Neutron Stars and Black Holes
... –! Fastest known have periods of 1.5-3 ms (rotate 300-600 times per second!). •! Very active subject of research… –! What is the structure of a neutron star? –! What determines how fast they spin? –! How do they beam emission? ...
... –! Fastest known have periods of 1.5-3 ms (rotate 300-600 times per second!). •! Very active subject of research… –! What is the structure of a neutron star? –! What determines how fast they spin? –! How do they beam emission? ...
Chapter13
... dwarfs are found in the lower left corner of the HertzsprungRussell diagram. The more massive a white dwarf, the smaller it is! ...
... dwarfs are found in the lower left corner of the HertzsprungRussell diagram. The more massive a white dwarf, the smaller it is! ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... Procedures Part 1: 1) Cut out the words on the sheet provided by your teacher 2) Using the words, create four different star life timelines from birth to death; one timeline for a low mass star (<0.5 solar masses), a medium mass star (0.6 – 1.5 solar masses), and two different high mass stars (1.5 – ...
... Procedures Part 1: 1) Cut out the words on the sheet provided by your teacher 2) Using the words, create four different star life timelines from birth to death; one timeline for a low mass star (<0.5 solar masses), a medium mass star (0.6 – 1.5 solar masses), and two different high mass stars (1.5 – ...
Nuclear Chemistry Radioactivity
... Predicting the Type of Radioactive Decay • Nuclides outside the band of stability (Figure 20.3) are generally radioactive. – In contrast, nuclides to the right of the band of stability have a neutron-to-proton ratio smaller than that needed for a stable nucleus. – These nuclides tend to decay by po ...
... Predicting the Type of Radioactive Decay • Nuclides outside the band of stability (Figure 20.3) are generally radioactive. – In contrast, nuclides to the right of the band of stability have a neutron-to-proton ratio smaller than that needed for a stable nucleus. – These nuclides tend to decay by po ...
Stellar Evolution: the Death of Stars
... • The core ends up as all neutron, with nuclear density (1017 km/m3) • The degenerate neutron pressure suddenly halts the core contract • The outer core bounce back and sends a powerful wave of pressure • The pressure wave becomes a powerful shock wave as it go outwards, and expel most stellar mater ...
... • The core ends up as all neutron, with nuclear density (1017 km/m3) • The degenerate neutron pressure suddenly halts the core contract • The outer core bounce back and sends a powerful wave of pressure • The pressure wave becomes a powerful shock wave as it go outwards, and expel most stellar mater ...
particle - Uplift North Hills
... and although they travel much faster (up to 0.9 c) they cause less intense ionisation than the a -particle. They have a charge of only – e so they are less reactive. The b -particle travels about 1 m in air before it is absorbed. It can be stopped by a few mm of Al or other metal ...
... and although they travel much faster (up to 0.9 c) they cause less intense ionisation than the a -particle. They have a charge of only – e so they are less reactive. The b -particle travels about 1 m in air before it is absorbed. It can be stopped by a few mm of Al or other metal ...
chp. 7
... which an unstable nucleus emits one or more particles or energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation ...
... which an unstable nucleus emits one or more particles or energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation ...
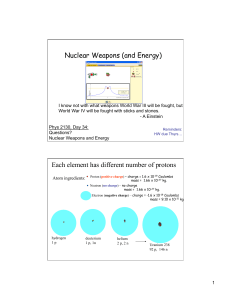
Nuclear Weapons (and Energy) Each element has different number
... blows things down. In atomic bomb, roughly 20% of Pl or Ur decays by induced fiss. This means that after explosion there are a. about 20% fewer atomic nuclei than before with correspondingly fewer total neutrons and protons, b. 20% fewer at. nucl. but about same total neut. and protons. c. about ...
... blows things down. In atomic bomb, roughly 20% of Pl or Ur decays by induced fiss. This means that after explosion there are a. about 20% fewer atomic nuclei than before with correspondingly fewer total neutrons and protons, b. 20% fewer at. nucl. but about same total neut. and protons. c. about ...
