(2 pts). - nslc.wustl.edu
... c. Is there any evidence for an interaction between selection and system of mating in the contrast of part a) to part b)? 2 points. Yes, the direction of change in allele frequencies is reversed for A and for B. ...
... c. Is there any evidence for an interaction between selection and system of mating in the contrast of part a) to part b)? 2 points. Yes, the direction of change in allele frequencies is reversed for A and for B. ...
2007GenomeInformaticsGMODPoster
... genome-scale biological databases. You can use it to create a small laboratory database of genome annotations, or a large webaccessible community database. GMOD includes a modular database schema called Chado that supports many common needs. ...
... genome-scale biological databases. You can use it to create a small laboratory database of genome annotations, or a large webaccessible community database. GMOD includes a modular database schema called Chado that supports many common needs. ...
Lecture 22 Speciation
... isolation both increase with the time. • in Drosophila, it takes about 1.5 to 3 million years for complete isolation to evolve. • in marine bivalves, it may take 4 to 6 million years! 2. Among recently separated groups, prezygotic isolation is generally stronger than postzygotic isolation. ...
... isolation both increase with the time. • in Drosophila, it takes about 1.5 to 3 million years for complete isolation to evolve. • in marine bivalves, it may take 4 to 6 million years! 2. Among recently separated groups, prezygotic isolation is generally stronger than postzygotic isolation. ...
Social Behavior
... r = the probability that two alleles in two individuals are identical by descent By helping a relative--> more of “your” genes are passed to the next generation ...
... r = the probability that two alleles in two individuals are identical by descent By helping a relative--> more of “your” genes are passed to the next generation ...
6.6 Selection: Winning and Losing
... (1)individualsvary in the expressionoftheir phenotypes, and (2) this variationcauses some individuals to perform better than others.Over many generations,Darwin and Wallace argued, selection can drive large-scaleevolutionary change,allowing new adaptationsto arise.In Chapter 10,we will considerthe o ...
... (1)individualsvary in the expressionoftheir phenotypes, and (2) this variationcauses some individuals to perform better than others.Over many generations,Darwin and Wallace argued, selection can drive large-scaleevolutionary change,allowing new adaptationsto arise.In Chapter 10,we will considerthe o ...
Condition-dependent mutation rates and sexual selection
... Far from being static and inflexible, mutation rates are highly variable and responsive to selection (Baer et al., 2007). Although mutations arise in all cell types, the most important mutational events for evolution are those that occur in the germline, as these are inherited by offspring. The majo ...
... Far from being static and inflexible, mutation rates are highly variable and responsive to selection (Baer et al., 2007). Although mutations arise in all cell types, the most important mutational events for evolution are those that occur in the germline, as these are inherited by offspring. The majo ...
Reproduction of Earthworms: Sexual Selection and
... two peaks of reproduction have been observed, with the largest peak occurring in the spring and the second peak occurring in autumn (Garvı́n et al. 2003). An excellent description of the earthworm reproductive system can be found in general zoology volumes and monographs such as Jamieson (2006), so ...
... two peaks of reproduction have been observed, with the largest peak occurring in the spring and the second peak occurring in autumn (Garvı́n et al. 2003). An excellent description of the earthworm reproductive system can be found in general zoology volumes and monographs such as Jamieson (2006), so ...
The stationary distribution of a continuously varying strategy in a
... inclusive fitness effect. The exploration of the phenotypic space varies exponentially with the cumulative inclusive fitness effect over state space, which determines an adaptive landscape. The peaks of the landscapes are those phenotypes that are candidate evolutionary stable strategies and can be ...
... inclusive fitness effect. The exploration of the phenotypic space varies exponentially with the cumulative inclusive fitness effect over state space, which determines an adaptive landscape. The peaks of the landscapes are those phenotypes that are candidate evolutionary stable strategies and can be ...
PDF
... Traditional theories of social evolution in structured populations use reproductive value to describe the fitness effects of variation in helping and harming traits [1–4]. They are applied to population structures such as the two sexes [1], juveniles and adults [3], dispersers and non-dispersers [5] ...
... Traditional theories of social evolution in structured populations use reproductive value to describe the fitness effects of variation in helping and harming traits [1–4]. They are applied to population structures such as the two sexes [1], juveniles and adults [3], dispersers and non-dispersers [5] ...
Antibiotics on a plate
... role in many areas of biology. Often, it is only by taking away a gene that you can work out exactly what it does. With bacteria such as Streptomyces, a knockout mutant may have a different morphology (it may look different) to the original bacteria, so taking photos of them is useful – see Image 1. ...
