
Cytology
... blood derived cells comparable to macrophages remove debris from the brain following injury and constitute an important defense system against pathogens. ...
... blood derived cells comparable to macrophages remove debris from the brain following injury and constitute an important defense system against pathogens. ...
Chapter 48 Reading Guide and Key Terms
... In the disease multiple sclerosis, myelin sheaths gradually harden and deteriorate. How would this affect nervous system function? ...
... In the disease multiple sclerosis, myelin sheaths gradually harden and deteriorate. How would this affect nervous system function? ...
Nervous System
... Motor – away from brain/spinal cord (efferent) Interneuron – conduct impulses from sensory to motor neurons. ...
... Motor – away from brain/spinal cord (efferent) Interneuron – conduct impulses from sensory to motor neurons. ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... Surround clusters of neuronal cell bodies in the PNS Unknown function ...
... Surround clusters of neuronal cell bodies in the PNS Unknown function ...
Action Potentials
... _________________________________________________ regulate composition of brain tissue fluid convert glucose to lactate to feed neurons secrete nerve growth factor promoting synapse formation electrical influence on synaptic signaling sclerosis – damaged neurons replace by hardened mass of astrocyte ...
... _________________________________________________ regulate composition of brain tissue fluid convert glucose to lactate to feed neurons secrete nerve growth factor promoting synapse formation electrical influence on synaptic signaling sclerosis – damaged neurons replace by hardened mass of astrocyte ...
Ch. 48 - 49
... are made by Schwanns cells or oligodendrocytes What is a Node of Ranvier? What is saltatory conduction? What is a synapse? ...
... are made by Schwanns cells or oligodendrocytes What is a Node of Ranvier? What is saltatory conduction? What is a synapse? ...
Exercise 17 - Harford Community College
... specialized cells that conduct messages in the form of electrical impulses throughout the body ...
... specialized cells that conduct messages in the form of electrical impulses throughout the body ...
Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses Quiz Answers
... a) one dendrite and many axons covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier b) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier c) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by the synapse d) one dendrite and many axon ...
... a) one dendrite and many axons covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier b) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier c) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by the synapse d) one dendrite and many axon ...
Neurons, Neurons, Neurons!
... spinal cord cannot reach other parts of the body. Damage, or scarring, occurs in many places throughout the central nervous system, hence the term "Multiple Sclerosis." ...
... spinal cord cannot reach other parts of the body. Damage, or scarring, occurs in many places throughout the central nervous system, hence the term "Multiple Sclerosis." ...
Biology 30 Unit 1: The Nervous System
... conduct nerve impulses away from the cell body. The axon carries nerve impulses toward other neurons or to effectors. Most nerves are comprised of many axons held together by connective tissue. ...
... conduct nerve impulses away from the cell body. The axon carries nerve impulses toward other neurons or to effectors. Most nerves are comprised of many axons held together by connective tissue. ...
bio 342 human physiology
... Eventually, the electrostatic force that impedes diffusion of K+ is exactly equal to the driving force favoring diffusion based on a concentration gradient. When these two driving forces are equal and opposite, the membrane potential reaches an equilibrium at which the voltage is called ...
... Eventually, the electrostatic force that impedes diffusion of K+ is exactly equal to the driving force favoring diffusion based on a concentration gradient. When these two driving forces are equal and opposite, the membrane potential reaches an equilibrium at which the voltage is called ...
Slide ()
... storehouse of genetic information, and gives rise to two types of cell processes: axons and dendrites. Axons are the transmitting element of neurons; they vary greatly in length, some extending more than 2 m within the body. Most axons in the central nervous system are very thin (between 0.2 μm and ...
... storehouse of genetic information, and gives rise to two types of cell processes: axons and dendrites. Axons are the transmitting element of neurons; they vary greatly in length, some extending more than 2 m within the body. Most axons in the central nervous system are very thin (between 0.2 μm and ...
• dendrite - Dental Decks
... • Cell body (perikaryon) - contains the nucleus and most of the cytoplasm. Located mostly in the central nervous system as clusters called nuclei, some found in the peripheral nervous system as groups called ganglia (two types: sensory and autonomic). - Sensory ganglia contain cell bodies of either ...