The Lifecycle of Stars
... When A Star Dies Supernova Some massive stars may explode in a large, bright display called a Supernova Supernova occur when a massive star collapses and throws its outer layers into space. This explosion is so powerful that it can be brighter than an entire galaxy for several days!! ...
... When A Star Dies Supernova Some massive stars may explode in a large, bright display called a Supernova Supernova occur when a massive star collapses and throws its outer layers into space. This explosion is so powerful that it can be brighter than an entire galaxy for several days!! ...
A Brief History of History
... under gravity formed the first galaxies and that the stars inside these clouds were formed later by the same process on a smaller scale. Stars come next A star is a ball of super-hot gas balanced between the twin tendencies to collapse under its own gravity, and the outward pressure of radiation ene ...
... under gravity formed the first galaxies and that the stars inside these clouds were formed later by the same process on a smaller scale. Stars come next A star is a ball of super-hot gas balanced between the twin tendencies to collapse under its own gravity, and the outward pressure of radiation ene ...
eta carinae – nature`s own hadron collider
... ETA CARINAE IS ONE OF THE MOST MASSIVE STARS KNOWN. IT IS AROUND 100 SOLAR MASSES. THE UPPER LIMIT OF STAR SIZE IS THOUGHT TO BE AROUND 150 SOLAR MASSES. BECAUSE OF ITS SIZE, AND THE HIGH ENERGIES PRODUCED BECAUSE OF GRAVITY, IT IS UNSTABLE. ...
... ETA CARINAE IS ONE OF THE MOST MASSIVE STARS KNOWN. IT IS AROUND 100 SOLAR MASSES. THE UPPER LIMIT OF STAR SIZE IS THOUGHT TO BE AROUND 150 SOLAR MASSES. BECAUSE OF ITS SIZE, AND THE HIGH ENERGIES PRODUCED BECAUSE OF GRAVITY, IT IS UNSTABLE. ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... • If you analyze a nuclear reaction & observe the products, you can determine the type of reaction that took place: 1- If both the mass number & atomic number decrease, alpha decay occurred. 2- If only the atomic number increases, beta decay has occurred. 3- If neither mass number or atomic number c ...
... • If you analyze a nuclear reaction & observe the products, you can determine the type of reaction that took place: 1- If both the mass number & atomic number decrease, alpha decay occurred. 2- If only the atomic number increases, beta decay has occurred. 3- If neither mass number or atomic number c ...
Chapter 21 Nuclear Chemistry - Ocean County Vocational
... • If you analyze a nuclear reaction & observe the products, you can determine the type of reaction that took place: 1- If both the mass number & atomic number decrease, alpha decay occurred. 2- If only the atomic number increases, beta decay has occurred. 3- If neither mass number or atomic number c ...
... • If you analyze a nuclear reaction & observe the products, you can determine the type of reaction that took place: 1- If both the mass number & atomic number decrease, alpha decay occurred. 2- If only the atomic number increases, beta decay has occurred. 3- If neither mass number or atomic number c ...
Document
... • 15-20 MeV for spherically-symmetrical collapse • 30-40 MeV for rotational-fission model is necessary to interpret the statistically significant signal from SN 1987A registered by the LSD neutrino detector Characteristic duration of the peak < 0.5 s About of 10% of total E is radiated in the peak ...
... • 15-20 MeV for spherically-symmetrical collapse • 30-40 MeV for rotational-fission model is necessary to interpret the statistically significant signal from SN 1987A registered by the LSD neutrino detector Characteristic duration of the peak < 0.5 s About of 10% of total E is radiated in the peak ...
Black Hole
... The surface gravity is so high that a 150 pound person would weigh a million tons. You would be squeezed flatter than a piece of paper. The fastest pulsar known has a period of 0.0014 s. The star spins 642 times per second. Dozens of such “millisecond pulsars” are known. More are being discovered. I ...
... The surface gravity is so high that a 150 pound person would weigh a million tons. You would be squeezed flatter than a piece of paper. The fastest pulsar known has a period of 0.0014 s. The star spins 642 times per second. Dozens of such “millisecond pulsars” are known. More are being discovered. I ...
