PLATE TECTONICS - Oakton Community College
... MOHO exposed at the surface located between crust and mantle (S&A 22) ...
... MOHO exposed at the surface located between crust and mantle (S&A 22) ...
HS Plate Tectonics
... Sediments, primarily muds and the shells of tiny sea creatures, coat the seafloor. Sediment is thickest near the shore where it comes off the continents in rivers and on wind currents. Continental crust is made up of many different types of igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks. The average co ...
... Sediments, primarily muds and the shells of tiny sea creatures, coat the seafloor. Sediment is thickest near the shore where it comes off the continents in rivers and on wind currents. Continental crust is made up of many different types of igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks. The average co ...
How does the challenge differ between plate boundaries, plate
... taken up several ways. About half occurs across locked Himalayan frontal faults such as the Main Central Thrust These faults are part of the interface associated with the underthrusting Indian continental crust, which thickens crust under high Himalayas. ...
... taken up several ways. About half occurs across locked Himalayan frontal faults such as the Main Central Thrust These faults are part of the interface associated with the underthrusting Indian continental crust, which thickens crust under high Himalayas. ...
Mountain belt growth inferred from histories of past plate
... in mantle related driving forces. One key controlling factor for these variations is the surface topography at convergent margins, as previous modeling shows that the topographic load of large mountain belts consumes a significant amount of the driving forces available for plate tectonics by increas ...
... in mantle related driving forces. One key controlling factor for these variations is the surface topography at convergent margins, as previous modeling shows that the topographic load of large mountain belts consumes a significant amount of the driving forces available for plate tectonics by increas ...
Nevado de Longaví Volcano (Chilean Andes, 36.2 ˚S): adakitic
... The formation of adakites by partial melting of oceanic lithosphere is limited to regions where young, hot slabs are subducted. Adakitic melts also occur in continental arcs related to subduction of cold oceanic lithosphere, where they have been explained in terms of remelting of basaltic material u ...
... The formation of adakites by partial melting of oceanic lithosphere is limited to regions where young, hot slabs are subducted. Adakitic melts also occur in continental arcs related to subduction of cold oceanic lithosphere, where they have been explained in terms of remelting of basaltic material u ...
The Puzzling Plates Part I
... The earth is broken into many plates. The boundaries of these plates are well-defined and can be identified by examining the locations of shallow focus earthquakes. Many seafloor features are formed at these plate boundaries, such as trenches and mid-ocean ridges. There are at least 14 major plates ...
... The earth is broken into many plates. The boundaries of these plates are well-defined and can be identified by examining the locations of shallow focus earthquakes. Many seafloor features are formed at these plate boundaries, such as trenches and mid-ocean ridges. There are at least 14 major plates ...
PPT - Margins
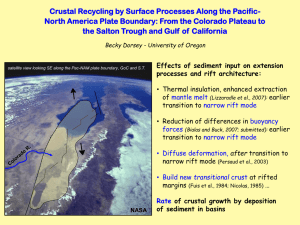
... of mantle melt (Lizzaradle et al., 2007): earlier transition to narrow rift mode • Reduction of differences in buoyancy forces (Bialas and Buck, 2007; submitted): earlier transition to narrow rift mode • Diffuse deformation, after transition to narrow rift mode (Persaud et al., 2003) • Build new tra ...
... of mantle melt (Lizzaradle et al., 2007): earlier transition to narrow rift mode • Reduction of differences in buoyancy forces (Bialas and Buck, 2007; submitted): earlier transition to narrow rift mode • Diffuse deformation, after transition to narrow rift mode (Persaud et al., 2003) • Build new tra ...
Evolution of the Helvetic Continental margin paper - RWTH
... surface. The Helvetic nappes were detached from their former crystalline basement of Penninic origin and massively thrusted over the Infrahelvetic complex and the external massif of the Alps. In Switzerland, Germany and Austria the Helvetic nappes are also partly thrusted over the Molasse Basin. Ove ...
... surface. The Helvetic nappes were detached from their former crystalline basement of Penninic origin and massively thrusted over the Infrahelvetic complex and the external massif of the Alps. In Switzerland, Germany and Austria the Helvetic nappes are also partly thrusted over the Molasse Basin. Ove ...
slide1
... boundary where ultramafics were already exposed at or near the surface; or 2. An additional much larger (than Chicxulub) fragment penetrated to and excavated mantle material from beneath the crust; or 3. Possibly both of the above. 4. If the lithosphere was breached then there may be implications fo ...
... boundary where ultramafics were already exposed at or near the surface; or 2. An additional much larger (than Chicxulub) fragment penetrated to and excavated mantle material from beneath the crust; or 3. Possibly both of the above. 4. If the lithosphere was breached then there may be implications fo ...
