Chapter 11
... • The circum-Pacific and the EurasianMelanesian mountain belts are both located along convergent plate boundaries. • Scientists think that the location of these two mountain belts provides evidence that most mountains form as a result of collisions between tectonic plates. ...
... • The circum-Pacific and the EurasianMelanesian mountain belts are both located along convergent plate boundaries. • Scientists think that the location of these two mountain belts provides evidence that most mountains form as a result of collisions between tectonic plates. ...
Plate Tectonics Crust Tab
... - Describe the differences between oceanic and continental crust. - Predict how changes in the temperature and composition of the crust (what it is made of) change the buoyancy of the crust (how easily ...
... - Describe the differences between oceanic and continental crust. - Predict how changes in the temperature and composition of the crust (what it is made of) change the buoyancy of the crust (how easily ...
Name: Section: Date: Plate Tectonics Learning Goals:
... - Describe the differences between oceanic and continental crust. - Predict how changes in the temperature and composition of the crust (what it is made of) change the buoyancy of the crust (how easily it “floats”). - Predict tectonic movement based on the characteristics of each plate. ____________ ...
... - Describe the differences between oceanic and continental crust. - Predict how changes in the temperature and composition of the crust (what it is made of) change the buoyancy of the crust (how easily it “floats”). - Predict tectonic movement based on the characteristics of each plate. ____________ ...
ch13
... Subduction Process in which one converging plate is forced beneath another, usu. oceanic plate under continental ...
... Subduction Process in which one converging plate is forced beneath another, usu. oceanic plate under continental ...
Plate Tectonics
... is the Earth’s lithosphere made up of? Where can a volcano form? What plate are the Hawaiian Islands on? Are they at a plate boundary or a hot spot? What is a hot spot? Does a hot spot move? So what is moving? How many islands has this hot spot formed to make the Hawaiian Island chain? ...
... is the Earth’s lithosphere made up of? Where can a volcano form? What plate are the Hawaiian Islands on? Are they at a plate boundary or a hot spot? What is a hot spot? Does a hot spot move? So what is moving? How many islands has this hot spot formed to make the Hawaiian Island chain? ...
Igneous Rock Associations 8. Arc Magmatism II: Geo
... those that are in equilibrium with mantle rocks, suggesting that even the most primitive arc magmas are fractionated to some degree and that true primary magmas (i.e. melts directly derived from the mantle) are rare. Mineral compositions are also susceptible to the tectonic environment in which they ...
... those that are in equilibrium with mantle rocks, suggesting that even the most primitive arc magmas are fractionated to some degree and that true primary magmas (i.e. melts directly derived from the mantle) are rare. Mineral compositions are also susceptible to the tectonic environment in which they ...
Objective: 1) TSW compare and contrast the composition of the
... 1. What is Continental Drift? 2. What is Pangaea? **draw a diagram on the board with convection on bottom** Set: (5 min) What is this a picture of? (A: The earth cut in half). What are the layers of the Earth? Which layer holds the continents that we live on? Which layer is broken into tectonic plat ...
... 1. What is Continental Drift? 2. What is Pangaea? **draw a diagram on the board with convection on bottom** Set: (5 min) What is this a picture of? (A: The earth cut in half). What are the layers of the Earth? Which layer holds the continents that we live on? Which layer is broken into tectonic plat ...
Climate change - ACT Government
... opportunities to understand and learn about: scientific aspects of their everyday activities and applications of science in their own lives (e.g. uses of energy in the home, ball games, pet care, decisions influenced by weather) and the place of science in the work of people in the community som ...
... opportunities to understand and learn about: scientific aspects of their everyday activities and applications of science in their own lives (e.g. uses of energy in the home, ball games, pet care, decisions influenced by weather) and the place of science in the work of people in the community som ...
How do we predict Weather and Climate?
... falls back to Earth on a parachute. So from one ‘launch’ we collect very detailed information both going up and coming down. It normally takes about an hour to reach burst height with observations coming every few seconds, so there is a lot of data. The top of the ascent usually is up to 20km or so ...
... falls back to Earth on a parachute. So from one ‘launch’ we collect very detailed information both going up and coming down. It normally takes about an hour to reach burst height with observations coming every few seconds, so there is a lot of data. The top of the ascent usually is up to 20km or so ...
ODP Greatest Hits
... Photo courtesy of Keir Becker. gas (methane) are frozen within deep-sea marine sediments as gas hydrates and now we’ve discovered that there is enough locked ...
... Photo courtesy of Keir Becker. gas (methane) are frozen within deep-sea marine sediments as gas hydrates and now we’ve discovered that there is enough locked ...
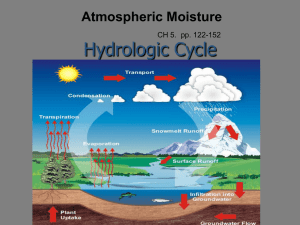
Lecture:Moisture
... <=49........................”Feels like the west”, very pleasant, feels a bit dry to some ...
