Convergent Boundaries
... called a deep-sea trench that forms along the boundary. Such trenches are the deepest parts of the ocean floor. Subduction boundaries can occur at the convergence of two oceanic plates or at the convergence of an oceanic plate with a continental plate. When two oceanic plates converge, the deep-sea ...
... called a deep-sea trench that forms along the boundary. Such trenches are the deepest parts of the ocean floor. Subduction boundaries can occur at the convergence of two oceanic plates or at the convergence of an oceanic plate with a continental plate. When two oceanic plates converge, the deep-sea ...
Partial melting
... seafloor grows older as its distance from the rift zone increases, and as it ages, it cools and becomes denser and is buried under marine sediments that are deposited on the seafloor. ...
... seafloor grows older as its distance from the rift zone increases, and as it ages, it cools and becomes denser and is buried under marine sediments that are deposited on the seafloor. ...
The solid, outer layer of Earth that consists of the crust and the rigid
... The process of one tectonic plate sinking beneath another into the mantle at a convergent plate boundary ...
... The process of one tectonic plate sinking beneath another into the mantle at a convergent plate boundary ...
Plate Tectonics
... The Great Rift Valley in east Africa is an example of a continent breaking apart. The Red Sea is a part of the rift. ...
... The Great Rift Valley in east Africa is an example of a continent breaking apart. The Red Sea is a part of the rift. ...
KEY
... 1. Explain the theory of plate tectonics. The theory of plate tectonics states that Earth’s lithosphere is broken into large slabs called tectonic plates, which are in constant motion. Many of Earth’s surface features form as the result of interactions among these plates. 2. Explain what happens at ...
... 1. Explain the theory of plate tectonics. The theory of plate tectonics states that Earth’s lithosphere is broken into large slabs called tectonic plates, which are in constant motion. Many of Earth’s surface features form as the result of interactions among these plates. 2. Explain what happens at ...
Plate tectonics: divergent, convergent, and transform plate boundaries
... convergent, and transform plate boundaries Plate tectonic theory envisions Earth's surface as consisting of plates of rigid lithosphere (the crust and uppermost mantle) moving over, and locally sinking into, a ductile asthenosphere (the rest of the mantle). Those plates move relative to each other ( ...
... convergent, and transform plate boundaries Plate tectonic theory envisions Earth's surface as consisting of plates of rigid lithosphere (the crust and uppermost mantle) moving over, and locally sinking into, a ductile asthenosphere (the rest of the mantle). Those plates move relative to each other ( ...
sci-10-18-1 - St John Brebeuf
... called slab pull. About 700 km down, the temperature and pressure soften the plate, recycling it into the mantle. ...
... called slab pull. About 700 km down, the temperature and pressure soften the plate, recycling it into the mantle. ...
Convergent Plate Boundary Diagrams
... c. What is thought to happen to the plate on the left once it reaches the asthenosphere and continues to subduct deeper and deeper? ...
... c. What is thought to happen to the plate on the left once it reaches the asthenosphere and continues to subduct deeper and deeper? ...
A. Continental Slope Transition from the Cont. Shelf to the ocean
... through the collision of oceanic plates. Subduction at these plate boundaries makes island arcs. Parallel deep-sea trenches. Oceanic islands are nearly all basaltic volcanoes. ...
... through the collision of oceanic plates. Subduction at these plate boundaries makes island arcs. Parallel deep-sea trenches. Oceanic islands are nearly all basaltic volcanoes. ...
Study Questions for Quiz #9
... What type of magma forms in continental collision zones? How is this magma formed, i.e. what melts to form it? What type of metamorphism occurs near the trench? What type of metamorphism occurs near the magmatic arc? In oceanic-oceanic convergence, what happens to the subducting plate as it descends ...
... What type of magma forms in continental collision zones? How is this magma formed, i.e. what melts to form it? What type of metamorphism occurs near the trench? What type of metamorphism occurs near the magmatic arc? In oceanic-oceanic convergence, what happens to the subducting plate as it descends ...
CIDER 2011 Research Discussion 1
... – Sdrolias & Mueller 200? G3 – Along arc seismic anisotropy with shrinking and growing lateral trench width (Long & Silver, ...
... – Sdrolias & Mueller 200? G3 – Along arc seismic anisotropy with shrinking and growing lateral trench width (Long & Silver, ...
study guide for plate tectonics assessment c example
... 10. What type of rock forms the Oceanic Plates? What type of rock forms the Continental Plates? 11. Where does new ocean crust form during seafloor spreading? Divergent boundaries by submarine (underwater) eruptions and intrusions of basaltic magma. 12. Where does old oceanic crust get removed? Subd ...
... 10. What type of rock forms the Oceanic Plates? What type of rock forms the Continental Plates? 11. Where does new ocean crust form during seafloor spreading? Divergent boundaries by submarine (underwater) eruptions and intrusions of basaltic magma. 12. Where does old oceanic crust get removed? Subd ...
Post Tectonic Quiz
... 3. Seafloor spreading explains how new seafloor forms at a mid- oceanic ridge. What discovery let to the theory of seafloor spreading? a. Older rocks are found farther away from the mid ocean ridge that younger rocks b. Fossils of similar plants were found on different continents c. Older rocks are ...
... 3. Seafloor spreading explains how new seafloor forms at a mid- oceanic ridge. What discovery let to the theory of seafloor spreading? a. Older rocks are found farther away from the mid ocean ridge that younger rocks b. Fossils of similar plants were found on different continents c. Older rocks are ...
