Speciation
... Both in space and time, we seem to be brought somewhat near to that great fact —that mystery of mysteries— the first appearance of new beings on this Earth. ...
... Both in space and time, we seem to be brought somewhat near to that great fact —that mystery of mysteries— the first appearance of new beings on this Earth. ...
Bio112HW3 - Napa Valley College
... c. Genetic drift d. Both a and b 6. Which process changes allele frequencies by chance alone? a. Disruptive selection b. Stabilizing selection c. Genetic drift d. Both a and b 7. Which statement about genetic drift is false? a. It affects allele frequencies the most when populations are small. b. It ...
... c. Genetic drift d. Both a and b 6. Which process changes allele frequencies by chance alone? a. Disruptive selection b. Stabilizing selection c. Genetic drift d. Both a and b 7. Which statement about genetic drift is false? a. It affects allele frequencies the most when populations are small. b. It ...
Title: The contribution of meiofauna to evolutionary ecology Authors
... to be aware of the challenges and limitations inherent to biodiversity assessments and to each methodological approach, in particular. Interdisciplinary studies face the challenges of improving sampling protocols and preservation methods in order to establish direct relationships between the differe ...
... to be aware of the challenges and limitations inherent to biodiversity assessments and to each methodological approach, in particular. Interdisciplinary studies face the challenges of improving sampling protocols and preservation methods in order to establish direct relationships between the differe ...
What is an advantage of sexual reproduction
... by good DNA of the mates. The same rejuvenation cannot work, by selfing of mating with yourself because you are more likely to have the same errors in multiple cells of your body that may have had the same parent cell. Mutations occur commonly in DNA. Evidence for this is the large amount of repair ...
... by good DNA of the mates. The same rejuvenation cannot work, by selfing of mating with yourself because you are more likely to have the same errors in multiple cells of your body that may have had the same parent cell. Mutations occur commonly in DNA. Evidence for this is the large amount of repair ...
IUCN - CMP Unified Classification of Stresses
... (usually adults) predated upon by invasive alien species (e.g., rats) Direct damage to a species. ...
... (usually adults) predated upon by invasive alien species (e.g., rats) Direct damage to a species. ...
Blue Biology Review Second Semester
... 17. Why are seeds highly nutritious? (Is it due to their oils, stored food, minerals, or calories?) 18. What feature of Darwin’s finches is an example of an adaptation that illustrates natural selection? 19. Why do population geneticists determine gene frequencies? 20. If a geneticist finds 25% of a ...
... 17. Why are seeds highly nutritious? (Is it due to their oils, stored food, minerals, or calories?) 18. What feature of Darwin’s finches is an example of an adaptation that illustrates natural selection? 19. Why do population geneticists determine gene frequencies? 20. If a geneticist finds 25% of a ...
Evolution of Populations Summary of Natural Selection
... Individual organisms differ, and some of this variation is inheritable Organisms produce more offspring than can survive thus creating a struggle for survival Organisms that are better suited survive and reproduce more than those that less suited to their ...
... Individual organisms differ, and some of this variation is inheritable Organisms produce more offspring than can survive thus creating a struggle for survival Organisms that are better suited survive and reproduce more than those that less suited to their ...
Theory of Natural Selection
... – Individuals within a species are not identical; they have variations. – These variations may affect the individual’s ability to get food, escape predators, find a mate, etc. – These variations can be passed on to offspring ...
... – Individuals within a species are not identical; they have variations. – These variations may affect the individual’s ability to get food, escape predators, find a mate, etc. – These variations can be passed on to offspring ...
4.2 Test Review File - Northwest ISD Moodle
... 11. Some organisms have genes that improve their ability to survive and reproduce. If the genes also help their offspring survive and reproduce, then what will most likely happen to the frequency of these genes in the population? ...
... 11. Some organisms have genes that improve their ability to survive and reproduce. If the genes also help their offspring survive and reproduce, then what will most likely happen to the frequency of these genes in the population? ...
Bio 120: Principles of Evolution Page 1 Exam 1 NAME
... In most populations it is polymorphic for flower color at the 'A' locus. At this locus there are two alleles, A and a. AA individuals have darkly pigmented flowers, Aa individuals have lightly pigmented flowers, and aa individuals have unpigmented, white flowers. In a recent study, equal numbers of ...
... In most populations it is polymorphic for flower color at the 'A' locus. At this locus there are two alleles, A and a. AA individuals have darkly pigmented flowers, Aa individuals have lightly pigmented flowers, and aa individuals have unpigmented, white flowers. In a recent study, equal numbers of ...
adaptations – ways living things change over generations so the
... Interdependence : How Plants and Animals Interact with and Adapt to their Environments Read chapter 1 to help answer the questions. ( Use another page if needed.) 1. What is the difference between inherited characteristics and learned behavior? Name 3 examples of each. ...
... Interdependence : How Plants and Animals Interact with and Adapt to their Environments Read chapter 1 to help answer the questions. ( Use another page if needed.) 1. What is the difference between inherited characteristics and learned behavior? Name 3 examples of each. ...
Chapter 23 Evolution of Populations
... chance fluctuations in the gene pool, genetic drift, can cause genotype frequencies to change ...
... chance fluctuations in the gene pool, genetic drift, can cause genotype frequencies to change ...
Evolution in Everyday Life - The Teacher
... can provide clues for how life will continue to evolve in the future. ...
... can provide clues for how life will continue to evolve in the future. ...
Evolution Tracing
... a common ancestor, which might Archaeopteryx look differently from both. A classic example for a transitional form is the oldest known bird, Archaeopteryx. Compared to modern reptiles and birds, this Jurassic animal shows a mosaic of characters. However, considering the fossil record, most of these ...