... • Cell body (perikaryon) - contains the nucleus and most of the cytoplasm. Located mostly in the central nervous system as clusters called nuclei, some found in the peripheral nervous system as groups called ganglia (two types: sensory and autonomic). - Sensory ganglia contain cell bodies of either ...
presentation source
... propagates continously along the axons by sequentially activating populations of Na+ channels in adjoining segments of axon ...
... propagates continously along the axons by sequentially activating populations of Na+ channels in adjoining segments of axon ...
Neuron and Neuroglial Review Worksheet
... B. Match the anatomical terms given in Column B with the appropriate descriptions of function provided in Column A. Place the correct term or letter response in the answer blanks. Column A 1. Releases neurotransmitters ____B_____ 2. Conducts electrical currents ___C_____ towards the cell body 3. Inc ...
... B. Match the anatomical terms given in Column B with the appropriate descriptions of function provided in Column A. Place the correct term or letter response in the answer blanks. Column A 1. Releases neurotransmitters ____B_____ 2. Conducts electrical currents ___C_____ towards the cell body 3. Inc ...
Nervous System Vocab1 - Everglades High School
... 28. Neurilemma: Part of the schwann cell, external to the myelin sheath 29. Nodes of Ranvier: gaps or indentations between the schwann cells 30. Ganglia: Small collection of cell bodies outside of the CNS 31. White Matter: Dense collection of myelinated fibers 32. Gray Matter: contains mostly unmyel ...
... 28. Neurilemma: Part of the schwann cell, external to the myelin sheath 29. Nodes of Ranvier: gaps or indentations between the schwann cells 30. Ganglia: Small collection of cell bodies outside of the CNS 31. White Matter: Dense collection of myelinated fibers 32. Gray Matter: contains mostly unmyel ...
Nervous System Neurons And Synapses
... the synapse (since its “uptake” is inhibited), thereby activating postsynaptic neurons that maintain a more positive mood. Common SSRIs include Prozac, Paxil, and Zoloft. ...
... the synapse (since its “uptake” is inhibited), thereby activating postsynaptic neurons that maintain a more positive mood. Common SSRIs include Prozac, Paxil, and Zoloft. ...
Nolte – Chapter 1 (Introduction to the Nervous
... o Provide metabolic support and electrical insulation in the PNS. o Some are flattened out as satellite cells. o Provide an infrastructure/scaffolding for new growth Emit NGF o Envelop unmylenated PNS axons Myelination o Myelin between two nodes of Ranvier is known as an internode. o Less myelin, ...
... o Provide metabolic support and electrical insulation in the PNS. o Some are flattened out as satellite cells. o Provide an infrastructure/scaffolding for new growth Emit NGF o Envelop unmylenated PNS axons Myelination o Myelin between two nodes of Ranvier is known as an internode. o Less myelin, ...
Neuron [or Nerve Cell]
... structure in the soma of the neuron that contains the chromosomes. The part of the neuron where the nucleus is found. Most of the protein production and energy storage is performed at this point in the cell. A layer of fatty cells that covers many axons and helps speed neural impulses The portion of ...
... structure in the soma of the neuron that contains the chromosomes. The part of the neuron where the nucleus is found. Most of the protein production and energy storage is performed at this point in the cell. A layer of fatty cells that covers many axons and helps speed neural impulses The portion of ...
Node of Ranvier

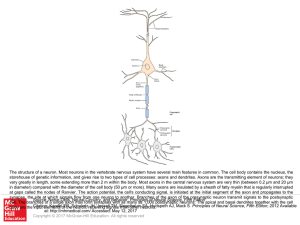
The nodes of Ranvier also known as myelin sheath gaps, are the gaps (approximately 1 micrometer in length) formed between the myelin sheaths generated by different cells. A myelin sheath is a many-layered coating, largely composed of a fatty substance called myelin, that wraps around the axon of a neuron and very efficiently insulates it. At nodes of Ranvier, the axonal membrane is uninsulated and, therefore, capable of generating electrical activity.






















![Neuron [or Nerve Cell]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000229750_1-5b124d2a0cf6014a7e82bd7195acd798-300x300.png)