Chapter 14 - AC Reynolds High
... 14-2 How Are the Earth’s Rocks Recycled? • Concept 14-2 The three major types of rocks found in the earth’s crust—sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic—are recycled very slowly by the process of erosion, melting, and metamorphism. ...
... 14-2 How Are the Earth’s Rocks Recycled? • Concept 14-2 The three major types of rocks found in the earth’s crust—sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic—are recycled very slowly by the process of erosion, melting, and metamorphism. ...
Chapter 20: The Earth Through Time
... Heating would cause the Earth that had been covered largely by continental crust to expand and then the continental crust would crack into fragments. As expansion continued, the cracks would grow into ocean basins and basaltic magma from the mantle would rise through the cracks to form the oceanic c ...
... Heating would cause the Earth that had been covered largely by continental crust to expand and then the continental crust would crack into fragments. As expansion continued, the cracks would grow into ocean basins and basaltic magma from the mantle would rise through the cracks to form the oceanic c ...
Intro to Plate Tectonics
... pushed into the earth's interior by colliding plates and being re-melted at the same rate new crust is formed. This happens at a convergent boundary. A convergent boundary is a boundary where two separate plates are pushing into each other. There are two kinds of surface features that are associate ...
... pushed into the earth's interior by colliding plates and being re-melted at the same rate new crust is formed. This happens at a convergent boundary. A convergent boundary is a boundary where two separate plates are pushing into each other. There are two kinds of surface features that are associate ...
Lecture 10
... How can plate tectonics help in earthquake prediction? We have seen that earthquakes occur at the following three kinds of plate boundary: ocean ridges where the plates are pulled apart, margins where the plates scrape past one another, and margins where one plate is thrust under the other. Thus, ...
... How can plate tectonics help in earthquake prediction? We have seen that earthquakes occur at the following three kinds of plate boundary: ocean ridges where the plates are pulled apart, margins where the plates scrape past one another, and margins where one plate is thrust under the other. Thus, ...
Section 2 - Burnet Middle School
... waves hit. Later, rescue workers and investigators were surprised to find very few dead animals among the devastation. Scientists speculate that animals can hear, smell, and feel subtle environmental changes that serve as warnings to flee. ...
... waves hit. Later, rescue workers and investigators were surprised to find very few dead animals among the devastation. Scientists speculate that animals can hear, smell, and feel subtle environmental changes that serve as warnings to flee. ...
Project-Based Inquiry Science: Ever
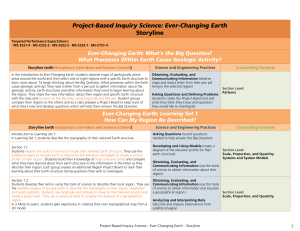
... Storyline (with Disciplinary Core Ideas) Introduction to Learning Set 3: Students look for patterns across geologically active regions and make predictions about the Earth’s plates. Section 3.1: Students simulate the movement of the Earth plates by pushing, pulling and sliding blocks of clay. They c ...
... Storyline (with Disciplinary Core Ideas) Introduction to Learning Set 3: Students look for patterns across geologically active regions and make predictions about the Earth’s plates. Section 3.1: Students simulate the movement of the Earth plates by pushing, pulling and sliding blocks of clay. They c ...
Chapter 8 Volcanoes Section 1, Why Volcanoes Form
... • A volcano is a vent or fissure in Earth’s surface through which melted rock and gases pass. • An estimated 1,500 volcanoes have been active above sea level during the past 10,000 years. • Many more volcanoes have been active beneath the ocean. ...
... • A volcano is a vent or fissure in Earth’s surface through which melted rock and gases pass. • An estimated 1,500 volcanoes have been active above sea level during the past 10,000 years. • Many more volcanoes have been active beneath the ocean. ...
Layers of the Earth (Density`s affect on Earth)
... A. The Oceans, Lakes, Glaciers, and clouds on top of the earth’s crust. B. The average density is 1 g/ml. ...
... A. The Oceans, Lakes, Glaciers, and clouds on top of the earth’s crust. B. The average density is 1 g/ml. ...
