The H-R Diagram
... exploded. These heavy elements can act as seeds, and neutrons freed in the fusion processes (mainly starting with C13 and Ne22) slamming into these heavy element seeds, can create about half of the isotopes of elements heavier than iron, by the S-Process . Follow link for more details. ...
... exploded. These heavy elements can act as seeds, and neutrons freed in the fusion processes (mainly starting with C13 and Ne22) slamming into these heavy element seeds, can create about half of the isotopes of elements heavier than iron, by the S-Process . Follow link for more details. ...
Physics 210 problems for week 2 Oct
... A thin rod of length ℓ and uniform charge per unit length λ lies along the x axis, as shown in Figure P23.35. (a) Show that the electric field at P, a distance y from the rod along its perpendicular bisector, has no x component and is given by E = 2ke λ sin θ0/y. (b) What If? Using your result to pa ...
... A thin rod of length ℓ and uniform charge per unit length λ lies along the x axis, as shown in Figure P23.35. (a) Show that the electric field at P, a distance y from the rod along its perpendicular bisector, has no x component and is given by E = 2ke λ sin θ0/y. (b) What If? Using your result to pa ...
Analysis of Experimental Results on Excess Heat Power Production, Impurity Nuclides... Cathode Material and Penetrating Radiation in Experiments with High-Current Glow Discharge International Conference on Cold Fusion
... is up to several tens of times, some main isotopes of impurity elements (with high natural abundance percentage) being absent. The following isotopes were registered as being absent: 58Ni, 70Ge, 73Ge, 74Ge, 113Cd, 116Cd. These peculiarities are also registered within 100nm thick surface layer (Fig. ...
... is up to several tens of times, some main isotopes of impurity elements (with high natural abundance percentage) being absent. The following isotopes were registered as being absent: 58Ni, 70Ge, 73Ge, 74Ge, 113Cd, 116Cd. These peculiarities are also registered within 100nm thick surface layer (Fig. ...
AST 341 Final Exam and Solutions
... What comes up must come down. Consider a two level atom with an upper state U and a lower state L. There are nL and nU electrons in the lower and upper states, respectively. Electrons in state L can be excited to state U by absorbing a photon; the rate for absorption is Iν BLU , where Iν is the inte ...
... What comes up must come down. Consider a two level atom with an upper state U and a lower state L. There are nL and nU electrons in the lower and upper states, respectively. Electrons in state L can be excited to state U by absorbing a photon; the rate for absorption is Iν BLU , where Iν is the inte ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... The quantum theory describes the behavior of matter on the smallest scales. It predicts that tiny particles and light are continuously created and destroyed on sub-atomic scales. Some of the light thus created actually has a very small chance of escaping before it is destroyed. To an outsider, it is ...
... The quantum theory describes the behavior of matter on the smallest scales. It predicts that tiny particles and light are continuously created and destroyed on sub-atomic scales. Some of the light thus created actually has a very small chance of escaping before it is destroyed. To an outsider, it is ...
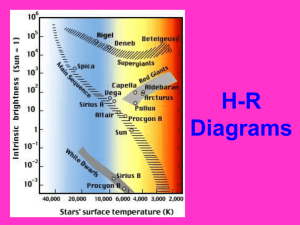
H-R Diagrams
... will show up on the Main Sequence – i.e., what spectral type the star will have while on the main sequence ...
... will show up on the Main Sequence – i.e., what spectral type the star will have while on the main sequence ...
The Life of a Star
... between planets and stars. 13.3: Rotation vs. Revolution, How does this relate to the Earth’s days, years, seasons. 13.4: Constellations – know how to locate on a star map. 14.7: Composition of the Sun, Parts of the Sun, How the Sun’s energy is made. *14.10: 5 key characteristics of the Sun: Colour, ...
... between planets and stars. 13.3: Rotation vs. Revolution, How does this relate to the Earth’s days, years, seasons. 13.4: Constellations – know how to locate on a star map. 14.7: Composition of the Sun, Parts of the Sun, How the Sun’s energy is made. *14.10: 5 key characteristics of the Sun: Colour, ...
Week 11 Answers
... temperatures all the way up to 20,000 degrees and more. These are stars that do not live for very long as main sequence stars, so this is a young cluster. At the other extreme, cluster C has no main sequence stars with surface temperatures above 5000 degrees, meaning that all of the stars with highe ...
... temperatures all the way up to 20,000 degrees and more. These are stars that do not live for very long as main sequence stars, so this is a young cluster. At the other extreme, cluster C has no main sequence stars with surface temperatures above 5000 degrees, meaning that all of the stars with highe ...