... <=49........................”Feels like the west”, very pleasant, feels a bit dry to some ...
Sea Floor Spreading
... In some cases, oceanic crust encounters an active plate margin. An active plate margin is an actual plate boundary, where oceanic crust and continental crust crash into each other. Active plate margins are often the site of earthquakes and volcanoes. Oceanic crust created by seafloor spreading in th ...
... In some cases, oceanic crust encounters an active plate margin. An active plate margin is an actual plate boundary, where oceanic crust and continental crust crash into each other. Active plate margins are often the site of earthquakes and volcanoes. Oceanic crust created by seafloor spreading in th ...
Weather and Climate - Lunar and Planetary Institute
... (10) Earth and space. The student knows that climatic interactions exist among Earth, ocean, and weather systems. The student is expected to: (A) recognize that the Sun provides the energy that drives convection within the atmosphere and oceans, producing winds and ocean currents; (B) identify how g ...
... (10) Earth and space. The student knows that climatic interactions exist among Earth, ocean, and weather systems. The student is expected to: (A) recognize that the Sun provides the energy that drives convection within the atmosphere and oceans, producing winds and ocean currents; (B) identify how g ...
Reading
... carrying continental crust, subduction occurs. Ocean crust, which is denser than continental crust, sinks beneath the continental crust forming a deep ocean trench. As the trench is formed, the oceanic crust is forced back into the mantle. As the rock material in the ocean crust begins to melt in th ...
... carrying continental crust, subduction occurs. Ocean crust, which is denser than continental crust, sinks beneath the continental crust forming a deep ocean trench. As the trench is formed, the oceanic crust is forced back into the mantle. As the rock material in the ocean crust begins to melt in th ...
7.2
... These new topographic maps showed large mountain ranges that stretched for many miles along the seafloor. The mountain ranges in the middle of the oceans are called mid-ocean ridges. Mid-ocean ridges, shown in the figure below, are much longer than any mountain range on land. ...
... These new topographic maps showed large mountain ranges that stretched for many miles along the seafloor. The mountain ranges in the middle of the oceans are called mid-ocean ridges. Mid-ocean ridges, shown in the figure below, are much longer than any mountain range on land. ...
Build a Barometer Grade 2
... A barometer measures atmospheric pressure. The air in the atmosphere exerts a force called pressure that constantly changes due to moving weather systems. Therefore, in conjunction with other meteorological instruments, a barometer helps to predict clear or rainy weather. In 1643, Evangelista Torric ...
... A barometer measures atmospheric pressure. The air in the atmosphere exerts a force called pressure that constantly changes due to moving weather systems. Therefore, in conjunction with other meteorological instruments, a barometer helps to predict clear or rainy weather. In 1643, Evangelista Torric ...
volcanic and metallogenic evolution of the momchilgrad depression
... The volcanic activity in the Momchilgrad depression took place in shallow marine basin as the volcanic cones are islands. Coral reefs often grew up around them as well as along the periphery of the basin. The tuffs of the Beli Plast rhyodacite and Perperek trachyrhyolite complexes deposited chiefly ...
... The volcanic activity in the Momchilgrad depression took place in shallow marine basin as the volcanic cones are islands. Coral reefs often grew up around them as well as along the periphery of the basin. The tuffs of the Beli Plast rhyodacite and Perperek trachyrhyolite complexes deposited chiefly ...
Kyle S
... many earthquake zones. Such as Redoubt, a volcano that erupted in the same area where most earthquakes have occurred. Lastly, for my final answer, I hypothesized that earthquakes occur when tectonic plates move. After reviewing all the data that I have been working on for the last few weeks, I was c ...
... many earthquake zones. Such as Redoubt, a volcano that erupted in the same area where most earthquakes have occurred. Lastly, for my final answer, I hypothesized that earthquakes occur when tectonic plates move. After reviewing all the data that I have been working on for the last few weeks, I was c ...
Chapter 1 - Beck-Shop
... Moho averages 5–7 km. Under some oceanic islands, its thickness reaches 18 km. The elevated density and small thickness of oceanic crust cause it to be less buoyant than continental crust, so that it occupies areas of lower elevation on Earth’s surface. As a result, most oceanic crust of normal thic ...
... Moho averages 5–7 km. Under some oceanic islands, its thickness reaches 18 km. The elevated density and small thickness of oceanic crust cause it to be less buoyant than continental crust, so that it occupies areas of lower elevation on Earth’s surface. As a result, most oceanic crust of normal thic ...
Tectonic–climatic interaction

Tectonic–climatic interaction is the interrelationship between tectonic processes and the climate system. The tectonic processes in question include orogenesis, volcanism, and erosion, while relevant climatic processes include atmospheric circulation, orographic lift, monsoon circulation and the rain shadow effect. As the geological record of past climate changes over millions of years is sparse and poorly resolved, many questions remain unresolved regarding the nature of tectonic-climate interaction, although it is an area of active research by geologists and palaeoclimatologists.