AICE Env Day 5 Evidence of Plate Tectonics Stations
... underwater objects and then records the echoes of these sound waves. The mid-ocean ridges curve along the sea floor, extending into all of Earth’s oceans. Most of the mountains in the mid-ocean ridges lie hidden under hundreds of meters of water. A steep-sided valley splits the top of some mid-ocean ...
... underwater objects and then records the echoes of these sound waves. The mid-ocean ridges curve along the sea floor, extending into all of Earth’s oceans. Most of the mountains in the mid-ocean ridges lie hidden under hundreds of meters of water. A steep-sided valley splits the top of some mid-ocean ...
science - Alpine School District
... Research locations where fossils are found in Utah and construct a simple fossil map. Objective 2: Explain how fossils can be used to make inferences about past life, climate, geology, and environments. a. Explain why fossils are usually found in sedimentary rock. b. Based on the fossils found in va ...
... Research locations where fossils are found in Utah and construct a simple fossil map. Objective 2: Explain how fossils can be used to make inferences about past life, climate, geology, and environments. a. Explain why fossils are usually found in sedimentary rock. b. Based on the fossils found in va ...
Overview Plate Tectonics
... 7. Rocks on the seafloor are much older than many continental rocks. 8. When plates collide, the denser plate will ride over the less-dense plate. 9. Earth’s magnetic field has always run from the north pole to the south pole. 10. The magnetic alignment in rocks on the ocean floor always runs from t ...
... 7. Rocks on the seafloor are much older than many continental rocks. 8. When plates collide, the denser plate will ride over the less-dense plate. 9. Earth’s magnetic field has always run from the north pole to the south pole. 10. The magnetic alignment in rocks on the ocean floor always runs from t ...
Dynamic Planet Test
... 19. Why are Bouguer anomalies (elevation-corrected gravity anomalies) negative in mountains? (2 points) ...
... 19. Why are Bouguer anomalies (elevation-corrected gravity anomalies) negative in mountains? (2 points) ...
Dynamic Planet Test 1. Label the plates on the map: (1 point each) A
... 19. Why are Bouguer anomalies (elevation-corrected gravity anomalies) negative in mountains? (2 points) ...
... 19. Why are Bouguer anomalies (elevation-corrected gravity anomalies) negative in mountains? (2 points) ...
The velocity structure of the Earth Nomenclature
... Using the arrival times of all these phases at stations around the globe we can calculate a 1D average velocity model for the Earth Uppermost mantle low-velocity zone Transition zone: 410-660 km Earthquakes stop at ~660km ...
... Using the arrival times of all these phases at stations around the globe we can calculate a 1D average velocity model for the Earth Uppermost mantle low-velocity zone Transition zone: 410-660 km Earthquakes stop at ~660km ...
Document
... Why is the river Sr isotope value the highest? Why is the hydrothermal Sr isotope value the lowest? Why is carbonate recrystallization Sr isotope value equal to that of seawater? ...
... Why is the river Sr isotope value the highest? Why is the hydrothermal Sr isotope value the lowest? Why is carbonate recrystallization Sr isotope value equal to that of seawater? ...
A Landforms Adventure
... We cross the Mississippi River on the way to the Great Plains. A plain is a large, flat area without many trees. The Great Plains formed when two plates smashed into each other and joined together. Some parts of the Great Plains are flat, and others have hills. ...
... We cross the Mississippi River on the way to the Great Plains. A plain is a large, flat area without many trees. The Great Plains formed when two plates smashed into each other and joined together. Some parts of the Great Plains are flat, and others have hills. ...
Name: ______ Date: Chapter 8 How Earth Changes Over Time
... causing the fine particles to ___squeeze____ together and harden into solid rock. Larger pieces of sediment become stuck, or ___cemented_____ together, as ___dissolved______ minerals form a kind of glue that holds the sediment together. Sedimentary rocks can also form when mineral crystals are l ...
... causing the fine particles to ___squeeze____ together and harden into solid rock. Larger pieces of sediment become stuck, or ___cemented_____ together, as ___dissolved______ minerals form a kind of glue that holds the sediment together. Sedimentary rocks can also form when mineral crystals are l ...
History of geology

The history of geology is concerned with the development of the natural science of geology. Geology is the scientific study of the origin, history, and structure of the Earth. Throughout the ages geology provides essential theories and data that shape how society conceptualizes the Earth.