Evidence of Evolution
... no longer used › Feature that was useful to an ancestor, but is no longer useful to the modern organism › Ex: ⚫ Human appendix ⚫ Whale and snake leg bones ...
... no longer used › Feature that was useful to an ancestor, but is no longer useful to the modern organism › Ex: ⚫ Human appendix ⚫ Whale and snake leg bones ...
File
... individuals in a population cultural transfer of information has the potential to alter behavioral phenotypes and, in turn, to influence the fitness of individuals in many species, mate choice is strongly influenced by social ...
... individuals in a population cultural transfer of information has the potential to alter behavioral phenotypes and, in turn, to influence the fitness of individuals in many species, mate choice is strongly influenced by social ...
What Darwin Never Knew Video Questions
... 1. Darwin went to school to study both _________ and then _________ 2. What was the most important stop on the trip? 3. What was interesting about the tortoises Darwin described? 4. The birds he collected on the islands were actually 13 different species of – 5. Darwin then realized that somehow and ...
... 1. Darwin went to school to study both _________ and then _________ 2. What was the most important stop on the trip? 3. What was interesting about the tortoises Darwin described? 4. The birds he collected on the islands were actually 13 different species of – 5. Darwin then realized that somehow and ...
Population - DigitalWebb.com
... and short limbs); direct descendants of a single couple who founded Lancaster County, Pennsylvania in 1744 ...
... and short limbs); direct descendants of a single couple who founded Lancaster County, Pennsylvania in 1744 ...
DO NOT USE MY WORDING in your answers!!!
... Explain why violating EACH of the above could cause a population to be out of equilibrium. 12. Why is mutation the least likely to cause a state of non-equilibrium (Hardy-Weinberg) within a large, sexually reproducing population? Most mutations are not beneficial, and even when they are beneficial c ...
... Explain why violating EACH of the above could cause a population to be out of equilibrium. 12. Why is mutation the least likely to cause a state of non-equilibrium (Hardy-Weinberg) within a large, sexually reproducing population? Most mutations are not beneficial, and even when they are beneficial c ...
PDF of PPT
... Both p athways force reproductive isolation between populations. Sympatric s peciation can occur through errors in meiosis that form gametes with extra chromosomes, called polyploidy. Autopolyploidy occurs within a single ...
... Both p athways force reproductive isolation between populations. Sympatric s peciation can occur through errors in meiosis that form gametes with extra chromosomes, called polyploidy. Autopolyploidy occurs within a single ...
27_3 The Process of Evolution - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... 2. Gene make-up of founders is random 3. Frequencies of certain rare alleles can be much more common in the new colony than the original population 4. E.g. polydactylism (extra fingers) and dwarfism (only affects lower arms and legs) in Amish ...
... 2. Gene make-up of founders is random 3. Frequencies of certain rare alleles can be much more common in the new colony than the original population 4. E.g. polydactylism (extra fingers) and dwarfism (only affects lower arms and legs) in Amish ...
Biology Final Review
... with each other is that they A. Have different mating behaviors B. Occupy the same niche C. Lack behavioral barriers D. Are genetically isolated 4. Farmers change the gene pool of a population by A. Artificial selection B. Adaptive radiation C. Natural selection D. Convergent evolution 5. The succes ...
... with each other is that they A. Have different mating behaviors B. Occupy the same niche C. Lack behavioral barriers D. Are genetically isolated 4. Farmers change the gene pool of a population by A. Artificial selection B. Adaptive radiation C. Natural selection D. Convergent evolution 5. The succes ...
Species Diversity ConceptsAE
... to the same category – For example, the probability of two trees, picked at random from a tropical rainforest being of the same species would be relatively low , whereas in the boreal forest would be relatively high. ...
... to the same category – For example, the probability of two trees, picked at random from a tropical rainforest being of the same species would be relatively low , whereas in the boreal forest would be relatively high. ...
Bacteria (multiple kingdoms)
... Natural selection is an editing mechanism – It results from exposure of heritable variations to environmental factors that favor some individuals over others – Over time this results in evolution of new species adapted to particular environments – Evolution is biology’s core theme and explains uni ...
... Natural selection is an editing mechanism – It results from exposure of heritable variations to environmental factors that favor some individuals over others – Over time this results in evolution of new species adapted to particular environments – Evolution is biology’s core theme and explains uni ...
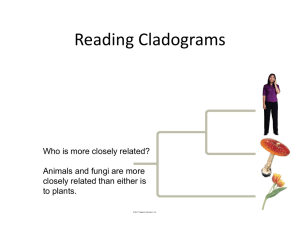
Reading Cladograms
... • Think of you + a second cousin • Who is your most recent common ancestor? • Provides a basis for assertion that you are more closely related to your first than your second cousin ...
... • Think of you + a second cousin • Who is your most recent common ancestor? • Provides a basis for assertion that you are more closely related to your first than your second cousin ...
Evolution - Newark City Schools
... Geology”. • Explained that the processes occurring now have shaped earth’s geological features over long periods of time. These processes are still changing earth today. • This idea led Darwin to realize that if the earth could change then so could life ...
... Geology”. • Explained that the processes occurring now have shaped earth’s geological features over long periods of time. These processes are still changing earth today. • This idea led Darwin to realize that if the earth could change then so could life ...
EaB 2.7 - 2011MrsHerbertYear11Biology
... When many related species evolve from a single common ancestor. This occurs as organisms spread into new habitats and evolve over millions of years, adapting to the environments they inhabit. Divergent evolution: This is a consequence of adaptive radiation and relates to the process where 2 or more ...
... When many related species evolve from a single common ancestor. This occurs as organisms spread into new habitats and evolve over millions of years, adapting to the environments they inhabit. Divergent evolution: This is a consequence of adaptive radiation and relates to the process where 2 or more ...
