Mating Systems 1 Mating According to Index Values
... effects). Inbreeding is a way to ’fix’ an allele in a population, so that all animals are homozygous for this allele, and therefore, all progeny receive this allele - which is hopefully beneficial to the population. In the process of ’fixing’ an allele, other alleles may also become ’fixed’ which ma ...
... effects). Inbreeding is a way to ’fix’ an allele in a population, so that all animals are homozygous for this allele, and therefore, all progeny receive this allele - which is hopefully beneficial to the population. In the process of ’fixing’ an allele, other alleles may also become ’fixed’ which ma ...
Establishment of a screening service for BM and UCMD
... • Initial cohort: 16 patients • 14 have definite pathogenic mutations • 87.5% pick-up (previous studies: 62%) • Why so high? – Patient selection • Phenotype screened by Hammersmith • Immunohistochemical analysis ...
... • Initial cohort: 16 patients • 14 have definite pathogenic mutations • 87.5% pick-up (previous studies: 62%) • Why so high? – Patient selection • Phenotype screened by Hammersmith • Immunohistochemical analysis ...
1 Epistasis Underlying a Fitness Trait within a Natural
... These results are consistent with Hard et al.'s (1992, 1993) assumption that there existed within ancestral populations the epistatic genetic variance from which additive genetic variance could have been released during successive, sequential founder events in the northward dispersal of W. smithii f ...
... These results are consistent with Hard et al.'s (1992, 1993) assumption that there existed within ancestral populations the epistatic genetic variance from which additive genetic variance could have been released during successive, sequential founder events in the northward dispersal of W. smithii f ...
Linking stress coping styles with the brain gene expression across
... Iden+fica+on of Target mRNAs: Common mRNA transcripts differen0ally expressed in zebrafish screened for coping styles (Rey et al. 2013) were used to iden0fy target genes in the other three species studied in ...
... Iden+fica+on of Target mRNAs: Common mRNA transcripts differen0ally expressed in zebrafish screened for coping styles (Rey et al. 2013) were used to iden0fy target genes in the other three species studied in ...
GENETIC COUNSELLING IN PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCY
... the phenotypic spectrum of these disorders varies considerably. Investigators have found great variability in the effects of different mutations, as well as the effects other genetic, epigenetic and environmental factors have in modifying the disease phenotype. The role of environmental agents on th ...
... the phenotypic spectrum of these disorders varies considerably. Investigators have found great variability in the effects of different mutations, as well as the effects other genetic, epigenetic and environmental factors have in modifying the disease phenotype. The role of environmental agents on th ...
Generic Chromosome Representation and Evaluation for Genetic
... – Create a starting population. Usually a set of random chromosomes are created. – Repeat the following until some termination criterion is met: • Evaluate each chromosome using a fitness function. • Select pairs of chromosomes using some scheme such as random selection or fitness-biased methods. • ...
... – Create a starting population. Usually a set of random chromosomes are created. – Repeat the following until some termination criterion is met: • Evaluate each chromosome using a fitness function. • Select pairs of chromosomes using some scheme such as random selection or fitness-biased methods. • ...
Genetic Art - Northwestern University
... repeatedly doing the following: Find each expression’s fitness. Use the fitness to select expressions for reproduction Apply genetic operators to selected expressions to create new expressions. ...
... repeatedly doing the following: Find each expression’s fitness. Use the fitness to select expressions for reproduction Apply genetic operators to selected expressions to create new expressions. ...
Marks 2002
... data is easy to compile, and attests to the simple fact that bio-history is just as difficult to infer from genetic as from anatomical data; there is just no substitute for ratiocination. And very likely our models of evolution need to become a bit more sophisticated than the simple bifurcations usu ...
... data is easy to compile, and attests to the simple fact that bio-history is just as difficult to infer from genetic as from anatomical data; there is just no substitute for ratiocination. And very likely our models of evolution need to become a bit more sophisticated than the simple bifurcations usu ...
Ethical Issues in Genetic Testing: the Duty to Warn At
... • Pate, 1994; Safer, 1996: judgements against physicians who did not warn family – what satisfies ‘warned’? ...