... role in many areas of biology. Often, it is only by taking away a gene that you can work out exactly what it does. With bacteria such as Streptomyces, a knockout mutant may have a different morphology (it may look different) to the original bacteria, so taking photos of them is useful – see Image 1. ...
Avian genetic diversity - UC Genetic Resources Conservation Program
... hatchability, viability, disease resistance, body the extinction of the line within a few generations. This is a particular concern in lines propasize and shape, and behavioral characteristics. gated by full-sib matings which also have large To change the population mean for one or more of these qua ...
... hatchability, viability, disease resistance, body the extinction of the line within a few generations. This is a particular concern in lines propasize and shape, and behavioral characteristics. gated by full-sib matings which also have large To change the population mean for one or more of these qua ...
Genetic Wheel - cloudfront.net
... Can you see all genetic variation? (No. Although some traits are visible, others are not visible.) Why is genetic variation important? (Having genetic variation within a species makes it more likely that some members of a population will survive under changing environmental conditions. Evolution ...
... Can you see all genetic variation? (No. Although some traits are visible, others are not visible.) Why is genetic variation important? (Having genetic variation within a species makes it more likely that some members of a population will survive under changing environmental conditions. Evolution ...
Actuarial Senescence in the Wild
... complete degeneration and then there is a complete regeneration by action of host myocyte stem cells that is poorer in older animals[36].) 3. With no turnover, e.g., neurons, with a few exceptions[37], but always with metabolic dependence on gliocytes that are cells with turnover. A simple spontaneo ...
... complete degeneration and then there is a complete regeneration by action of host myocyte stem cells that is poorer in older animals[36].) 3. With no turnover, e.g., neurons, with a few exceptions[37], but always with metabolic dependence on gliocytes that are cells with turnover. A simple spontaneo ...
Drosophila Fruit Fly Culture Care, LM00045 • eNasco.com/science
... Flies to be examined need to be anesthetized. A number of very effective, commercially-prepared anesthetizers are available, along with complete instructions for their use. Homemade anethetizers are easily constructed. Ether is normally used as the anesthetizing gas. Caution should be used in the ap ...
... Flies to be examined need to be anesthetized. A number of very effective, commercially-prepared anesthetizers are available, along with complete instructions for their use. Homemade anethetizers are easily constructed. Ether is normally used as the anesthetizing gas. Caution should be used in the ap ...
Chapter 7 Darwin, Mendel and Theories of Inheritance
... • That mechanism had to explain phenotypic constancy and variation • Constancy has the evolutionary significance that all life processes depend on the transmission of information from previous generations ...
... • That mechanism had to explain phenotypic constancy and variation • Constancy has the evolutionary significance that all life processes depend on the transmission of information from previous generations ...
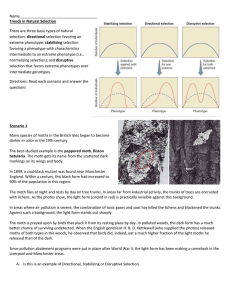
Name Trends in Natural Selection There are three basic types of
... C. With the advent of modern medical technologies and procedures, how might those babies at the “upper end and lower ends” (those with lighter and heavier birth weights) may have a higher survival rate when compared to those earlier in human history? ...
... C. With the advent of modern medical technologies and procedures, how might those babies at the “upper end and lower ends” (those with lighter and heavier birth weights) may have a higher survival rate when compared to those earlier in human history? ...
Mate Choice and Learning - DigitalCommons@University of
... While an individual’s genetic framework is a major contributor in determining its eventual mate choice, the role of the environment in further influencing mating decisions has long been recognized. Animals gather information from the environment throughout life, and in some cases, may apply this inf ...
... While an individual’s genetic framework is a major contributor in determining its eventual mate choice, the role of the environment in further influencing mating decisions has long been recognized. Animals gather information from the environment throughout life, and in some cases, may apply this inf ...
06 Life Histories 2010
... • As life history traits contribute to reproductive success, they influence evolutionary fitness. • Life histories vary consistently with environmental factors; hence may be molded by natural selection. ...
... • As life history traits contribute to reproductive success, they influence evolutionary fitness. • Life histories vary consistently with environmental factors; hence may be molded by natural selection. ...
(Phalaris, Poaceae): Molecular phylogenetics, polyploidy and floret
... species having x = 7. Species in this clade form three strongly supported lineages, which we will refer to informally as lineage 1, 2, and 3. Lineage 1 (95% BS, 1.00 PP) represents species endemic to North and South America (P. californica, P. caroliniana, P. amethystina, P. platensis, P. lemmonii) ...