Plate Tectonics Review Worksheet
... 1. Continental Drift: A theory proposed by Alfred Wegner that said all continents were once joined 300 million years ago in a single land mass called Pangaea. Over time the continents moved to their present day locations. 2. What are four pieces of evidence for continental drift? Fossils, puzzle fit ...
... 1. Continental Drift: A theory proposed by Alfred Wegner that said all continents were once joined 300 million years ago in a single land mass called Pangaea. Over time the continents moved to their present day locations. 2. What are four pieces of evidence for continental drift? Fossils, puzzle fit ...
Appalachian Mountain Building
... Orogeny is the process that for all mountain ranges. Orogeny results in broad, linear regions of deformation known as orogenic belts. Most orogenic belts are associated with plate boundaries. The greatest variety and the tallest of these belts Are found at convergent Boundaries. ...
... Orogeny is the process that for all mountain ranges. Orogeny results in broad, linear regions of deformation known as orogenic belts. Most orogenic belts are associated with plate boundaries. The greatest variety and the tallest of these belts Are found at convergent Boundaries. ...
Chapter 17 Geo Reading Questions KEY
... 1. Explain the theory of plate tectonics. The theory of plate tectonics states that Earth’s lithosphere is broken into large slabs called tectonic plates, which are in constant motion. Many of Earth’s ...
... 1. Explain the theory of plate tectonics. The theory of plate tectonics states that Earth’s lithosphere is broken into large slabs called tectonic plates, which are in constant motion. Many of Earth’s ...
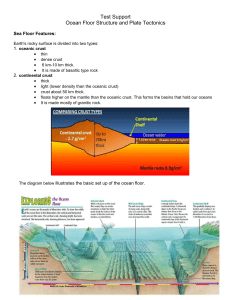
Unit 5: Ocean Floor Structure and Plate Tectonics
... a seamount with a flat top created by wave action when the seamount was at sea level ...
... a seamount with a flat top created by wave action when the seamount was at sea level ...
plate boundaries lab - Hastings Middle School
... What type of boundary is in the middle of the Atlantic ocean between The Americas and Europe/Africa plates? a. Transform b. Divergent c. Convergent The boundary in #3 is in an ocean, what is forming here? a. Mid ocean ridge b. Trench c. Rift Valley Where is the ocean rock the oldest in the Atlantic? ...
... What type of boundary is in the middle of the Atlantic ocean between The Americas and Europe/Africa plates? a. Transform b. Divergent c. Convergent The boundary in #3 is in an ocean, what is forming here? a. Mid ocean ridge b. Trench c. Rift Valley Where is the ocean rock the oldest in the Atlantic? ...
Get out your pieces for Tectonicland Have your HOMEWORK
... – Inner core is solid, Iron and Nickel ...
... – Inner core is solid, Iron and Nickel ...
Day 5 Subduction Trenches
... http://www2.wwnorton.com/college/geo/egeo/flash/2_9.swf Watch Blue planet video on deep ocean trench life: http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid=6616117576614575795 &q=deep+sea+creatures&total=945&start=0&num=10&so=0&type=se arch&plindex=1 ...
... http://www2.wwnorton.com/college/geo/egeo/flash/2_9.swf Watch Blue planet video on deep ocean trench life: http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid=6616117576614575795 &q=deep+sea+creatures&total=945&start=0&num=10&so=0&type=se arch&plindex=1 ...
The Plates of the Earth
... India, and Pakistan. The crust beneath the Himalaya, the most towering mountain range on Earth, is still the process of being compressed. Here, the Indian plate is colliding northward with the Eurasian plate. Continental Collision along the Convergent boundary between the Indo-Australian plate and t ...
... India, and Pakistan. The crust beneath the Himalaya, the most towering mountain range on Earth, is still the process of being compressed. Here, the Indian plate is colliding northward with the Eurasian plate. Continental Collision along the Convergent boundary between the Indo-Australian plate and t ...
Key Ideas and Vocabulary—Suggested Answers
... 29. If tectonic activity has slowed or ceased in an area, the effects of weathering and erosion will no longer be “balanced” by mountain-building processes, causing the particular landform to become smaller. 30. A 31. Oceanic crust and continental crust have different compositions (are made up of di ...
... 29. If tectonic activity has slowed or ceased in an area, the effects of weathering and erosion will no longer be “balanced” by mountain-building processes, causing the particular landform to become smaller. 30. A 31. Oceanic crust and continental crust have different compositions (are made up of di ...
Oceanic trench
The oceanic trenches are hemispheric-scale long but narrow topographic depressions of the sea floor. They are also the deepest parts of the ocean floor. Oceanic trenches are a distinctive morphological feature of convergent plate boundaries, along which lithospheric plates move towards each other at rates that vary from a few mm to over ten cm per year. A trench marks the position at which the flexed, subducting slab begins to descend beneath another lithospheric slab. Trenches are generally parallel to a volcanic island arc, and about 200 km (120 mi) from a volcanic arc. Oceanic trenches typically extend 3 to 4 km (1.9 to 2.5 mi) below the level of the surrounding oceanic floor. The greatest ocean depth to be sounded is in the Challenger Deep of the Mariana Trench, at a depth of 11,034 m (36,201 ft) below sea level. Oceanic lithosphere moves into trenches at a global rate of about 3 km2/yr.