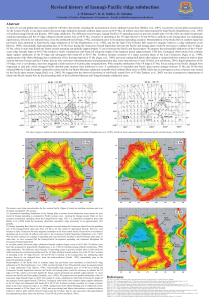
Revised history of Izanagi-Pacific ridge subduction
... rate of the Izanagi-Pacific plate pair from 118 Ma to 83 Ma cannot be determined directly. However, Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous M-series magnetic anomalies in the west-central Pacific Ocean show no variation in spreading rate for at least 10 million years prior to the Cretaceous Normal Superch ...
... rate of the Izanagi-Pacific plate pair from 118 Ma to 83 Ma cannot be determined directly. However, Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous M-series magnetic anomalies in the west-central Pacific Ocean show no variation in spreading rate for at least 10 million years prior to the Cretaceous Normal Superch ...
Jeopardy Sem. 1 Review
... The type of collision that occurs when two lithospheric plates converge is determined primarily by this characteristic of plates ...
... The type of collision that occurs when two lithospheric plates converge is determined primarily by this characteristic of plates ...
New insights into the subducting oceanic crust in the Middle
... the result of faulting (near-vertical fault) perpendicular to the seismic profile. The subducted oceanic plate is characterized by an apparent dip of 8-10' up to CDP 3500, where the reflectivity becomes horizontal. The reflectivity at this location (CDPs 3300-3500) is also characterized by arcuate e ...
... the result of faulting (near-vertical fault) perpendicular to the seismic profile. The subducted oceanic plate is characterized by an apparent dip of 8-10' up to CDP 3500, where the reflectivity becomes horizontal. The reflectivity at this location (CDPs 3300-3500) is also characterized by arcuate e ...
IDS 102 Plate Tectonics Questions Part I: Observations
... alone does not explain why there are mountains here.) The mountains at divergent boundaries are due to outpouring of basaltic lavas AND the isostatic rise of the crust because it is hot and less dense than the surrounding rocks. 2. What types of faults would you expect to see (normal, reverse, thrus ...
... alone does not explain why there are mountains here.) The mountains at divergent boundaries are due to outpouring of basaltic lavas AND the isostatic rise of the crust because it is hot and less dense than the surrounding rocks. 2. What types of faults would you expect to see (normal, reverse, thrus ...
Chapter 2: Global Tectonics Our Dynamic Planet Introduction
... The continental slope (大陸斜坡) is the flooded continental margin. The continental rise (大陸隆起) descends more gently from the base of the continental slope. Earthquakes and volcanoes are common along active margins. ...
... The continental slope (大陸斜坡) is the flooded continental margin. The continental rise (大陸隆起) descends more gently from the base of the continental slope. Earthquakes and volcanoes are common along active margins. ...
class outline - WordPress.com
... C. A tectonic plate consists of the crust and the top layer in the mantle. D. A tectonic plate is made up of Earth’s outer layer that is found in the upper mantle. E. A tectonic plate is a rigid layer of Earth that moves in the asthenosphere. F. A tectonic plate is lithosphere. ...
... C. A tectonic plate consists of the crust and the top layer in the mantle. D. A tectonic plate is made up of Earth’s outer layer that is found in the upper mantle. E. A tectonic plate is a rigid layer of Earth that moves in the asthenosphere. F. A tectonic plate is lithosphere. ...
Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics
... the process by which new oceanic lithosphere is created as older materials are pulled away. ...
... the process by which new oceanic lithosphere is created as older materials are pulled away. ...
Name - Cobb Learning
... coldest" will subduct. What do you know about density that makes this saying likely to be true? ...
... coldest" will subduct. What do you know about density that makes this saying likely to be true? ...
Geology (Chernicoff) - GEO
... B) compression of a rock unit. C) any deformation of a rock unit. D) forces that might cause deformation of a rock unit. 2) Rocks in which elastic deformation occurs: A) return to their original shape when the stress is released. B) remain in their deformed shape when the stress is released. C) beco ...
... B) compression of a rock unit. C) any deformation of a rock unit. D) forces that might cause deformation of a rock unit. 2) Rocks in which elastic deformation occurs: A) return to their original shape when the stress is released. B) remain in their deformed shape when the stress is released. C) beco ...
Plate Boundaries Lab
... Plate tectonics is the idea that the Earth’s outer shell consists of individual plates, which interact in various ways and thereby produce earthquakes, volcanoes, mountains, and the crust itself. ...
... Plate tectonics is the idea that the Earth’s outer shell consists of individual plates, which interact in various ways and thereby produce earthquakes, volcanoes, mountains, and the crust itself. ...
PlateTectwebquest
... and answer the questions below. 1. What are the three types of plate boundaries? ...
... and answer the questions below. 1. What are the three types of plate boundaries? ...
Effects of mantle and subduction-interface rheologies on slab
... Let us now look more closely at the process of subhorizontal buckling occurring in the reference model case with rollback. Fig. 3 shows six snapshots of viscosity distribution in the zoomed images that illustrate formation of the first two horizontal buckles. The following general outline of the dyna ...