14-black-holes
... • What is the life cycle of a low mass star (<8 solar masses when on the main sequence)? • What is the life cycle of a high mass star (>8 solar masses when on the main sequence)? • After a supernova, what are the two fates of the core of the star? • What determines whether the core will be a neutron ...
... • What is the life cycle of a low mass star (<8 solar masses when on the main sequence)? • What is the life cycle of a high mass star (>8 solar masses when on the main sequence)? • After a supernova, what are the two fates of the core of the star? • What determines whether the core will be a neutron ...
Word doc - UC-HiPACC - University of California, Santa Cruz
... the event so that, as seen from telescopes on Earth, the explosions seemed to unfold in slow motion. But another big mystery remained: how could those supernovae be so phenomenally brilliant? Power source? Supernovae are not alike. For decades, astronomers had known that supernovae fell into differe ...
... the event so that, as seen from telescopes on Earth, the explosions seemed to unfold in slow motion. But another big mystery remained: how could those supernovae be so phenomenally brilliant? Power source? Supernovae are not alike. For decades, astronomers had known that supernovae fell into differe ...
OVERVIEW ABSTRACT HST/COS chemical abundance analysis of
... We present new Near-UltraViolet (NUV) elemental abundance analysis, for the hyper metal-poor star HE1327-2326 ([Fe/H] = -5.2) using COS/HST data. We detect for the first time 4 Fe II lines, in addition to Zn I and Ni II absorption lines. Fitting the abundances to SNe yield models, lead to Pop III pr ...
... We present new Near-UltraViolet (NUV) elemental abundance analysis, for the hyper metal-poor star HE1327-2326 ([Fe/H] = -5.2) using COS/HST data. We detect for the first time 4 Fe II lines, in addition to Zn I and Ni II absorption lines. Fitting the abundances to SNe yield models, lead to Pop III pr ...
5Stars_Part_Two
... Black Holes: 1. If the mass of the neutron star is bigger than about 2 or 3 solar masses, it don’t care about no neutron exclusion principle. 2. Gravity collapses the neutron star even further. 3. The star becomes a black hole - an object from which even light cannot escape. 4. Light is really fast ...
... Black Holes: 1. If the mass of the neutron star is bigger than about 2 or 3 solar masses, it don’t care about no neutron exclusion principle. 2. Gravity collapses the neutron star even further. 3. The star becomes a black hole - an object from which even light cannot escape. 4. Light is really fast ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... • Lasts up to 7 billion years (usually less) • At least 10 times the size of our Sun • When a high mass star runs out of fuel it collapses and expands to form a Supergiant • Supergiants end in a massive explosion called a supernova • End result: 1) cosmic debris - nebula 2) a neutron star (or pulsar ...
... • Lasts up to 7 billion years (usually less) • At least 10 times the size of our Sun • When a high mass star runs out of fuel it collapses and expands to form a Supergiant • Supergiants end in a massive explosion called a supernova • End result: 1) cosmic debris - nebula 2) a neutron star (or pulsar ...
The Life Cycles of Stars
... waves. If the radio waves are emitted in pulses (due to the star’s spin), these neutron stars are called pulsars. The core of a massive star that has 8 or more times the mass of our Sun remains massive after the supernova. No nuclear fusion is taking place to support the core, so it is swallowed by ...
... waves. If the radio waves are emitted in pulses (due to the star’s spin), these neutron stars are called pulsars. The core of a massive star that has 8 or more times the mass of our Sun remains massive after the supernova. No nuclear fusion is taking place to support the core, so it is swallowed by ...
part 2 - Stardome
... the star can no longer the star This is the point where and d, war out ng iati rad of energy of gravity with the force ire ent the in – the largest explosion explodes in a supernova nts heavier rks the creation of eleme spa on losi exp universe. The supernovae are rs outer layers of these sta than i ...
... the star can no longer the star This is the point where and d, war out ng iati rad of energy of gravity with the force ire ent the in – the largest explosion explodes in a supernova nts heavier rks the creation of eleme spa on losi exp universe. The supernovae are rs outer layers of these sta than i ...
Handout 30
... The band that runs diagonally through the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram and extends from cool, dim, red stars at the lower right to hot, bright, blue stars at the upper left. ...
... The band that runs diagonally through the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram and extends from cool, dim, red stars at the lower right to hot, bright, blue stars at the upper left. ...
P-nuclei
p-Nuclei (p stands for proton-rich) are certain proton-rich, naturally occurring isotopes of some elements between selenium and mercury which cannot be produced in either s- or r-process.