Evolution – Just A Theory?
... Famous for Theory of Natural Selection – In a population, naturally occurring variations affect which individuals survive and reproduce – Natural selection - the force which acts on populations, and the best adapted organisms survive – Evolution - the process by which populations change over time ...
... Famous for Theory of Natural Selection – In a population, naturally occurring variations affect which individuals survive and reproduce – Natural selection - the force which acts on populations, and the best adapted organisms survive – Evolution - the process by which populations change over time ...
Evolution & Creation - Mrs. Standish
... The most famous scientist that studied and discussed evolution is Charles Darwin. In 1831 Charles Darwin undertook a five year scientific study on the H.M.S. Beagle. He traveled to the Galapagos Islands where he discovered his greatest proof to support evolution. On the Galapagos islands Darwi ...
... The most famous scientist that studied and discussed evolution is Charles Darwin. In 1831 Charles Darwin undertook a five year scientific study on the H.M.S. Beagle. He traveled to the Galapagos Islands where he discovered his greatest proof to support evolution. On the Galapagos islands Darwi ...
File
... Students often suggest that extant species have evolved from other extant species, e.g. humans have evolved from chimps, rather than from a common ancestor. Some students will have a view of evolution based on faith – try to help them distinguish between science and religion as two separate systems. ...
... Students often suggest that extant species have evolved from other extant species, e.g. humans have evolved from chimps, rather than from a common ancestor. Some students will have a view of evolution based on faith – try to help them distinguish between science and religion as two separate systems. ...
Unit IIIA Practice Exam Unit_IIIA_Practice_Exam_2012_2
... (B) similar behavior patterns (C) interbreeding capabilities (D) polyploidy (E) similar genotypes ...
... (B) similar behavior patterns (C) interbreeding capabilities (D) polyploidy (E) similar genotypes ...
Handout
... • between different cellular components: nucleusmitochondrion • between different genetic components: genomeselfish gene ...
... • between different cellular components: nucleusmitochondrion • between different genetic components: genomeselfish gene ...
Freeman, Evolutionary Analysis 4th ed
... Darwin did not know about the principles of genetics - how variation is created and how it is inherited. Kelvin's (inaccurate) estimate of the age of the Earth also presented a problem for evolutionary theory. 14. What is blending inheritance, and why did it pose a problem for Darwin's theory? Why i ...
... Darwin did not know about the principles of genetics - how variation is created and how it is inherited. Kelvin's (inaccurate) estimate of the age of the Earth also presented a problem for evolutionary theory. 14. What is blending inheritance, and why did it pose a problem for Darwin's theory? Why i ...
lesson Plans - Lemon Bay High School
... and artificial selection on the conclusions and answer genetic makeup of a ...
... and artificial selection on the conclusions and answer genetic makeup of a ...
Four types of evolution
... evolution may be something else: creation programmed from the beginning to adapt and diversify, not a Neverland creation which, like Peter Pan, never grows old. The genetic code appears to be optimal The biological instructions that make an organism what it is, be it plant or animal, are coded in it ...
... evolution may be something else: creation programmed from the beginning to adapt and diversify, not a Neverland creation which, like Peter Pan, never grows old. The genetic code appears to be optimal The biological instructions that make an organism what it is, be it plant or animal, are coded in it ...
General Biology – Diversity of Life
... Life is extremely uniform in structure/composition: ! all life is composed of cells ! all cells are built according to same basic principles ! from same basic building blocks ...
... Life is extremely uniform in structure/composition: ! all life is composed of cells ! all cells are built according to same basic principles ! from same basic building blocks ...
Koinophilia

Koinophilia is an evolutionary hypothesis concerning sexual selection which proposes that animals seeking mate preferentially choose individuals with a minimum of unusual features. Koinophilia intends to explain the clustering of organisms into species and other issues described by Darwin's Dilemma. The term derives from the Greek, koinos, ""the usual"", and philos, ""fondness"".Natural selection causes beneficial inherited features to become more common and eventually replace their disadvantageous counterparts. A sexually-reproducing animal would be expected to avoid individuals with unusual features, and to prefer to mate with individuals displaying a predominance of common or average features. This means that mates displaying mutant features are also avoided. This is advantageous because most mutations that manifest themselves as changes in appearance, functionality or behavior, are disadvantageous. Because it is impossible to judge whether a new mutation is beneficial or not, koinophilic animals avoid them all, at the cost of avoiding the occasional beneficial mutation. Thus, koinophilia, although not infallible in its ability to distinguish fit from unfit mates, is a good strategy when choosing a mate. A koinophilic choice ensures that offspring are likely to inherit features that have been successful in the past.Koinophilia differs from assortative mating, where ""like prefers like"". If like preferred like, leucistic animals (such as white peacocks) would be sexually attracted to one another, and a leucistic subspecies would come into being. Koinophilia predicts that this is unlikely because leucistic animals are attracted to the average in the same way as other animals. Since non-leucistic animals are not attracted by leucism, few leucistic individuals find mates, and leucistic lineages will rarely form.Koinophilia provides simple explanations for the rarity of speciation (in particular Darwin's Dilemma), evolutionary stasis, punctuated equilibria, and the evolution of cooperation. Koinophilia might also contribute to the maintenance of sexual reproduction, preventing its reversion to the much simpler and inherently more advantageous asexual form of reproduction.The koinophilia hypothesis is supported by research into the physical attractiveness of human faces by Judith Langlois and her co-workers. They found that the average of two human faces was more attractive than either of the faces from which that average was derived. The more faces (of the same gender and age) that were used in the averaging process the more attractive and appealing the average face became. This work into averageness supports koinophilia as an explanation of what constitutes a beautiful face, and how the individuality of a face is recognized.