earth
... Bridge across the Álfagjá rift valley in southwest Iceland, the boundary between the Eurasian and North American continental tectonic plates. ...
... Bridge across the Álfagjá rift valley in southwest Iceland, the boundary between the Eurasian and North American continental tectonic plates. ...
Tectonic landscapes- Understanding hotspots
... These are fixed points in the mantle that generate intense heat (in a mantle plume). Small, long lasting, exceptionally hot areas of magma exist under the Earth's surface which in turn sustains longlasting volcanic activity. At areas where the pressure is greater in the mantle, magma erupts through ...
... These are fixed points in the mantle that generate intense heat (in a mantle plume). Small, long lasting, exceptionally hot areas of magma exist under the Earth's surface which in turn sustains longlasting volcanic activity. At areas where the pressure is greater in the mantle, magma erupts through ...
EPSC233ArcheanEarth2
... This magma is less dense than the mantle and tends to rise through faults (large cracks in the rocks)... This magma may crystallize near the Earth’s surface and be remelted again to produce a more felsic composition, more like continental crust. ...
... This magma is less dense than the mantle and tends to rise through faults (large cracks in the rocks)... This magma may crystallize near the Earth’s surface and be remelted again to produce a more felsic composition, more like continental crust. ...
Journey to the Center of Earth
... constantly changes is called theory of plate tectonic. • The theory states that the earth’s outer shell, the lithosphere is divided into eight large plates. • Because each plate moves as a single unit, the interiors of the plates are generally stable. All major activity such as ...
... constantly changes is called theory of plate tectonic. • The theory states that the earth’s outer shell, the lithosphere is divided into eight large plates. • Because each plate moves as a single unit, the interiors of the plates are generally stable. All major activity such as ...
Earth Structure and Plate Tectonics
... ◦ 1. Orderly pattern of oceanic ridges and volcanoes suggesting the Earth’s crust is divided into sections. ◦ 2. Sediment samples – the layers were thin or absent at the oceanic ridges, and thicker away from the oceanic ridges. This suggests newer crust at the ridges. ◦ 3. Radiometric dating was us ...
... ◦ 1. Orderly pattern of oceanic ridges and volcanoes suggesting the Earth’s crust is divided into sections. ◦ 2. Sediment samples – the layers were thin or absent at the oceanic ridges, and thicker away from the oceanic ridges. This suggests newer crust at the ridges. ◦ 3. Radiometric dating was us ...
Inside the Earth
... as the intervening oceanic crust is subducted. Map by Ron Blakey, Northern Arizona University. ...
... as the intervening oceanic crust is subducted. Map by Ron Blakey, Northern Arizona University. ...
Document
... 3. Why do less dense compounds make up Earth’s crust while the densest compounds make up the core? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 4. List the three layers of the Earth, based on their chemical compositio ...
... 3. Why do less dense compounds make up Earth’s crust while the densest compounds make up the core? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 4. List the three layers of the Earth, based on their chemical compositio ...
01 - Mayfield City Schools
... 3. Why do less dense compounds make up Earth’s crust while the densest compounds make up the core? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 4. List the three layers of the Earth, based on their chemical compositio ...
... 3. Why do less dense compounds make up Earth’s crust while the densest compounds make up the core? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 4. List the three layers of the Earth, based on their chemical compositio ...
directed reading inside earth
... 3. Why do less dense compounds make up Earth’s crust while the densest compounds make up the core? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 4. List the three layers of the Earth, based on their chemical compositio ...
... 3. Why do less dense compounds make up Earth’s crust while the densest compounds make up the core? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 4. List the three layers of the Earth, based on their chemical compositio ...
Plate Tectonics Powerpoint
... A subduction zone occurs when one oceanic plate is forced down into the mantle beneath a second plate. Oceanic-Continental - Denser oceanic slab sinks into the asthenosphere. - Pockets of magma develop and rise. - Continental volcanic arcs form in part by volcanic activity caused by the subducti ...
... A subduction zone occurs when one oceanic plate is forced down into the mantle beneath a second plate. Oceanic-Continental - Denser oceanic slab sinks into the asthenosphere. - Pockets of magma develop and rise. - Continental volcanic arcs form in part by volcanic activity caused by the subducti ...