... species having x = 7. Species in this clade form three strongly supported lineages, which we will refer to informally as lineage 1, 2, and 3. Lineage 1 (95% BS, 1.00 PP) represents species endemic to North and South America (P. californica, P. caroliniana, P. amethystina, P. platensis, P. lemmonii) ...
The Origin of Artificial Species: Genetic Robot
... The voice learning unit teaches the artificial creature to respond with an appropriate behavior when instructed. This is an important aspect of the interaction required between artificial creature and its master. Internally, the unit adjusts weights associating voice commands with behaviors. If the ...
... The voice learning unit teaches the artificial creature to respond with an appropriate behavior when instructed. This is an important aspect of the interaction required between artificial creature and its master. Internally, the unit adjusts weights associating voice commands with behaviors. If the ...
Oviparity or viviparity? That is the question…
... fertilized eggs’’ and viviparity is defined as ‘‘any mechanism for live-bearing or maintenance of development, by either maternal or paternal parent in or on any part of the body’’, while ovoviviparity straddles both modes [15]. In fact, this classification of different modes of reproduction into th ...
... fertilized eggs’’ and viviparity is defined as ‘‘any mechanism for live-bearing or maintenance of development, by either maternal or paternal parent in or on any part of the body’’, while ovoviviparity straddles both modes [15]. In fact, this classification of different modes of reproduction into th ...
Lecture 10 Population Genetics
... competition to survive and reproduce and that this was governed by a process he called natural selection That any being, if it vary however slightly, in any manner profitable to itself………will have a better chance of surviving This implies a better chance of reproducing – leaving offspring If the var ...
... competition to survive and reproduce and that this was governed by a process he called natural selection That any being, if it vary however slightly, in any manner profitable to itself………will have a better chance of surviving This implies a better chance of reproducing – leaving offspring If the var ...
The Role of the HOW Gene in Morphogenesis in Drosophila
... how Gene The how gene found in Drosophila melanogaster encodes a KH RNA binding protein, and is involved in processes such as muscle development. There are different how mutant alleles, some stronger than others. Example: howe44 and howstruthio are strong mutant alleles that results in embryonic de ...
... how Gene The how gene found in Drosophila melanogaster encodes a KH RNA binding protein, and is involved in processes such as muscle development. There are different how mutant alleles, some stronger than others. Example: howe44 and howstruthio are strong mutant alleles that results in embryonic de ...
Markscheme
... Award [1 max] if the correct order is reversed horizontally (ie from cat on the left to Amoeba on the right). ...
... Award [1 max] if the correct order is reversed horizontally (ie from cat on the left to Amoeba on the right). ...
Koinophilia

Koinophilia is an evolutionary hypothesis concerning sexual selection which proposes that animals seeking mate preferentially choose individuals with a minimum of unusual features. Koinophilia intends to explain the clustering of organisms into species and other issues described by Darwin's Dilemma. The term derives from the Greek, koinos, ""the usual"", and philos, ""fondness"".Natural selection causes beneficial inherited features to become more common and eventually replace their disadvantageous counterparts. A sexually-reproducing animal would be expected to avoid individuals with unusual features, and to prefer to mate with individuals displaying a predominance of common or average features. This means that mates displaying mutant features are also avoided. This is advantageous because most mutations that manifest themselves as changes in appearance, functionality or behavior, are disadvantageous. Because it is impossible to judge whether a new mutation is beneficial or not, koinophilic animals avoid them all, at the cost of avoiding the occasional beneficial mutation. Thus, koinophilia, although not infallible in its ability to distinguish fit from unfit mates, is a good strategy when choosing a mate. A koinophilic choice ensures that offspring are likely to inherit features that have been successful in the past.Koinophilia differs from assortative mating, where ""like prefers like"". If like preferred like, leucistic animals (such as white peacocks) would be sexually attracted to one another, and a leucistic subspecies would come into being. Koinophilia predicts that this is unlikely because leucistic animals are attracted to the average in the same way as other animals. Since non-leucistic animals are not attracted by leucism, few leucistic individuals find mates, and leucistic lineages will rarely form.Koinophilia provides simple explanations for the rarity of speciation (in particular Darwin's Dilemma), evolutionary stasis, punctuated equilibria, and the evolution of cooperation. Koinophilia might also contribute to the maintenance of sexual reproduction, preventing its reversion to the much simpler and inherently more advantageous asexual form of reproduction.The koinophilia hypothesis is supported by research into the physical attractiveness of human faces by Judith Langlois and her co-workers. They found that the average of two human faces was more attractive than either of the faces from which that average was derived. The more faces (of the same gender and age) that were used in the averaging process the more attractive and appealing the average face became. This work into averageness supports koinophilia as an explanation of what constitutes a beautiful face, and how the individuality of a face is recognized.