Ch. 11 and 12 Study Guide (ANSWERS)
... A low-mass star will run out of H to fuse with helium its core cannot withstand the crushing force of gravity. The core collapses and H fusion begins to take place on the outside of the core. This causes the star to expand and cool, creating a red giant. Over time, the red giant loses mass from its ...
... A low-mass star will run out of H to fuse with helium its core cannot withstand the crushing force of gravity. The core collapses and H fusion begins to take place on the outside of the core. This causes the star to expand and cool, creating a red giant. Over time, the red giant loses mass from its ...
Friday, November 7 - Otterbein University
... • Sun is a gas ball of hydrogen & helium • Density and temperature increase towards center • Very hot & dense core produces all the energy by hydrogen nuclear fusion • Energy is released in the form of EM radiation and particles (neutrinos) • Energy transport well understood in physics ...
... • Sun is a gas ball of hydrogen & helium • Density and temperature increase towards center • Very hot & dense core produces all the energy by hydrogen nuclear fusion • Energy is released in the form of EM radiation and particles (neutrinos) • Energy transport well understood in physics ...
astr study guide ex 3 s`16
... the time interval between pulses? 32. Why would an isolated black hole in empty intergalactic space be difficult to detect? 33. The material that accretes onto a neutron star or black hole is expected to emit X-rays because 34. What is the difference between a neutron star and a pulsar? 35. What det ...
... the time interval between pulses? 32. Why would an isolated black hole in empty intergalactic space be difficult to detect? 33. The material that accretes onto a neutron star or black hole is expected to emit X-rays because 34. What is the difference between a neutron star and a pulsar? 35. What det ...
Study Notes for Chapter 30: Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe
... 1. A galaxy is made of stars, dust, and gas bound together by gravity. 2. A large, bright star whose hot core has used most of its hydrogen is a nova. 3. A light-year is the distance light travels in a year. 4. A small, hot, extremely dense core left after a star collapses is a white dwarf. 5. A sta ...
... 1. A galaxy is made of stars, dust, and gas bound together by gravity. 2. A large, bright star whose hot core has used most of its hydrogen is a nova. 3. A light-year is the distance light travels in a year. 4. A small, hot, extremely dense core left after a star collapses is a white dwarf. 5. A sta ...
Homework #3
... a) Assuming uniform density, how does the average density of a star vary with mass on the main sequence? If the mass is halved, does the density go up or down and by what factor? b) Assuming hydrostatic equilibrium continuing to assume constant density and the dominance of ideal gas pressure, how do ...
... a) Assuming uniform density, how does the average density of a star vary with mass on the main sequence? If the mass is halved, does the density go up or down and by what factor? b) Assuming hydrostatic equilibrium continuing to assume constant density and the dominance of ideal gas pressure, how do ...
firstannouncement - Predeal International Summer School in
... D.H.E. Gross: Nuclear multifragmentation explores fundamentals of statistical mechanics F. Gulminelli: I.From multifragmentation to supernovae and neutron stars II. Signals of phase transitions in nuclei and other finite systems III. Statistical ensembles for time dependent systems and applications ...
... D.H.E. Gross: Nuclear multifragmentation explores fundamentals of statistical mechanics F. Gulminelli: I.From multifragmentation to supernovae and neutron stars II. Signals of phase transitions in nuclei and other finite systems III. Statistical ensembles for time dependent systems and applications ...
Chapter 12: Stellar Evolution - Otto
... Stage 9 - Red Giant branch H depleted at center, He core grows Core pressure decreases, gravity doesn’t He core contracts, H shell burning increases Star’s radius increases, surface cools, ...
... Stage 9 - Red Giant branch H depleted at center, He core grows Core pressure decreases, gravity doesn’t He core contracts, H shell burning increases Star’s radius increases, surface cools, ...
b) Formation of Heavy Elements
... d) Determining the Energy that is produced (Uncertain about how to do this? Check you lecture notes and/or your book.) In the process of turning hydrogen to helium, mass is lost. This mass gets transformed to energy (remember Einstein’s E=mc2?). Calculate how much energy is released when burning 1 ...
... d) Determining the Energy that is produced (Uncertain about how to do this? Check you lecture notes and/or your book.) In the process of turning hydrogen to helium, mass is lost. This mass gets transformed to energy (remember Einstein’s E=mc2?). Calculate how much energy is released when burning 1 ...