... • Pate, 1994; Safer, 1996: judgements against physicians who did not warn family – what satisfies ‘warned’? ...
MGA 2e Chapter 17
... eliminate the gene product, or change the ratio of it to all other gene products. All three outcomes upset a previously balanced system. While a new and “better” balance may be achieved, this is less likely than being deleterious. 14. Wild-type alleles are usually dominant because most mutations res ...
... eliminate the gene product, or change the ratio of it to all other gene products. All three outcomes upset a previously balanced system. While a new and “better” balance may be achieved, this is less likely than being deleterious. 14. Wild-type alleles are usually dominant because most mutations res ...
Biodiversity: Conservation and Utilization of Oman`s Genetic
... To look at the National priorities on biodiversity conservation Identify areas of gaps and look at ways to fill those gaps Work on strengthening existing centers Bring about coordination of APGR activities amongst the stakeholders There is a need to have a board of directors at a high level The cent ...
... To look at the National priorities on biodiversity conservation Identify areas of gaps and look at ways to fill those gaps Work on strengthening existing centers Bring about coordination of APGR activities amongst the stakeholders There is a need to have a board of directors at a high level The cent ...
Inheritance - PGS Science
... A sample of seeds were exposed to radiation. Some seeds then had more than the normal number of chromosomes and grew into plants which gave higher yields. Example 2 A new variety of tomato is produced by crossing suitable parent plants. The new variety has tomatoes that are yellow in colour and much ...
... A sample of seeds were exposed to radiation. Some seeds then had more than the normal number of chromosomes and grew into plants which gave higher yields. Example 2 A new variety of tomato is produced by crossing suitable parent plants. The new variety has tomatoes that are yellow in colour and much ...
popgen2c1 - eweb.furman.edu
... 1. Historically, all phenotypic variation was interpreted as adaptive. - many studies confirmed that under one environmental condition or another, there was a difference in fitness among variations. - Mayr (1963) "it is altogether unlikely that two genes would have identical selective value under al ...
... 1. Historically, all phenotypic variation was interpreted as adaptive. - many studies confirmed that under one environmental condition or another, there was a difference in fitness among variations. - Mayr (1963) "it is altogether unlikely that two genes would have identical selective value under al ...
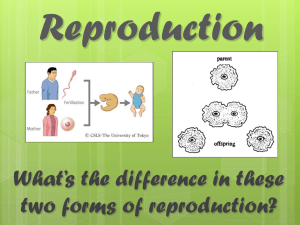
Asexual & Sexual Reproduction
... Sexual Reproduction Type of reproduction in which two parent cells (male and female reproductive cells) combine to form offspring with genetic material from both cells. ...
... Sexual Reproduction Type of reproduction in which two parent cells (male and female reproductive cells) combine to form offspring with genetic material from both cells. ...
mutations
... Harmful and Helpful Mutations The effects of mutations on genes vary widely. Some have little or no effect; and some produce beneficial variations. Some negatively disrupt gene function. Whether a mutation is negative or beneficial depends on how its DNA changes relative to the organism’s situation. ...
... Harmful and Helpful Mutations The effects of mutations on genes vary widely. Some have little or no effect; and some produce beneficial variations. Some negatively disrupt gene function. Whether a mutation is negative or beneficial depends on how its DNA changes relative to the organism’s situation. ...
06 Life Histories 2009
... • As life history traits contribute to reproductive success, they influence evolutionary fitness. • Life histories vary consistently with environmental factors; hence may be molded by natural selection. ...
... • As life history traits contribute to reproductive success, they influence evolutionary fitness. • Life histories vary consistently with environmental factors; hence may be molded by natural selection. ...
Genetic Techniques for Biological Research Chapter4
... The first step in a genetic analysis of a process it to isolate mutant individuals that areunable to carry outthat process orcarry it out in anaberrant way. The researcher must hypothesize what characteristics, changes in growth capabilities, morphology, etc. will be exhibited by this individual and ...
