Thermal isostasy —a new look at its potential to advance diluvial
... the Ontong Java Plateau).4 The terrestrial LIPs rocks have not formed by sea floor spreading or subduction. Based on the study of volcanoes on other planets (Venus and Mars) where there is no evidence for plate tectonics (so- ca ...
... the Ontong Java Plateau).4 The terrestrial LIPs rocks have not formed by sea floor spreading or subduction. Based on the study of volcanoes on other planets (Venus and Mars) where there is no evidence for plate tectonics (so- ca ...
Plate Tectonics - Nutley Public Schools
... Fault: a fracture in bedrock, along which blocks of rock on opposite sides of the fracture move Ex. San Andreas Fault, California Plate Tectonics: Theory that lithosphere is broken into segments/plates that float on the asthenosphere and is associated with earthquakes, and volcanic activity. ...
... Fault: a fracture in bedrock, along which blocks of rock on opposite sides of the fracture move Ex. San Andreas Fault, California Plate Tectonics: Theory that lithosphere is broken into segments/plates that float on the asthenosphere and is associated with earthquakes, and volcanic activity. ...
Plate Tectonics Notes
... - Where does the heat source come from? Mostly from the decay of radioisotopes in the earth’s interior. - About 94% of the heat comes from the Mantle, and about 6% from the core material - The release of heat (=energy) from the mantle causes volcanoes - Core heat causes the formation of hot spots, a ...
... - Where does the heat source come from? Mostly from the decay of radioisotopes in the earth’s interior. - About 94% of the heat comes from the Mantle, and about 6% from the core material - The release of heat (=energy) from the mantle causes volcanoes - Core heat causes the formation of hot spots, a ...
File
... – Think about things that you can do here that you may not be able to do in other countries. ...
... – Think about things that you can do here that you may not be able to do in other countries. ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... Most scientists agree that soon after its formation, the Earth was a large ball of molten rocky material. As time passed, the molten material cooled, hardened, and separated into layers. By studying such things as seismic waves that are sent out by earthquakes, scientists have found that the Earth i ...
... Most scientists agree that soon after its formation, the Earth was a large ball of molten rocky material. As time passed, the molten material cooled, hardened, and separated into layers. By studying such things as seismic waves that are sent out by earthquakes, scientists have found that the Earth i ...
No Slide Title
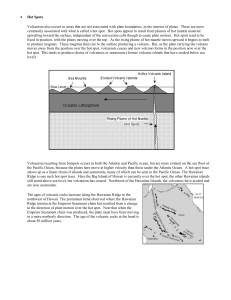
... Not associated with plate boundary As plate moves over hot spot, island chains form Example: Hawaii ...
... Not associated with plate boundary As plate moves over hot spot, island chains form Example: Hawaii ...
What Happens During Convection?
... cells in Earth’s mantle. A convection cell is one complete loop of convection current. Use the figure to answer the questions that follow. ...
... cells in Earth’s mantle. A convection cell is one complete loop of convection current. Use the figure to answer the questions that follow. ...
Bell Ringer Answers 1-31-11
... ways to make new minerals Because most rocks contain several types of minerals. Nonfoliated; because it would have been changed by heat of lava flows and not by high pressure. ...
... ways to make new minerals Because most rocks contain several types of minerals. Nonfoliated; because it would have been changed by heat of lava flows and not by high pressure. ...
Length scales of mantle heterogeneities from seismological
... Contour line spacing is every 20 deg in epicentral distance ...
... Contour line spacing is every 20 deg in epicentral distance ...
Earth`s Surface
... began to collide and clump together. These clumps collided with other clumps until eventually, the Earth and other planets were formed. The early Earth was likely extremely hot and the rock was molten in nature. This allowed the materials that make up the Earth to settle according to their density. ...
... began to collide and clump together. These clumps collided with other clumps until eventually, the Earth and other planets were formed. The early Earth was likely extremely hot and the rock was molten in nature. This allowed the materials that make up the Earth to settle according to their density. ...
Plate Tectonics Lecture Notes Page
... 3. Pacific Ring of Fire (1935-1940): Earthquakes & volcanoes in Pacific associated with C. Drift Pacific Basin: Zone of frequent earthquakes & volcanic eruptions, oceanic trenches Patterns of 10,000 earthquakes = Earth is divided into sectionsEcho Soundings revealed a submerged, mid-oceanic mountain ...
