CH 9 Plate tectonics
... Signs of glaciers on multiple continents, some near equator. Found in cold areas but need tropical climate to form. ...
... Signs of glaciers on multiple continents, some near equator. Found in cold areas but need tropical climate to form. ...
Plate Tectonics (Chap. 3)
... Mantle: composed of Fe/Mg- rich silicates (olivine, pyroxene) Crust: continental – 20–90 km thick (old) Ocean crust- 5–10 km thick (young) Lithosphere: crust + upper mantle = “Plates” Asthenosphere: partially molten upper mantle Mantle: convection due to radioactive heating 3 types of plate boundary ...
... Mantle: composed of Fe/Mg- rich silicates (olivine, pyroxene) Crust: continental – 20–90 km thick (old) Ocean crust- 5–10 km thick (young) Lithosphere: crust + upper mantle = “Plates” Asthenosphere: partially molten upper mantle Mantle: convection due to radioactive heating 3 types of plate boundary ...
Ch 9 4 Testing Plate Tectonics
... Some of the best evidence has come from deep-sea drilling into the sediments on the ocean floor The data on the ages of seafloor sediment confirmed what the seafloor spreading hypothesis predicted The youngest oceanic crust is at the ridge crest and the oldest oceanic crust is at the continental ...
... Some of the best evidence has come from deep-sea drilling into the sediments on the ocean floor The data on the ages of seafloor sediment confirmed what the seafloor spreading hypothesis predicted The youngest oceanic crust is at the ridge crest and the oldest oceanic crust is at the continental ...
Chapter 17- Plate Tectonics
... deep sea trenches – Magma forced toward crust – Fills gaps and hardens – Forms new ocean floor ...
... deep sea trenches – Magma forced toward crust – Fills gaps and hardens – Forms new ocean floor ...
108-SeaFloor Spreading
... but the hotspot under the Big Island appears to have been there for 70+ million years. • The evidence is the chain of islands stretching out to the NW from Hawaii to Kure – and on along the Emperor Seamount chain. ...
... but the hotspot under the Big Island appears to have been there for 70+ million years. • The evidence is the chain of islands stretching out to the NW from Hawaii to Kure – and on along the Emperor Seamount chain. ...
Word
... D. volcanoes along an Andean-type plate margin E. all of the above 25. Island arc volcanoes form: A. whenever subduction occurs B. when a continent subducts underneath another continent C. at ocean-ocean plate boundaries D. along the Cascadia subduction zone E. somewhere beneath the continental slop ...
... D. volcanoes along an Andean-type plate margin E. all of the above 25. Island arc volcanoes form: A. whenever subduction occurs B. when a continent subducts underneath another continent C. at ocean-ocean plate boundaries D. along the Cascadia subduction zone E. somewhere beneath the continental slop ...
Introduction to Plate Tectonics California Geology 20
... aspect of the natural world; an organized system of accepted knowledge that applies in a variety of circumstances to explain a specific set of phenomena. ...
... aspect of the natural world; an organized system of accepted knowledge that applies in a variety of circumstances to explain a specific set of phenomena. ...
Plate Tectonics Diagram Questions
... interactions that occur in this region and why the occurrence of earthquakes is so high. _There are convergent boundaries all around the Pacific Ocean where subduction zones occur. When the plates move there are earthquakes.___ ...
... interactions that occur in this region and why the occurrence of earthquakes is so high. _There are convergent boundaries all around the Pacific Ocean where subduction zones occur. When the plates move there are earthquakes.___ ...
Chapter 7 Vocabulary List
... 1. Asthenosphere- The subdivision of a mantle situated below the lithosphere. The zone of weak material exists below the depths of about 100 kilometers and in some region extends as deep as 700 kilometers. The rock within this zone is easily deformed. 2. Continental drift theory- A theory that origi ...
... 1. Asthenosphere- The subdivision of a mantle situated below the lithosphere. The zone of weak material exists below the depths of about 100 kilometers and in some region extends as deep as 700 kilometers. The rock within this zone is easily deformed. 2. Continental drift theory- A theory that origi ...
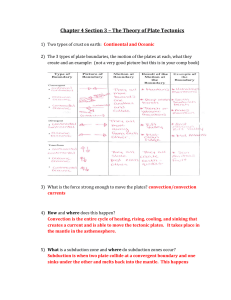
Chapter 4 Section 3 – The Theory of Plate Tectonics
... 8) Review the characteristics of the Lithosphere and Asthenosphere. Lithosphere = Made up of the earth’s crust and upper mantle and this layer is all solid. Asthenosphere = Part of the mantle, plastic like (semi-liquid), tectonic plates float on this layer. ...