... a common ancestor, which might Archaeopteryx look differently from both. A classic example for a transitional form is the oldest known bird, Archaeopteryx. Compared to modern reptiles and birds, this Jurassic animal shows a mosaic of characters. However, considering the fossil record, most of these ...
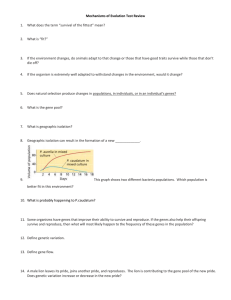
Speciation
... range. Gene flow from the other parts of the range stops, and the separated populations evolve to suit their new, restricted environment. This encourages the genetic divergence of the separated populations, and might become so great that if the two populations were rejoined they would no longer be s ...
... range. Gene flow from the other parts of the range stops, and the separated populations evolve to suit their new, restricted environment. This encourages the genetic divergence of the separated populations, and might become so great that if the two populations were rejoined they would no longer be s ...
VOCAB PRACTICE QUIZ # 10 (part 1) 2016
... 1) ______ When organisms of the same species are separated they will evolve differently 2) ______ This happens when variations that are passed on through generations will accumulate and the result is an ENTIRELY different organism. 3) ______ Alfred Russel Wallace, Herbert Spencer, Charles Darwin 4) ...
... 1) ______ When organisms of the same species are separated they will evolve differently 2) ______ This happens when variations that are passed on through generations will accumulate and the result is an ENTIRELY different organism. 3) ______ Alfred Russel Wallace, Herbert Spencer, Charles Darwin 4) ...
Name - Humble ISD
... D. As organisms ____________ and adapt, _________________ may occur. Speciation is the formation of new species - a group of similar organisms that ___________ with one another and produce __________________________________. E. The failure of an organism to _______________ to changes in its environm ...
... D. As organisms ____________ and adapt, _________________ may occur. Speciation is the formation of new species - a group of similar organisms that ___________ with one another and produce __________________________________. E. The failure of an organism to _______________ to changes in its environm ...
Evolution
... Increasing the amount of a certain gene (trait) over time due to an advantage gained from that trait. Imagine that green beetles are easier for birds to spot (and hence, eat). Brown beetles are a little more likely to survive to produce offspring. They pass their genes for brown coloration on to the ...
... Increasing the amount of a certain gene (trait) over time due to an advantage gained from that trait. Imagine that green beetles are easier for birds to spot (and hence, eat). Brown beetles are a little more likely to survive to produce offspring. They pass their genes for brown coloration on to the ...
Patterns of Evolution
... Convergent evolution is when organisms with different ancestry have similar phenotypes This occurs because of the environment the organisms live in causes similar characteristics to be fit, therefore leading to similar characteristics being passed on. Structures are usually analogous to one another ...
... Convergent evolution is when organisms with different ancestry have similar phenotypes This occurs because of the environment the organisms live in causes similar characteristics to be fit, therefore leading to similar characteristics being passed on. Structures are usually analogous to one another ...
ppt - Language Log
... geologist, Charles Lyell said the same thing to Charles Darwin in the 1840s when Darwin was working on his theory. Darwin rejected Lyell’s assertions, believing that if the geological record of earth history were complete, transitions would be found. Over 150 years later, there are still very few ex ...
... geologist, Charles Lyell said the same thing to Charles Darwin in the 1840s when Darwin was working on his theory. Darwin rejected Lyell’s assertions, believing that if the geological record of earth history were complete, transitions would be found. Over 150 years later, there are still very few ex ...
Creationism and Evolution Overviews
... The use of the Argument from Intelligent design, often in a circular way. ...
... The use of the Argument from Intelligent design, often in a circular way. ...
Koinophilia

Koinophilia is an evolutionary hypothesis concerning sexual selection which proposes that animals seeking mate preferentially choose individuals with a minimum of unusual features. Koinophilia intends to explain the clustering of organisms into species and other issues described by Darwin's Dilemma. The term derives from the Greek, koinos, ""the usual"", and philos, ""fondness"".Natural selection causes beneficial inherited features to become more common and eventually replace their disadvantageous counterparts. A sexually-reproducing animal would be expected to avoid individuals with unusual features, and to prefer to mate with individuals displaying a predominance of common or average features. This means that mates displaying mutant features are also avoided. This is advantageous because most mutations that manifest themselves as changes in appearance, functionality or behavior, are disadvantageous. Because it is impossible to judge whether a new mutation is beneficial or not, koinophilic animals avoid them all, at the cost of avoiding the occasional beneficial mutation. Thus, koinophilia, although not infallible in its ability to distinguish fit from unfit mates, is a good strategy when choosing a mate. A koinophilic choice ensures that offspring are likely to inherit features that have been successful in the past.Koinophilia differs from assortative mating, where ""like prefers like"". If like preferred like, leucistic animals (such as white peacocks) would be sexually attracted to one another, and a leucistic subspecies would come into being. Koinophilia predicts that this is unlikely because leucistic animals are attracted to the average in the same way as other animals. Since non-leucistic animals are not attracted by leucism, few leucistic individuals find mates, and leucistic lineages will rarely form.Koinophilia provides simple explanations for the rarity of speciation (in particular Darwin's Dilemma), evolutionary stasis, punctuated equilibria, and the evolution of cooperation. Koinophilia might also contribute to the maintenance of sexual reproduction, preventing its reversion to the much simpler and inherently more advantageous asexual form of reproduction.The koinophilia hypothesis is supported by research into the physical attractiveness of human faces by Judith Langlois and her co-workers. They found that the average of two human faces was more attractive than either of the faces from which that average was derived. The more faces (of the same gender and age) that were used in the averaging process the more attractive and appealing the average face became. This work into averageness supports koinophilia as an explanation of what constitutes a beautiful face, and how the individuality of a face is recognized.