... The first step in a genetic analysis of a process it to isolate mutant individuals that areunable to carry outthat process orcarry it out in anaberrant way. The researcher must hypothesize what characteristics, changes in growth capabilities, morphology, etc. will be exhibited by this individual and ...
Neutral Theory
... Abundant genetic variation exists, but perhaps not driven by balancing or diversifying selection: selectionists find a new foe: Neutralists! Neutral Theory (1968): most genetic mutations are neutral with respect to each other Deleterious mutations quickly eliminated Advantageous mutations ex ...
... Abundant genetic variation exists, but perhaps not driven by balancing or diversifying selection: selectionists find a new foe: Neutralists! Neutral Theory (1968): most genetic mutations are neutral with respect to each other Deleterious mutations quickly eliminated Advantageous mutations ex ...
Introduction to Genetic Algorithms
... a set of feasible solutions Introduction to Genetic Algorithms ...
... a set of feasible solutions Introduction to Genetic Algorithms ...
Realized Heritability
... Then the progeny from the selected subpopulations are counted for hairs and averaged. The difference between average number of hairs from the original population, Generation 0 and the average of Generation 1 is known as the response to selection. The inherited change in the population due to the 10 ...
... Then the progeny from the selected subpopulations are counted for hairs and averaged. The difference between average number of hairs from the original population, Generation 0 and the average of Generation 1 is known as the response to selection. The inherited change in the population due to the 10 ...
Assessing natural variation in genes affecting Drosophila lifespan
... histone deacetylase rpd 3 have been found to prolong adult lifespan in Drosophila (Helfand and Rogina, 2003). Yet, despite the rapidly expanding list of candidate genes for aging, molecular genetic analyses are not informative about whether standing genetic variation at these loci contributes to phe ...
... histone deacetylase rpd 3 have been found to prolong adult lifespan in Drosophila (Helfand and Rogina, 2003). Yet, despite the rapidly expanding list of candidate genes for aging, molecular genetic analyses are not informative about whether standing genetic variation at these loci contributes to phe ...
Koinophilia

Koinophilia is an evolutionary hypothesis concerning sexual selection which proposes that animals seeking mate preferentially choose individuals with a minimum of unusual features. Koinophilia intends to explain the clustering of organisms into species and other issues described by Darwin's Dilemma. The term derives from the Greek, koinos, ""the usual"", and philos, ""fondness"".Natural selection causes beneficial inherited features to become more common and eventually replace their disadvantageous counterparts. A sexually-reproducing animal would be expected to avoid individuals with unusual features, and to prefer to mate with individuals displaying a predominance of common or average features. This means that mates displaying mutant features are also avoided. This is advantageous because most mutations that manifest themselves as changes in appearance, functionality or behavior, are disadvantageous. Because it is impossible to judge whether a new mutation is beneficial or not, koinophilic animals avoid them all, at the cost of avoiding the occasional beneficial mutation. Thus, koinophilia, although not infallible in its ability to distinguish fit from unfit mates, is a good strategy when choosing a mate. A koinophilic choice ensures that offspring are likely to inherit features that have been successful in the past.Koinophilia differs from assortative mating, where ""like prefers like"". If like preferred like, leucistic animals (such as white peacocks) would be sexually attracted to one another, and a leucistic subspecies would come into being. Koinophilia predicts that this is unlikely because leucistic animals are attracted to the average in the same way as other animals. Since non-leucistic animals are not attracted by leucism, few leucistic individuals find mates, and leucistic lineages will rarely form.Koinophilia provides simple explanations for the rarity of speciation (in particular Darwin's Dilemma), evolutionary stasis, punctuated equilibria, and the evolution of cooperation. Koinophilia might also contribute to the maintenance of sexual reproduction, preventing its reversion to the much simpler and inherently more advantageous asexual form of reproduction.The koinophilia hypothesis is supported by research into the physical attractiveness of human faces by Judith Langlois and her co-workers. They found that the average of two human faces was more attractive than either of the faces from which that average was derived. The more faces (of the same gender and age) that were used in the averaging process the more attractive and appealing the average face became. This work into averageness supports koinophilia as an explanation of what constitutes a beautiful face, and how the individuality of a face is recognized.