Plate Tectonics PhET Simulation Part 1: Describing differences
... Type of Boundary? What is the effect/outcome of this plate movement? Divergent Convergent Transform Example 3: Drag an oceanic (either young or old) crust and continental crust onto the screen. Drag the plate in the direction of the GREEN arrow. ...
... Type of Boundary? What is the effect/outcome of this plate movement? Divergent Convergent Transform Example 3: Drag an oceanic (either young or old) crust and continental crust onto the screen. Drag the plate in the direction of the GREEN arrow. ...
View - GFZpublic
... 1. Introduction [2] Collisions between continents and volcanic island arcs are common elements in the ancient to recent tectonic history of the Earth. Many of these collisions are oblique and diachronous, starting where the two plates first collide then closing gradually like a zipper. This implies ...
... 1. Introduction [2] Collisions between continents and volcanic island arcs are common elements in the ancient to recent tectonic history of the Earth. Many of these collisions are oblique and diachronous, starting where the two plates first collide then closing gradually like a zipper. This implies ...
a 22 page PDF of this title
... basins has always presented daunting obstacles. Amazing as robots and satellites and multi-beam systems are, though, sometimes there is no substitute for actually seeing— focusing a well-trained set of eyes on the ocean floor. The most difficult problem is to reach ...
... basins has always presented daunting obstacles. Amazing as robots and satellites and multi-beam systems are, though, sometimes there is no substitute for actually seeing— focusing a well-trained set of eyes on the ocean floor. The most difficult problem is to reach ...
Structural Geology and Plate Tectonics Sections 21.1-21.6
... two plates are moving apart – a divergent boundary. The initially molten magma is shouldered to each side of the rift and causes the lithospheric plates to slowly ...
... two plates are moving apart – a divergent boundary. The initially molten magma is shouldered to each side of the rift and causes the lithospheric plates to slowly ...
13.7 plate tectonics MH - The University of Texas at Dallas
... researchers are hoping to settle the matter with a field trip. An excursion is already planned for next year, to re-examine the evidence for plate tectonics in the western Pilbara. Field trips don’t always resolve things. In the Wind River Mountains, the meeting attendees continued to argue about pl ...
... researchers are hoping to settle the matter with a field trip. An excursion is already planned for next year, to re-examine the evidence for plate tectonics in the western Pilbara. Field trips don’t always resolve things. In the Wind River Mountains, the meeting attendees continued to argue about pl ...
Drifting Continents
... Divergent/widen Boundaries – Additional General Info C. BOTH types of divergent boundaries add(create) new crust D. Divergent boundaries widen ocean basins and lengthen/widen earth’s surface C. The Atlantic Ocean is widening an average of 2-3cm / year. E. Volcanoes and earthquakes are common along b ...
... Divergent/widen Boundaries – Additional General Info C. BOTH types of divergent boundaries add(create) new crust D. Divergent boundaries widen ocean basins and lengthen/widen earth’s surface C. The Atlantic Ocean is widening an average of 2-3cm / year. E. Volcanoes and earthquakes are common along b ...
theme 5: the deeper earth
... mantle is that isotopic evidence points to long-term separation of chemically distinct reservoirs while geophysical evidence suggests convection extending over its entire depth. Geochemical observations: isotopic variations of midocean ridge basalts and the continental crust, budgets and fluxes of n ...
... mantle is that isotopic evidence points to long-term separation of chemically distinct reservoirs while geophysical evidence suggests convection extending over its entire depth. Geochemical observations: isotopic variations of midocean ridge basalts and the continental crust, budgets and fluxes of n ...
macpherson_hall_2001 IBM boninites
... into early Middle Eocene sediments in the Daito Basin (at DSDP Site 446; [37,39]) and have yielded early Middle Eocene radiometric ages [37,40] suggesting this source was available throughout the newly forming rift. Further north, Middle Eocene conglomerates from DSDP Site 445 (Fig. 1) commonly cont ...
... into early Middle Eocene sediments in the Daito Basin (at DSDP Site 446; [37,39]) and have yielded early Middle Eocene radiometric ages [37,40] suggesting this source was available throughout the newly forming rift. Further north, Middle Eocene conglomerates from DSDP Site 445 (Fig. 1) commonly cont ...
Investigating tectonic-erosion interactions
... propagation of intraplate faulting. A multidisciplinary approach that integrates structural and stratigraphic field investigations with geochronological (OSL) and thermochronological (U-Th)/He apatite, AHe) analyses is adopted to reconstruct the spatio-temporal evolution of the Kuh-e-Faghan Fault (K ...
... propagation of intraplate faulting. A multidisciplinary approach that integrates structural and stratigraphic field investigations with geochronological (OSL) and thermochronological (U-Th)/He apatite, AHe) analyses is adopted to reconstruct the spatio-temporal evolution of the Kuh-e-Faghan Fault (K ...