... 3. Pacific Ring of Fire (1935-1940): Earthquakes & volcanoes in Pacific associated with C. Drift Pacific Basin: Zone of frequent earthquakes & volcanic eruptions, oceanic trenches Patterns of 10,000 earthquakes = Earth is divided into sectionsEcho Soundings revealed a submerged, mid-oceanic mountain ...
Chapter 4 (Plate Tectonics)
... Search for a mechanism • Earth’s internal heat – Conduction • Slow release of heat ...
... Search for a mechanism • Earth’s internal heat – Conduction • Slow release of heat ...
Document
... still stand above sea level, but volcanism has ceased. Northwest of the Hawaiian Islands, the volcanoes have eroded and are now seamounts. The ages of volcanic rocks increase along the Hawaiian Ridge to the northwest of Hawaii. The prominent bend observed where the Hawaiian Ridge intersects the Empe ...
... still stand above sea level, but volcanism has ceased. Northwest of the Hawaiian Islands, the volcanoes have eroded and are now seamounts. The ages of volcanic rocks increase along the Hawaiian Ridge to the northwest of Hawaii. The prominent bend observed where the Hawaiian Ridge intersects the Empe ...
Get out your pieces for Tectonicland Have your HOMEWORK out
... Answer these questions in your notebook: ...
... Answer these questions in your notebook: ...
Name
... 15. According to Wegener’s hypothesis of continental drift, the continents were once joined together in a single landmass. 16. The name of the supercontinent that existed millions of years ago is Pangaea. 17. What type of evidence was used by Alfred Wegener to support his continental drift hypothesi ...
... 15. According to Wegener’s hypothesis of continental drift, the continents were once joined together in a single landmass. 16. The name of the supercontinent that existed millions of years ago is Pangaea. 17. What type of evidence was used by Alfred Wegener to support his continental drift hypothesi ...
Olivia-module3
... Early Earth surely didn't exist in a gravitybound plasma state; internal temperature was probably pretty much as it is today – perhaps a little cooler, perhaps a little hotter. ...
... Early Earth surely didn't exist in a gravitybound plasma state; internal temperature was probably pretty much as it is today – perhaps a little cooler, perhaps a little hotter. ...
Pangea Location of different fossils, location of different types of
... where lava comes out. The oldest rocks are next to the continents. ...
... where lava comes out. The oldest rocks are next to the continents. ...
The Earth`s Interior & Plate Tectonics
... Continental-continental convergence When subducting plates contain continental material, two continents collide Can produce new mountain ranges such as the Himalayas ...
... Continental-continental convergence When subducting plates contain continental material, two continents collide Can produce new mountain ranges such as the Himalayas ...
The Earth`s Layers and Plate Tectonics Study Guide #1 Unit 3
... Suggested the theory of convection currents to explain how the continents moved around the Earth’s surface. ...
... Suggested the theory of convection currents to explain how the continents moved around the Earth’s surface. ...
Mantle plume
A mantle plume is a mechanism proposed in 1971 to explain volcanic regions of the earth that were not thought to be explicable by the then-new theory of plate tectonics. Some such volcanic regions lie far from tectonic plate boundaries, for example, Hawaii. Others represent unusually large-volume volcanism, whether on plate boundaries, e.g. Iceland, or basalt floods such as the Deccan or Siberian traps.A mantle plume is posited to exist where hot rock nucleates at the core-mantle boundary and rises through the Earth's mantle becoming a diapir in the Earth's crust. The currently active volcanic centers are known as ""hot spots"". In particular, the concept that mantle plumes are fixed relative to one another, and anchored at the core-mantle boundary, was thought to provide a natural explanation for the time-progressive chains of older volcanoes seen extending out from some such hot spots, such as the Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain.The hypothesis of mantle plumes from depth is not universally accepted as explaining all such volcanism. It has required progressive hypothesis-elaboration leading to variant propositions such as mini-plumes and pulsing plumes. Another hypothesis for unusual volcanic regions is the ""Plate model"". This proposes shallower, passive leakage of magma from the mantle onto the Earth's surface where extension of the lithosphere permits it, attributing most volcanism to plate tectonic processes, with volcanoes far from plate boundaries resulting from intraplate extension.