracks of relativistic fragments remain in an em ...
... energy range, the pattern of the relativistic fragmentation loses sensitivity either to the collision energy or to the particular properties of a target nucleus. As an illustration, a 3.65 A GeV/c 28Si fragmentation in emulsion is shown in fig. 1. The tracks of relativistic fragments remain in an em ...
Closed books and notes, 1 hour. Please PRINT
... The rate of nuclear fusion would increase, driving the temperature still higher An explosion would be triggered due to a runaway nuclear fusion reaction The core would expand, reducing the pressure and temperature back to their original values Hydrogen fusion would cease, and the Sun would cool down ...
... The rate of nuclear fusion would increase, driving the temperature still higher An explosion would be triggered due to a runaway nuclear fusion reaction The core would expand, reducing the pressure and temperature back to their original values Hydrogen fusion would cease, and the Sun would cool down ...
Document
... • Gravitational tides pull matter off big low density objects towards small high density objects. ...
... • Gravitational tides pull matter off big low density objects towards small high density objects. ...
neutrino
... • Must!collide!at!very!high!speeds,!to!get!close! enough!for!the!strong%nuclear%force%to!take!over! • This!is!why!fusion!can!only!happen!at!very!very! high!temperatures! – Speed!of!protons!depend!on!temperature,!and! temperature!of!at!least!10!million!K!required! for!fusion:!only!in!center%of%Sun% ...
... • Must!collide!at!very!high!speeds,!to!get!close! enough!for!the!strong%nuclear%force%to!take!over! • This!is!why!fusion!can!only!happen!at!very!very! high!temperatures! – Speed!of!protons!depend!on!temperature,!and! temperature!of!at!least!10!million!K!required! for!fusion:!only!in!center%of%Sun% ...
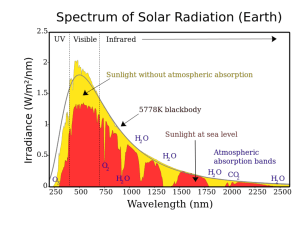
The Sun: Example of Radiation Laws
... The production of neutrinos and the nucleosynthesis and ejection of heavy nuclei in Type II supernovae was confirmed by SN 1987a in the Large Magellenic Cloud, a nearby galaxy, on February 23, 1987. Neutrino detectors in Ohio and Japan detected a total of about 20 neutrinos even though this supernov ...
... The production of neutrinos and the nucleosynthesis and ejection of heavy nuclei in Type II supernovae was confirmed by SN 1987a in the Large Magellenic Cloud, a nearby galaxy, on February 23, 1987. Neutrino detectors in Ohio and Japan detected a total of about 20 neutrinos even though this supernov ...
Star Energy Packet:
... This process is called fusion because the 4 small atoms are fused (joined) to form a larger atom. (Fusion is the opposite process from fission, which is used to power nuclear reactors on earth. Fission breaks a larger atom apart and makes smaller ones). When the hydrogen fuses into helium, a small a ...
... This process is called fusion because the 4 small atoms are fused (joined) to form a larger atom. (Fusion is the opposite process from fission, which is used to power nuclear reactors on earth. Fission breaks a larger atom apart and makes smaller ones). When the hydrogen fuses into helium, a small a ...
Death of Massive Stars
... How fast do you have to throw a ball up for it to escape The Earth completely? • Depends on the mass of the Earth and your distance from the center of the Earth. • At Earth’s surface: 25,000 mph (11km/s) • From the top of a 1000 mile high tower, 22,000 mph (10km/s) • From the surface of the Sun? (Ma ...
... How fast do you have to throw a ball up for it to escape The Earth completely? • Depends on the mass of the Earth and your distance from the center of the Earth. • At Earth’s surface: 25,000 mph (11km/s) • From the top of a 1000 mile high tower, 22,000 mph (10km/s) • From the surface of the Sun? (Ma ...
Exit Slip: Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry-1
... A. both negatively charged and repel each other C. both positively charged and repel each other B. oppositely charged and attract each other D. oppositely charged and repel each other 5. Most atomic nuclei are stable, even though they contain positively charged protons that repel each other. Which f ...
... A. both negatively charged and repel each other C. both positively charged and repel each other B. oppositely charged and attract each other D. oppositely charged and repel each other 5. Most atomic nuclei are stable, even though they contain positively charged protons that repel each other. Which f ...
Star Factories: Nuclear Fusion and the Creation of the Elements
... * The only place we know that fusion can build heavy elements is inside the cores of stars. The question now is: What is it about the environment inside stars that makes nuclear fusion possible? High temperature; and high density. ...
... * The only place we know that fusion can build heavy elements is inside the cores of stars. The question now is: What is it about the environment inside stars that makes nuclear fusion possible? High temperature; and high density. ...
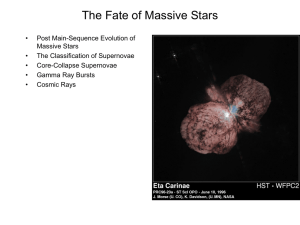
The Fate of Massive Stars
... •Classification by Spectral Lines and Light Curve Shape •Brightness to rival entire galaxies •What is happening? ...
... •Classification by Spectral Lines and Light Curve Shape •Brightness to rival entire galaxies •What is happening? ...
Page 1 of 4 Name PSCI 1055 Test #4 (Form B) Spring 2008 Buckley
... 6. (10 points) An old manuscript is found and carbon-14 dating is used to estimate its age. Carbon-14 decays to N-14 with a half-life of 5730 years. A measurement of the abundance of these two nuclides indicates there are now 4 parts of carbon14 to 12 parts of nitrogen-14. a. How many parts of carb ...
... 6. (10 points) An old manuscript is found and carbon-14 dating is used to estimate its age. Carbon-14 decays to N-14 with a half-life of 5730 years. A measurement of the abundance of these two nuclides indicates there are now 4 parts of carbon14 to 12 parts of nitrogen-14. a. How many parts of carb ...
Hubblecast Episode 64: It All Ends with a Bang! — The incineration of
... pressure in the centre drops dramatically and the star collapses in on itself, and then explodes. ...
... pressure in the centre drops dramatically and the star collapses in on itself, and then explodes. ...
Detection Explosives FinalUsing Neutron Source
... size of the screen is smaller than 10 cm. Then it is possible to withhold the proton beam in the transverse direction by means of the longitudinal solenoid magnetic field. When you have a great acceleration energy rate and high accelerated beam intensity, it is required to have a big magnetic field ...
... size of the screen is smaller than 10 cm. Then it is possible to withhold the proton beam in the transverse direction by means of the longitudinal solenoid magnetic field. When you have a great acceleration energy rate and high accelerated beam intensity, it is required to have a big magnetic field ...
Due: January 15, 2014 Name
... 12. Which effect has been useful (and successful) in the search for and identification of black holes in the universe? a. their magnetic fields and their influence on nearby matter. b. the effect of their angular momentum or spin on nearby matter. c. the influence of their intense gravitational fiel ...
... 12. Which effect has been useful (and successful) in the search for and identification of black holes in the universe? a. their magnetic fields and their influence on nearby matter. b. the effect of their angular momentum or spin on nearby matter. c. the influence of their intense gravitational fiel ...
P-nuclei
p-Nuclei (p stands for proton-rich) are certain proton-rich, naturally occurring isotopes of some elements between selenium and mercury which cannot be produced in either s- or r-process.