國立彰化師範大學八十八學年度碩士班招生考試試題
... 3. (a) A proton of mass 1.0 u traveling with a speed of 2104 m/s has an elastic head-on collision with a helium nucleus of mass 4.0 u initially at rest. The velocity of the proton after the collision is vP=_________ m/s. (b) If these two particles are observed to move off at 45, proton above the x ...
... 3. (a) A proton of mass 1.0 u traveling with a speed of 2104 m/s has an elastic head-on collision with a helium nucleus of mass 4.0 u initially at rest. The velocity of the proton after the collision is vP=_________ m/s. (b) If these two particles are observed to move off at 45, proton above the x ...
Lectures 12 & 13 powerpoint (stellar death)
... Q: The Helium core contracts and heats the star enough to induce a hydrogen-burning shell… so what stops the helium core from contracting to zero radius (keep in mind that He fusion has not set in yet….)? ...
... Q: The Helium core contracts and heats the star enough to induce a hydrogen-burning shell… so what stops the helium core from contracting to zero radius (keep in mind that He fusion has not set in yet….)? ...
NSCL - Michigan State University
... The parameters of the nuclear liquid drop model, such as the volume, surface, symmetry, and curvature constants, as well as bulk radii, are extracted from the non-relativistic and relativistic energy density functionals used in microscopic calculations for finite nuclei. The microscopic liquid drop ...
... The parameters of the nuclear liquid drop model, such as the volume, surface, symmetry, and curvature constants, as well as bulk radii, are extracted from the non-relativistic and relativistic energy density functionals used in microscopic calculations for finite nuclei. The microscopic liquid drop ...
5 log5 − = − d . N
... Stellar remnants in close binary systems may gravitationally attract material away from their companion stars. This material flows onto the surface of the remnant in a process called accretion. Consider the gravitational potential in a binary system. The region of space around a star in which materi ...
... Stellar remnants in close binary systems may gravitationally attract material away from their companion stars. This material flows onto the surface of the remnant in a process called accretion. Consider the gravitational potential in a binary system. The region of space around a star in which materi ...
12_physics_notes_ch13_nuclei
... The difference between the rest mass of a nucleus and the sum of the rest masses of its constituent nucleons is called its mass defect. It is given by, m ∆ = [ Zm + ( A− Z) m ]− m p n • Binding Energy: a) It may be defined as the energy required to break a nucleus into its constituent protons and ne ...
... The difference between the rest mass of a nucleus and the sum of the rest masses of its constituent nucleons is called its mass defect. It is given by, m ∆ = [ Zm + ( A− Z) m ]− m p n • Binding Energy: a) It may be defined as the energy required to break a nucleus into its constituent protons and ne ...
Calcium Built From Scratch, Much Smaller Than Expected
... Calcium Built From Scratch, Much Smaller Than Expected TRIUMF theorists contribute to discovery resulting from massive computation on America’s largest supercomputer (Vancouver, BC) – An international team of theoretical physicists has succeeded for the first time in calculating important properties ...
... Calcium Built From Scratch, Much Smaller Than Expected TRIUMF theorists contribute to discovery resulting from massive computation on America’s largest supercomputer (Vancouver, BC) – An international team of theoretical physicists has succeeded for the first time in calculating important properties ...
Document
... Indicated the best answer to the following questions on the answer sheet provided. All questions are worth two points unless stated otherwise. 1. Magnetic fields inside sunspots are __________ those in surrounding regions. a) much stronger than, b) slightly stronger than, c) the same as, d) much wea ...
... Indicated the best answer to the following questions on the answer sheet provided. All questions are worth two points unless stated otherwise. 1. Magnetic fields inside sunspots are __________ those in surrounding regions. a) much stronger than, b) slightly stronger than, c) the same as, d) much wea ...
P-nuclei
p-Nuclei (p stands for proton-rich) are certain proton-rich, naturally occurring isotopes of some elements between selenium and mercury which cannot be produced in either s- or r-process.