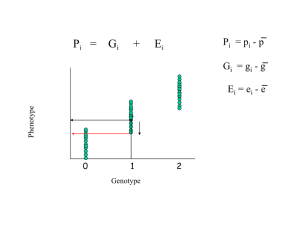User Manual of ClusterProject
... The column of Rep is indispensable whether the experiment has replication or not. If there is no replication, all values of this column are set to one. It can have additional factors in the input file such as dye, treatment or array et al. This is tab-delimited text file. Mixed model approaches are ...
... The column of Rep is indispensable whether the experiment has replication or not. If there is no replication, all values of this column are set to one. It can have additional factors in the input file such as dye, treatment or array et al. This is tab-delimited text file. Mixed model approaches are ...
design and optimisation of animal breeding programmes
... both the wild and domestic species. All animals with lethal genetic defects, for example, are naturally selected against- they never live to become parents. Natural selection cannot be ignored but the kind of selection of primary interest in animal breeding is artificial selection. The idea behind s ...
... both the wild and domestic species. All animals with lethal genetic defects, for example, are naturally selected against- they never live to become parents. Natural selection cannot be ignored but the kind of selection of primary interest in animal breeding is artificial selection. The idea behind s ...
Document
... counter-defence has been observed to change the productivity, stability and diversity of predator- ...
... counter-defence has been observed to change the productivity, stability and diversity of predator- ...
Genetics of hybrid incompatibility between Lycopersicon esculentum
... nonetheless, all species are to some degree intercrossable (Rick 1979). The two parental species analyzed here differ in several biologically significant features. L. hirsutum (Solanum habrochaites) is a wild, short-lived herbaceous, perennial species, that predominantly occurs from mid to high ele ...
... nonetheless, all species are to some degree intercrossable (Rick 1979). The two parental species analyzed here differ in several biologically significant features. L. hirsutum (Solanum habrochaites) is a wild, short-lived herbaceous, perennial species, that predominantly occurs from mid to high ele ...
Chapter 8
... Chapter 8: Meiosis and variation And the number of combinations of different alleles in these gametes is vast. We can calculate the number of different combinations of chromosomes that can be present in the gametes using the formula 2n, where n is the haploid number of chromosomes. In the example s ...
... Chapter 8: Meiosis and variation And the number of combinations of different alleles in these gametes is vast. We can calculate the number of different combinations of chromosomes that can be present in the gametes using the formula 2n, where n is the haploid number of chromosomes. In the example s ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... finches that have different beak depths. The range of beak depths is equal to the difference between the largest and smallest beaks. A. What is the average beak depth of the current finch population? ________________ B. What is the range in beak depths in the population? __________________________ C ...
... finches that have different beak depths. The range of beak depths is equal to the difference between the largest and smallest beaks. A. What is the average beak depth of the current finch population? ________________ B. What is the range in beak depths in the population? __________________________ C ...
Sexual selection can constrain sympatric speciation
... A key assumption of several of these models is that individuals have equal reproductive success, a situation we refer to as ‘non-selective mating’. Mating success in most species is highly variable, however, generating ample opportunity for sexual selection (Bateman 1998; Beeching & Hopp 1999; Harar ...
... A key assumption of several of these models is that individuals have equal reproductive success, a situation we refer to as ‘non-selective mating’. Mating success in most species is highly variable, however, generating ample opportunity for sexual selection (Bateman 1998; Beeching & Hopp 1999; Harar ...
We have, using a unique data base, successfully genotyped
... Most of the presumably recombinant haplotypes appear to be ancient crossovers that became common and not to be common because of frequent ongoing recombination. The implication is that since humans expanded out of Africa each extant copy of each of the 17 haplotypes has a history of evolving by desc ...
... Most of the presumably recombinant haplotypes appear to be ancient crossovers that became common and not to be common because of frequent ongoing recombination. The implication is that since humans expanded out of Africa each extant copy of each of the 17 haplotypes has a history of evolving by desc ...
Genetic Algorithms
... FOR population_size / 2 DO Select two parents from old generation; /* biased to the fitter ones */ Recombine parents for two offspring; Compute fitness of offspring; Insert offspring in new generation END FOR UNTIL population has converged END ...
... FOR population_size / 2 DO Select two parents from old generation; /* biased to the fitter ones */ Recombine parents for two offspring; Compute fitness of offspring; Insert offspring in new generation END FOR UNTIL population has converged END ...