... 8) Review the characteristics of the Lithosphere and Asthenosphere. Lithosphere = Made up of the earth’s crust and upper mantle and this layer is all solid. Asthenosphere = Part of the mantle, plastic like (semi-liquid), tectonic plates float on this layer. ...
Oceanic Crust
... Trenches • Due to one plate subducting (going below) another plate • Earthquakes • Many volcanoes and volcanic island arcs form here ...
... Trenches • Due to one plate subducting (going below) another plate • Earthquakes • Many volcanoes and volcanic island arcs form here ...
Lithosphere Part 2
... • Volcanic island arc is usually formed fairly close to, but not right next to, the trench. (ex: Mariana Islands, Aleutian Islands, Solomon Islands, Lesser Antilles) ...
... • Volcanic island arc is usually formed fairly close to, but not right next to, the trench. (ex: Mariana Islands, Aleutian Islands, Solomon Islands, Lesser Antilles) ...
Get out your pieces for Tectonicland Have your HOMEWORK out
... plates move apart from each other Mid-Ocean Ridges Rift valleys – long narrow depressions Rift valley in East Africa ...
... plates move apart from each other Mid-Ocean Ridges Rift valleys – long narrow depressions Rift valley in East Africa ...
Convection Cell Slab Pull Ridge Push
... 14. Identify three different ways climate is affected by plate tectonics. ...
... 14. Identify three different ways climate is affected by plate tectonics. ...
plate tectonics post-test
... Which has the greatest mass (most space)? Which is least dense? 3. 5 mechanical/physical layers: Lost Ants March On Ice Which is the strong, lower layer of the mantle? Which is rigid? Which is rock that slowly flows (stretchy)? Which is solid iron and nickel? Which is liquid? 4. Be abl ...
... Which has the greatest mass (most space)? Which is least dense? 3. 5 mechanical/physical layers: Lost Ants March On Ice Which is the strong, lower layer of the mantle? Which is rigid? Which is rock that slowly flows (stretchy)? Which is solid iron and nickel? Which is liquid? 4. Be abl ...
CH 9 Plate tectonics
... • Move slowly about 5 cm or 2.5” per year • Plate movement causes EQs, volcanoes, mts • Lithosphere – plates • outer and rigid • Crust and upper mantle • Moves over the asthenosphere • Asthenosphere • below and plastic like • Lower mantle ...
... • Move slowly about 5 cm or 2.5” per year • Plate movement causes EQs, volcanoes, mts • Lithosphere – plates • outer and rigid • Crust and upper mantle • Moves over the asthenosphere • Asthenosphere • below and plastic like • Lower mantle ...
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 1 of 1
... parts of the ocean—and some of the deepest natural spots on Earth. Ocean trenches are found in every ocean basin on the planet, although the deepest ocean trenches ring the Pacific as part of the so-called “Ring of Fire” that also includes active volcanoes and earthquake zones.Ocean trenches are a r ...
... parts of the ocean—and some of the deepest natural spots on Earth. Ocean trenches are found in every ocean basin on the planet, although the deepest ocean trenches ring the Pacific as part of the so-called “Ring of Fire” that also includes active volcanoes and earthquake zones.Ocean trenches are a r ...
Ocean Topography
... -know how to draw both Atlantic and Pacific Ocean floor Continental shelf, slope and rise, trench, submarine canyon, seamount, guyot, mid-ocean ridge, rift valley, abyssal plain. Active Continental Margin vs Passive Continental Margin Sediments: 4 kinds and how they are created Tectonic Plates: Fe ...
... -know how to draw both Atlantic and Pacific Ocean floor Continental shelf, slope and rise, trench, submarine canyon, seamount, guyot, mid-ocean ridge, rift valley, abyssal plain. Active Continental Margin vs Passive Continental Margin Sediments: 4 kinds and how they are created Tectonic Plates: Fe ...
Oceanic trench
The oceanic trenches are hemispheric-scale long but narrow topographic depressions of the sea floor. They are also the deepest parts of the ocean floor. Oceanic trenches are a distinctive morphological feature of convergent plate boundaries, along which lithospheric plates move towards each other at rates that vary from a few mm to over ten cm per year. A trench marks the position at which the flexed, subducting slab begins to descend beneath another lithospheric slab. Trenches are generally parallel to a volcanic island arc, and about 200 km (120 mi) from a volcanic arc. Oceanic trenches typically extend 3 to 4 km (1.9 to 2.5 mi) below the level of the surrounding oceanic floor. The greatest ocean depth to be sounded is in the Challenger Deep of the Mariana Trench, at a depth of 11,034 m (36,201 ft) below sea level. Oceanic lithosphere moves into trenches at a global rate of about 3 km2/yr.