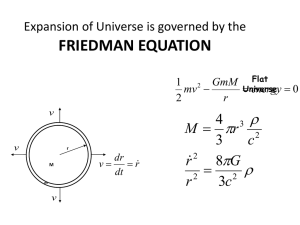
2 - Helios Home Page
... difference between the potential energies for dipole orientations r parallel and antiparallel to E ? ...
... difference between the potential energies for dipole orientations r parallel and antiparallel to E ? ...
The Lives of Stars
... Low-mass stars die by gently ejecting their outer layers, creating planetary nebulae • Helium shell flashes in an old, low-mass star produce thermal pulses during which more than half the star’s mass may be ejected into space • This exposes the hot carbon-oxygen core of the star • Ultraviolet radia ...
... Low-mass stars die by gently ejecting their outer layers, creating planetary nebulae • Helium shell flashes in an old, low-mass star produce thermal pulses during which more than half the star’s mass may be ejected into space • This exposes the hot carbon-oxygen core of the star • Ultraviolet radia ...
To understand the deaths of stars and how it depends on
... • Slow: you add 1 neutron at a time and wait. If you add too many neutrons to an atom 1 neutron will turn into a proton and you suddenly have a different atom. • Fast: you add them all at once. Then some neutrons convert to protons. • These methods create different atoms and/or isotopes. • However, ...
... • Slow: you add 1 neutron at a time and wait. If you add too many neutrons to an atom 1 neutron will turn into a proton and you suddenly have a different atom. • Fast: you add them all at once. Then some neutrons convert to protons. • These methods create different atoms and/or isotopes. • However, ...
2008 - UCL
... Star 'A' appears 10 times brighter than star 'B'. What is the appa,rent magnitude t2] difference between these two stars? Give the general expression relating flux ratios and magnitude differences. Ignoring intersteliar extinction, use this general expression to derive the relation- [4] ship between ...
... Star 'A' appears 10 times brighter than star 'B'. What is the appa,rent magnitude t2] difference between these two stars? Give the general expression relating flux ratios and magnitude differences. Ignoring intersteliar extinction, use this general expression to derive the relation- [4] ship between ...
Death of Stars notes
... • A core with remaining mass of 1.4 to 3 M, composed of tightly packed neutrons. • These tiny stars are much smaller than planet Earth -- in fact, they are about the diameter of a large city (~20 km). • One cubic centimeter (like a sugar cube) of a neutron star, would have a mass of about 1011 kg! ...
... • A core with remaining mass of 1.4 to 3 M, composed of tightly packed neutrons. • These tiny stars are much smaller than planet Earth -- in fact, they are about the diameter of a large city (~20 km). • One cubic centimeter (like a sugar cube) of a neutron star, would have a mass of about 1011 kg! ...
Energy production in stars
... other nuclei, going up in the periodic system. Reactions between H and 4He lead nowhere, there being no stable nucleus of mass 5. Reactions of H with Li, Be and B, as well as with deuterons, are all very fast at the central temperature of the sun, but just this speed of the reaction rules them out: ...
... other nuclei, going up in the periodic system. Reactions between H and 4He lead nowhere, there being no stable nucleus of mass 5. Reactions of H with Li, Be and B, as well as with deuterons, are all very fast at the central temperature of the sun, but just this speed of the reaction rules them out: ...
Slide 1
... The sun is only going to have enough pressure to get to the point where it fuses carbon. After it stops, the rest of the sun collapsing down just isn’t hot enough to let it do more fusion. So what happens next? This is where it gets a bit ...
... The sun is only going to have enough pressure to get to the point where it fuses carbon. After it stops, the rest of the sun collapsing down just isn’t hot enough to let it do more fusion. So what happens next? This is where it gets a bit ...
OUR UNIVERSE Problem Set 7 Solutions Question A1 Question A2
... However, the fusion of iron results in the consumption (not release of energy), which results in a massive core collapse. When the core mass exceeds Chandrasekhar's limit (1.44 Msun), a type II supernova occurs [1]. The star explodes releasing the iron into space where is can go on to be involved in ...
... However, the fusion of iron results in the consumption (not release of energy), which results in a massive core collapse. When the core mass exceeds Chandrasekhar's limit (1.44 Msun), a type II supernova occurs [1]. The star explodes releasing the iron into space where is can go on to be involved in ...
Section 1
... A model atmosphere is a numerical simulation of a real stellar atmosphere, typically presented as the run of physical parameters (such as temperature) as a function of depth; here ‘depth’ generally refers to optical depth (§3.4), measured inwards. Observationally, the most easily accessible part of ...
... A model atmosphere is a numerical simulation of a real stellar atmosphere, typically presented as the run of physical parameters (such as temperature) as a function of depth; here ‘depth’ generally refers to optical depth (§3.4), measured inwards. Observationally, the most easily accessible part of ...