Wright`s adaptive landscape versus Fisher`s fundamental theorem
... isolated populations, but also large populations, that experience fluctuations in gene ratio. If this is the case, whatever other results isolation into small communities may have, any effects which flow from fluctuating variability in the gene ratios will not be confined to such subdivided species, ...
... isolated populations, but also large populations, that experience fluctuations in gene ratio. If this is the case, whatever other results isolation into small communities may have, any effects which flow from fluctuating variability in the gene ratios will not be confined to such subdivided species, ...
Document
... CovO,P = 1/2 VA + 1/2 Cov (A,D) + 1/2 Cov (A,EP ) + Cov (A,EO ) + Cov (D,EO ) + Cov (EP,EO ) ...
... CovO,P = 1/2 VA + 1/2 Cov (A,D) + 1/2 Cov (A,EP ) + Cov (A,EO ) + Cov (D,EO ) + Cov (EP,EO ) ...
Large-Scale Variation Among Human and Great Ape Genomes
... comparative genomic hybridization (array CGH), measuring copy-number gains and losses among these species. Using an array of 2460 human bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs) (12% of the genome), we identified a total of 63 sites of putative DNA copy-number variation between humans and the great ap ...
... comparative genomic hybridization (array CGH), measuring copy-number gains and losses among these species. Using an array of 2460 human bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs) (12% of the genome), we identified a total of 63 sites of putative DNA copy-number variation between humans and the great ap ...
The Effects of a Bottleneck on Inbreeding Depression and the
... is negligible. Inbreeding depression decreases immediately after a sudden reduction of population size, but the drop is at most only several percentage points, even for severe bottlenecks. Highly recessive mutations experience a purging process that causes inbreeding depression to decline for a numb ...
... is negligible. Inbreeding depression decreases immediately after a sudden reduction of population size, but the drop is at most only several percentage points, even for severe bottlenecks. Highly recessive mutations experience a purging process that causes inbreeding depression to decline for a numb ...
NEW EVIDENCE FOR THE HOMOLOGY OF THE SHORT
... D. melanogaster, the mutation described here undoubtedly is a homologue of the phenotypically similar microchromosomal mutation Cell. The other X chromosomal mutations #960 (10-7. 1958) and #969 (10-9, 1958) were found in the progeny of X-rayed males of a wild strain from the population at Princeton ...
... D. melanogaster, the mutation described here undoubtedly is a homologue of the phenotypically similar microchromosomal mutation Cell. The other X chromosomal mutations #960 (10-7. 1958) and #969 (10-9, 1958) were found in the progeny of X-rayed males of a wild strain from the population at Princeton ...
Genetic enhancers
... developmental roles individually, which are apparent in single mutants, but that they also provide some functions redundantly, which is made evident by the synthetic lethality of the double mutant. Many examples of enhancement between mutations in homologous genes are now known, largely as a consequ ...
... developmental roles individually, which are apparent in single mutants, but that they also provide some functions redundantly, which is made evident by the synthetic lethality of the double mutant. Many examples of enhancement between mutations in homologous genes are now known, largely as a consequ ...
Hodgkin 1980
... animals are male. A procedure for isolating 2A;XO animals that are transformed into hermaphrodites has been developed. Nine mutations causing this transformation have been obtained: eight are recessive, and all of these fall into a new autosomal complementation group, her4 V. The remaining mutation ...
... animals are male. A procedure for isolating 2A;XO animals that are transformed into hermaphrodites has been developed. Nine mutations causing this transformation have been obtained: eight are recessive, and all of these fall into a new autosomal complementation group, her4 V. The remaining mutation ...
Chapter 4
... Figure 4.3 Comparative evidence for correlated evolutionary changes in SSD and several measures of sexual selection (top panels) and fecundity selection (bottom panels) in lizards. Values are ‘positivized’ independent contrast scores from phylogenetically based statistical analyses (see Cox et al. 2 ...
... Figure 4.3 Comparative evidence for correlated evolutionary changes in SSD and several measures of sexual selection (top panels) and fecundity selection (bottom panels) in lizards. Values are ‘positivized’ independent contrast scores from phylogenetically based statistical analyses (see Cox et al. 2 ...
The Diversity of Self-Incompatibility Systems in Flowering Plants
... are expressed co-dominantly in the pistil whereas in SSI systems, complex dominance interactions are possible between S alleles. In SSI, dominance interactions between S alleles can act independently in pollen and pistil and can allow successful matings to occur between individuals that share one re ...