Chapter 12
... Black holes are thought to be the endpoints of stars that exceed 25-30 solar masses on the main sequence •They are concentrations of mass where gravity is so strong that nothing (including light) can escape! •In terms of theory of relativity, the mass of the black hole distort and curve the space-t ...
... Black holes are thought to be the endpoints of stars that exceed 25-30 solar masses on the main sequence •They are concentrations of mass where gravity is so strong that nothing (including light) can escape! •In terms of theory of relativity, the mass of the black hole distort and curve the space-t ...
The Evolution of Elements and Isotopes
... The isotopes found today in our solar system (Lodders et stars) and in the cores of massive stars, where heliumal. 2009) were formed in numerous cycles of nucleosynburning nuclear reactions can produce neutrons that are thesis over the ~10 billion years from the Big Bang to the then captured on iron ...
... The isotopes found today in our solar system (Lodders et stars) and in the cores of massive stars, where heliumal. 2009) were formed in numerous cycles of nucleosynburning nuclear reactions can produce neutrons that are thesis over the ~10 billion years from the Big Bang to the then captured on iron ...
Nuclear Chemistry - Duplin County Schools
... • Cancer cells grow quickly, they are more susceptible to absorbing radiation and being damaged than healthy cells are. • However, other cells in the body that grow quickly also are damaged, which is why cancer patients who have ...
... • Cancer cells grow quickly, they are more susceptible to absorbing radiation and being damaged than healthy cells are. • However, other cells in the body that grow quickly also are damaged, which is why cancer patients who have ...
Review Packet
... _____ Hydrogen atoms are fused together generating an enormous amount of energy igniting the star causing it to shine. ...
... _____ Hydrogen atoms are fused together generating an enormous amount of energy igniting the star causing it to shine. ...
galaxies - GEOCITIES.ws
... – If a star has between 1.4 and 9 solar masses, it will become a neutron star. – A neutron star is a star made entirely of neutrons, as the name suggests. After a star goes supernova, the remaining core collapses. Gravity shrinks and condenses it into a sphere about the size of Manhattan (fifteen mi ...
... – If a star has between 1.4 and 9 solar masses, it will become a neutron star. – A neutron star is a star made entirely of neutrons, as the name suggests. After a star goes supernova, the remaining core collapses. Gravity shrinks and condenses it into a sphere about the size of Manhattan (fifteen mi ...
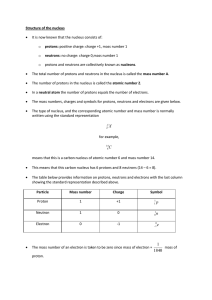
Structure of the nucleus • It is now known that the nucleus consists of
... In beta decay, a neutron within the unstable nucleus changes into a proton, with the emission of a fast-moving electron from with the nucleus (discussed in more detail in Key Area - Standard Model) ...
... In beta decay, a neutron within the unstable nucleus changes into a proton, with the emission of a fast-moving electron from with the nucleus (discussed in more detail in Key Area - Standard Model) ...
Study Notes for Chapter 30:
... By analyzing the light that a star emits, astronomers can determine the ______ and ________ of a star. ...
... By analyzing the light that a star emits, astronomers can determine the ______ and ________ of a star. ...
Study Notes for Chapter 30:
... By analyzing the light that a star emits, astronomers can determine the ______ and ________ of a star. ...
... By analyzing the light that a star emits, astronomers can determine the ______ and ________ of a star. ...
Star Life Cycle
... This is the 3rd predicted result to a star. This is the most dense core of a star that can be left. Gravity is so strong, light cannot escape. Makes it look like a dark hole in space. If the star's remaining mass is greater than three times the mass of the Sun, the star contracts tremendously ...
... This is the 3rd predicted result to a star. This is the most dense core of a star that can be left. Gravity is so strong, light cannot escape. Makes it look like a dark hole in space. If the star's remaining mass is greater than three times the mass of the Sun, the star contracts tremendously ...
Ch. 27 Stars & Galaxies
... All the Hydrogen is fused into Helium The core of the star contracts High temperatures cause the helium atoms to fuse forming Carbon. The combined hydrogen fusion and helium fusion causes the outer shell to expand forming a Giant Star. ...
... All the Hydrogen is fused into Helium The core of the star contracts High temperatures cause the helium atoms to fuse forming Carbon. The combined hydrogen fusion and helium fusion causes the outer shell to expand forming a Giant Star. ...
P-nuclei
p-Nuclei (p stands for proton-rich) are certain proton-rich, naturally occurring isotopes of some elements between selenium and mercury which cannot be produced in either s- or r-process.