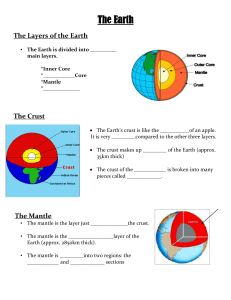
The Earth The Layers of the Earth • The Earth is divided into ______
... Remember, there are two types of crust: ________________ crust, which extends all over the earth and is broken into the 12 large and many smaller plates; and, _______________________ crust, which “rides around” on top of the oceanic crustal plates ...
... Remember, there are two types of crust: ________________ crust, which extends all over the earth and is broken into the 12 large and many smaller plates; and, _______________________ crust, which “rides around” on top of the oceanic crustal plates ...
Tectonics III - MSU Billings
... a. Long columns of hot, less dense rock, rising from deep in the mantle which are responsible for the volcanism at mid-ocean ridge spreading zones such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge b. Long columns of hot, less dense rock, rising from deep in the mantle and usually erupting in the middle of oceanic and ...
... a. Long columns of hot, less dense rock, rising from deep in the mantle which are responsible for the volcanism at mid-ocean ridge spreading zones such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge b. Long columns of hot, less dense rock, rising from deep in the mantle and usually erupting in the middle of oceanic and ...
Plate Tectonics
... The crust and upper mantle is made up of plates. The crust and upper mantle is called the lithosphere Scientists believe that the plates move about 2 inches per year. The lithosphere is broken into giant plates that fit around the globe like puzzle pieces. they slide on top of a somewhat fluid part ...
... The crust and upper mantle is made up of plates. The crust and upper mantle is called the lithosphere Scientists believe that the plates move about 2 inches per year. The lithosphere is broken into giant plates that fit around the globe like puzzle pieces. they slide on top of a somewhat fluid part ...
Earth`s 4 main Layers
... different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and has the ability to flow. The outer core and inner core are even hotter with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ball smaller than a marble if you wer ...
... different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and has the ability to flow. The outer core and inner core are even hotter with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ball smaller than a marble if you wer ...
What is the name of the SUPERCONTINENT that was once one land
... • Heat transfers by movement of currents in liquids and gasses. This is caused by differences in temperature and density. An example of this type of heat transfer occurs when mantle rock moves from near the core, towards the crust, and back again. A. Radiation B. Conduction C. Convection D. Compact ...
... • Heat transfers by movement of currents in liquids and gasses. This is caused by differences in temperature and density. An example of this type of heat transfer occurs when mantle rock moves from near the core, towards the crust, and back again. A. Radiation B. Conduction C. Convection D. Compact ...
Earth`s Layers Vocabulary
... Crust: A thin outer layer of rock above a planet’s mantle, including all dry land and ocean basins made of silicates. Mantle: The layer of rock between Earth’s core and crust, in which most rock is hot enough to flow in convection currents; Earth’s thickest layer. Mainly made of iron, magnesium and ...
... Crust: A thin outer layer of rock above a planet’s mantle, including all dry land and ocean basins made of silicates. Mantle: The layer of rock between Earth’s core and crust, in which most rock is hot enough to flow in convection currents; Earth’s thickest layer. Mainly made of iron, magnesium and ...
Mantle plume
A mantle plume is a mechanism proposed in 1971 to explain volcanic regions of the earth that were not thought to be explicable by the then-new theory of plate tectonics. Some such volcanic regions lie far from tectonic plate boundaries, for example, Hawaii. Others represent unusually large-volume volcanism, whether on plate boundaries, e.g. Iceland, or basalt floods such as the Deccan or Siberian traps.A mantle plume is posited to exist where hot rock nucleates at the core-mantle boundary and rises through the Earth's mantle becoming a diapir in the Earth's crust. The currently active volcanic centers are known as ""hot spots"". In particular, the concept that mantle plumes are fixed relative to one another, and anchored at the core-mantle boundary, was thought to provide a natural explanation for the time-progressive chains of older volcanoes seen extending out from some such hot spots, such as the Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain.The hypothesis of mantle plumes from depth is not universally accepted as explaining all such volcanism. It has required progressive hypothesis-elaboration leading to variant propositions such as mini-plumes and pulsing plumes. Another hypothesis for unusual volcanic regions is the ""Plate model"". This proposes shallower, passive leakage of magma from the mantle onto the Earth's surface where extension of the lithosphere permits it, attributing most volcanism to plate tectonic processes, with volcanoes far from plate boundaries resulting from intraplate extension.