... are expressed co-dominantly in the pistil whereas in SSI systems, complex dominance interactions are possible between S alleles. In SSI, dominance interactions between S alleles can act independently in pollen and pistil and can allow successful matings to occur between individuals that share one re ...
New Perspectives on Rickettsial Evolution from New
... A wide variety of repetitive sequence elements are found in bacteria. These range from duplicated genes which exhibit varying degrees of homology like the ATP/ADP translocase genes, proline-betaine transporters, and sca gene families in Rickettsia, to the small palindromic repeat elements which are ...
... A wide variety of repetitive sequence elements are found in bacteria. These range from duplicated genes which exhibit varying degrees of homology like the ATP/ADP translocase genes, proline-betaine transporters, and sca gene families in Rickettsia, to the small palindromic repeat elements which are ...
Chapter 26 - Phylogeny and the Tree of Life
... (b) Artist’s reconstruction of the dinosaur’s posture ...
... (b) Artist’s reconstruction of the dinosaur’s posture ...
Lesson 2 | Asexual Reproduction
... 11. Asexual reproduction also enables some organisms to rapidly produce a large number of ...
... 11. Asexual reproduction also enables some organisms to rapidly produce a large number of ...
The Power of Memes - Dr Susan Blackmore
... organisms, cannot directly justify such riches. Expressed in modern terms, this theory holds that genes control the traits of organisms; over the course of many generations, genes that give their bearers a survival advantage and that favor production of many offspring (who will inherit the genes) te ...
... organisms, cannot directly justify such riches. Expressed in modern terms, this theory holds that genes control the traits of organisms; over the course of many generations, genes that give their bearers a survival advantage and that favor production of many offspring (who will inherit the genes) te ...
Page 1 Heredity (1977), 39 (3), 373
... L, three lines selected for low bristle number; N, three lines in which I hoped to observe any effects of natural selection; and C, three control lines in which neither artificial nor natural selection would operate. The experimental lines S, L and N were set up and maintained by mating M-5 males wi ...
... L, three lines selected for low bristle number; N, three lines in which I hoped to observe any effects of natural selection; and C, three control lines in which neither artificial nor natural selection would operate. The experimental lines S, L and N were set up and maintained by mating M-5 males wi ...
Koinophilia

Koinophilia is an evolutionary hypothesis concerning sexual selection which proposes that animals seeking mate preferentially choose individuals with a minimum of unusual features. Koinophilia intends to explain the clustering of organisms into species and other issues described by Darwin's Dilemma. The term derives from the Greek, koinos, ""the usual"", and philos, ""fondness"".Natural selection causes beneficial inherited features to become more common and eventually replace their disadvantageous counterparts. A sexually-reproducing animal would be expected to avoid individuals with unusual features, and to prefer to mate with individuals displaying a predominance of common or average features. This means that mates displaying mutant features are also avoided. This is advantageous because most mutations that manifest themselves as changes in appearance, functionality or behavior, are disadvantageous. Because it is impossible to judge whether a new mutation is beneficial or not, koinophilic animals avoid them all, at the cost of avoiding the occasional beneficial mutation. Thus, koinophilia, although not infallible in its ability to distinguish fit from unfit mates, is a good strategy when choosing a mate. A koinophilic choice ensures that offspring are likely to inherit features that have been successful in the past.Koinophilia differs from assortative mating, where ""like prefers like"". If like preferred like, leucistic animals (such as white peacocks) would be sexually attracted to one another, and a leucistic subspecies would come into being. Koinophilia predicts that this is unlikely because leucistic animals are attracted to the average in the same way as other animals. Since non-leucistic animals are not attracted by leucism, few leucistic individuals find mates, and leucistic lineages will rarely form.Koinophilia provides simple explanations for the rarity of speciation (in particular Darwin's Dilemma), evolutionary stasis, punctuated equilibria, and the evolution of cooperation. Koinophilia might also contribute to the maintenance of sexual reproduction, preventing its reversion to the much simpler and inherently more advantageous asexual form of reproduction.The koinophilia hypothesis is supported by research into the physical attractiveness of human faces by Judith Langlois and her co-workers. They found that the average of two human faces was more attractive than either of the faces from which that average was derived. The more faces (of the same gender and age) that were used in the averaging process the more attractive and appealing the average face became. This work into averageness supports koinophilia as an explanation of what constitutes a beautiful face, and how the individuality of a face is recognized.