In-Situ Plate Tectonic Model of the Gulf of Mexico (GOM) and
... 6. Provides a complicated model that has no present-day equivalent. All of the above points create a negative prospectivity perception with a lack of reservoir, source rocks and think overburden that would not provide sufficient maturity for formation of hydrocarbons in this region. In order to unde ...
... 6. Provides a complicated model that has no present-day equivalent. All of the above points create a negative prospectivity perception with a lack of reservoir, source rocks and think overburden that would not provide sufficient maturity for formation of hydrocarbons in this region. In order to unde ...
Tectonostratigraphy of passive margin in Mesopotamia Zone
... (2) Initial Collision Stage (Eocene-Oligocene): The first indication that a collision is imminent occurred when the edge of continental Arabian plate begins to rise and stretch as it bend around the outer swell just prior to being pulled into the subduction system by the downgoing slab, stretching o ...
... (2) Initial Collision Stage (Eocene-Oligocene): The first indication that a collision is imminent occurred when the edge of continental Arabian plate begins to rise and stretch as it bend around the outer swell just prior to being pulled into the subduction system by the downgoing slab, stretching o ...
Earth`s Moving Plates: A Look Back
... middle to late 1800s, claimed that the scratches and gouges from glaciers line up along the boundaries of separated continents. He also noted similarities among plant fossils on different continents. He hypothesized that these fossil similarities were evidence that long land bridges had once connect ...
... middle to late 1800s, claimed that the scratches and gouges from glaciers line up along the boundaries of separated continents. He also noted similarities among plant fossils on different continents. He hypothesized that these fossil similarities were evidence that long land bridges had once connect ...
Where and why do large shallow slab earthquakes occur?
... (1997) inferred that this event occurred within the Philippine Sea slab at the 40-50 km depth, based on the fact that severe damage was localized at the epicenter, but strong shaking was felt in a wide area, which is a characteristic feature to the slab events in this area. The 1905 Geiyo earthquake ...
... (1997) inferred that this event occurred within the Philippine Sea slab at the 40-50 km depth, based on the fact that severe damage was localized at the epicenter, but strong shaking was felt in a wide area, which is a characteristic feature to the slab events in this area. The 1905 Geiyo earthquake ...
Ridge push, mantle plumes and the speed of the Indian plate
... The buoyancy of lithospheric slabs in subduction zones is widely thought to dominate the torques driving plate tectonics. In late Cretaceous and early Paleogene times, the Indian plate moved more rapidly over the mantle than freely subducting slabs sink within it. This signal event has been attribut ...
... The buoyancy of lithospheric slabs in subduction zones is widely thought to dominate the torques driving plate tectonics. In late Cretaceous and early Paleogene times, the Indian plate moved more rapidly over the mantle than freely subducting slabs sink within it. This signal event has been attribut ...
Plate tectonics
... ocean-to-ocean rifting, divergent boundaries form by seafloor spreading, allowing for the formation of new ocean basin. As the continent splits, the ridge forms at the spreading center, the ocean basin expands, and finally, the plate area increases causing many small volcanoes and/or shallow earthquak ...
... ocean-to-ocean rifting, divergent boundaries form by seafloor spreading, allowing for the formation of new ocean basin. As the continent splits, the ridge forms at the spreading center, the ocean basin expands, and finally, the plate area increases causing many small volcanoes and/or shallow earthquak ...
Imaging subduction from the trench to 300 km depth beneath the
... Recent dense deployments of portable digital seismographs have provided excellent control on earthquakes beneath the central North Island of New Zealand. Here we use a subset of the best-recorded earthquakes in an inversion for the 3-D Vp and Vp/Vs structure. The data set includes 39 123 P observati ...
... Recent dense deployments of portable digital seismographs have provided excellent control on earthquakes beneath the central North Island of New Zealand. Here we use a subset of the best-recorded earthquakes in an inversion for the 3-D Vp and Vp/Vs structure. The data set includes 39 123 P observati ...
Oceanic trench
The oceanic trenches are hemispheric-scale long but narrow topographic depressions of the sea floor. They are also the deepest parts of the ocean floor. Oceanic trenches are a distinctive morphological feature of convergent plate boundaries, along which lithospheric plates move towards each other at rates that vary from a few mm to over ten cm per year. A trench marks the position at which the flexed, subducting slab begins to descend beneath another lithospheric slab. Trenches are generally parallel to a volcanic island arc, and about 200 km (120 mi) from a volcanic arc. Oceanic trenches typically extend 3 to 4 km (1.9 to 2.5 mi) below the level of the surrounding oceanic floor. The greatest ocean depth to be sounded is in the Challenger Deep of the Mariana Trench, at a depth of 11,034 m (36,201 ft) below sea level. Oceanic lithosphere moves into trenches at a global rate of about 3 km2/yr.