... Let us now look more closely at the process of subhorizontal buckling occurring in the reference model case with rollback. Fig. 3 shows six snapshots of viscosity distribution in the zoomed images that illustrate formation of the first two horizontal buckles. The following general outline of the dyna ...
plate tectonics
... A. Moving Plates - current theory is that Earth’s surface is composed of sections of the lithosphere called plates - Lithosphere is composed of the crust and the rigid mantle - The study of the movement of these plates is called plate tectonics - original concept was proposed by Alfred Wegener as pa ...
... A. Moving Plates - current theory is that Earth’s surface is composed of sections of the lithosphere called plates - Lithosphere is composed of the crust and the rigid mantle - The study of the movement of these plates is called plate tectonics - original concept was proposed by Alfred Wegener as pa ...
Chapter 4 Marine Sedimentation
... " They face the edges of diverging tectonic plates " Very little volcanic or earthquake activity Active margins (= ―Pacific-type‖ margins) " Located near the edges of converging plates, where one plate subducts beneath another at an oceanic trench " Extensive volcanic and earthquake activity ...
... " They face the edges of diverging tectonic plates " Very little volcanic or earthquake activity Active margins (= ―Pacific-type‖ margins) " Located near the edges of converging plates, where one plate subducts beneath another at an oceanic trench " Extensive volcanic and earthquake activity ...
Convection and Plate Motion - Alaska Tsunami Education Program
... Display VISUAL AID: “Convection and Plates.” Guide the class in examining the visual aid and comparing components displayed in the model. The crack between the tables represents an ocean floor spreading center, and the colored strips on the paper represent different ages of rock. The point where the ...
... Display VISUAL AID: “Convection and Plates.” Guide the class in examining the visual aid and comparing components displayed in the model. The crack between the tables represents an ocean floor spreading center, and the colored strips on the paper represent different ages of rock. The point where the ...
Plate Tectonics - Physiographic Chart of the Sea Floor
... Step 7 - Essay #2 – Must be hand written Write a short essay that explains the relationship between Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics. Is there a relationship between the type of rock formed (Andesite, Rhyolite and Basalt) and the volcanoes location relative to a tectonic feature? Is there a relationshi ...
... Step 7 - Essay #2 – Must be hand written Write a short essay that explains the relationship between Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics. Is there a relationship between the type of rock formed (Andesite, Rhyolite and Basalt) and the volcanoes location relative to a tectonic feature? Is there a relationshi ...
Slide 1
... causes the more dense oceanic plate to sink (subduction). Subduction can cause a chain of volcanoes to form parallel to the plate boundary. ...
... causes the more dense oceanic plate to sink (subduction). Subduction can cause a chain of volcanoes to form parallel to the plate boundary. ...
Plate Tectonics
... • Hot spots are locations where stationary columns of magma originating deep within the mantle, called mantle plumes slowly rise to the surface ...
... • Hot spots are locations where stationary columns of magma originating deep within the mantle, called mantle plumes slowly rise to the surface ...
Homework Set 1
... i) What is meant by the term lithostatic stress and why is it pretty much the same thing as a “pressure” inside the Earth? ...
... i) What is meant by the term lithostatic stress and why is it pretty much the same thing as a “pressure” inside the Earth? ...
File - Mrs. Leachman Science
... away from one another resulting in a divergent plate boundary, they can converge, meaning they move towards one another resulting in a convergent plate boundary, or they can move parallel to one another, resulting in a transform plate boundary. Each of these different interactions results in differe ...
... away from one another resulting in a divergent plate boundary, they can converge, meaning they move towards one another resulting in a convergent plate boundary, or they can move parallel to one another, resulting in a transform plate boundary. Each of these different interactions results in differe ...
Earth`s Structure
... The Earth’s crust consists of several sections called tectonic plates. Where they meet is called a plate boundary. Convection currents in the mantle move these tectonic plates. In some locations the tectonic plates are moving towards each other, in others they are moving away from each other and in ...
... The Earth’s crust consists of several sections called tectonic plates. Where they meet is called a plate boundary. Convection currents in the mantle move these tectonic plates. In some locations the tectonic plates are moving towards each other, in others they are moving away from each other and in ...
Earthquake California - Berkeley County Schools
... away from one another resulting in a divergent plate boundary, they can converge, meaning they move towards one another resulting in a convergent plate boundary, or they can move parallel to one another, resulting in a transform plate boundary. Each of these different interactions results in differe ...
... away from one another resulting in a divergent plate boundary, they can converge, meaning they move towards one another resulting in a convergent plate boundary, or they can move parallel to one another, resulting in a transform plate boundary. Each of these different interactions results in differe ...
Oceanic trench
The oceanic trenches are hemispheric-scale long but narrow topographic depressions of the sea floor. They are also the deepest parts of the ocean floor. Oceanic trenches are a distinctive morphological feature of convergent plate boundaries, along which lithospheric plates move towards each other at rates that vary from a few mm to over ten cm per year. A trench marks the position at which the flexed, subducting slab begins to descend beneath another lithospheric slab. Trenches are generally parallel to a volcanic island arc, and about 200 km (120 mi) from a volcanic arc. Oceanic trenches typically extend 3 to 4 km (1.9 to 2.5 mi) below the level of the surrounding oceanic floor. The greatest ocean depth to be sounded is in the Challenger Deep of the Mariana Trench, at a depth of 11,034 m (36,201 ft) below sea level. Oceanic lithosphere moves into trenches at a global rate of about 3 km2/yr.