Star formation, feedback and the role of SNe II and SNe Ia in the
... • Mashchenko et al 2005 made N-body simulations of the formation of dwarf spheroidal galaxies and found that the best fitting models for Draco have a large range of DM halo virial masses (108-109 MO) • Mashchenko et al 2006 made simulations of the interaction of Draco with our Galaxy and ruled out t ...
... • Mashchenko et al 2005 made N-body simulations of the formation of dwarf spheroidal galaxies and found that the best fitting models for Draco have a large range of DM halo virial masses (108-109 MO) • Mashchenko et al 2006 made simulations of the interaction of Draco with our Galaxy and ruled out t ...
Cosmology and Astrophysics II
... mass, irrespective of the initial conditions of the universe. As long as the universe was hot enough for protons and neutrons to transform into each other easily, their ratio, determined solely by their relative masses, was about 1 neutron to 7 protons (allowing for some decay of neutrons into proto ...
... mass, irrespective of the initial conditions of the universe. As long as the universe was hot enough for protons and neutrons to transform into each other easily, their ratio, determined solely by their relative masses, was about 1 neutron to 7 protons (allowing for some decay of neutrons into proto ...
Phys 100 – Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for
... 39. The energy a white dwarf emits into space is a. replaced by fusion of hydrogen atoms into helium. b. replaced by fusion of helium atoms into carbon. * c. not replaced. 40. A Type I supernova is believed to occur when a. the core of a massive star collapses. b. carbon detonation occurs. * c. a wh ...
... 39. The energy a white dwarf emits into space is a. replaced by fusion of hydrogen atoms into helium. b. replaced by fusion of helium atoms into carbon. * c. not replaced. 40. A Type I supernova is believed to occur when a. the core of a massive star collapses. b. carbon detonation occurs. * c. a wh ...
NUCLEOSYNTHESIS
... resonance at Ep = 460 keV. Shown as a hatched band is the range of effective stellar energies near E0 (see Fig. 2.5). At that energy the protons are captured into the wing of the 460 keV resonance. Figure from Clayton. ...
... resonance at Ep = 460 keV. Shown as a hatched band is the range of effective stellar energies near E0 (see Fig. 2.5). At that energy the protons are captured into the wing of the 460 keV resonance. Figure from Clayton. ...
Thermodynamic properties of nuclear" pasta" in neutron star crusts
... With increasing density, weak interactions render nuclei neutron-rich via electron captures. Then, at a density of about ∼ 4 × 1011 g cm−3 , neutrons begin to drip out of these nuclei. The crystalline region of the star (not) including a gas of the dripped neutrons is usually referred to as an inner ...
... With increasing density, weak interactions render nuclei neutron-rich via electron captures. Then, at a density of about ∼ 4 × 1011 g cm−3 , neutrons begin to drip out of these nuclei. The crystalline region of the star (not) including a gas of the dripped neutrons is usually referred to as an inner ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... While uranium-235 is the naturally occuring fissionable isotope, there are other isotopes which can be induced to fission by neutron bombardment. Plutonium-239 is also fissionable by bombardment with slow neutrons, and both it and uranium-235 have been used to make nuclear fission bombs. Plutonium-2 ...
... While uranium-235 is the naturally occuring fissionable isotope, there are other isotopes which can be induced to fission by neutron bombardment. Plutonium-239 is also fissionable by bombardment with slow neutrons, and both it and uranium-235 have been used to make nuclear fission bombs. Plutonium-2 ...
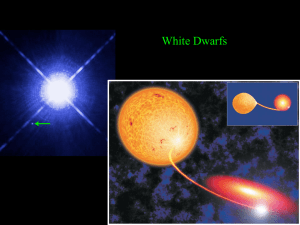
HOU Supernova Light Curves
... dwarf star, a dense ball primarily composed of carbon and oxygen atoms, is intrinsically the most stable of stars, as long as its mass remains below the so-called Chandrasekhar limit of 1.4 solar masses. ...
... dwarf star, a dense ball primarily composed of carbon and oxygen atoms, is intrinsically the most stable of stars, as long as its mass remains below the so-called Chandrasekhar limit of 1.4 solar masses. ...
Lecture 42
... emission and absorption lines are much weaker and excess infrared emission is absent. The inference is that the disk has largely dissipated by this stage. Like classical T-Tauri stars, weak-lined T-Tauri stars are cooler yet more luminous than mature main sequence stars of similar mass, but they are ...
... emission and absorption lines are much weaker and excess infrared emission is absent. The inference is that the disk has largely dissipated by this stage. Like classical T-Tauri stars, weak-lined T-Tauri stars are cooler yet more luminous than mature main sequence stars of similar mass, but they are ...
P-nuclei
p-Nuclei (p stands for proton-rich) are certain proton-rich, naturally occurring isotopes of some elements between selenium and mercury which cannot be produced in either s- or r-process.