Structure and Physiology of Neurons
... current towards cell body) – Cell body – Axon (conducts electrical current away from cell body) ...
... current towards cell body) – Cell body – Axon (conducts electrical current away from cell body) ...
Intro to Nervous System
... • Have similar function as oligodendrocytes and form the myelin sheaths (neurilemma) around axons. Satellite cells or Amphicytes • Only found in the ganglia of the PNS • Function is similar to that of astrocytes • Regulate environment around neuron cell bodies ...
... • Have similar function as oligodendrocytes and form the myelin sheaths (neurilemma) around axons. Satellite cells or Amphicytes • Only found in the ganglia of the PNS • Function is similar to that of astrocytes • Regulate environment around neuron cell bodies ...
Chapter 13 - Nervous Tissue
... -Consists of ganglia, cranial nerves, spinal nerves and peripheral receptors Ganglia = a collection of nerve cell bodies in the PNS Nerve = bundle of nerve fibers in the PNS ...
... -Consists of ganglia, cranial nerves, spinal nerves and peripheral receptors Ganglia = a collection of nerve cell bodies in the PNS Nerve = bundle of nerve fibers in the PNS ...
CHAPTER 11 Nervous Tissue - Austin Community College
... -Consists of ganglia, cranial nerves, spinal nerves and peripheral receptors Ganglia = a collection of nerve cell bodies in the PNS Nerve = bundle of nerve fibers in the PNS ...
... -Consists of ganglia, cranial nerves, spinal nerves and peripheral receptors Ganglia = a collection of nerve cell bodies in the PNS Nerve = bundle of nerve fibers in the PNS ...
Document
... • The membrane is electrically charged, “polarized” due to Na+ and K+ ions o Greater concentration of sodium ions outside and potassium ions inside. o Potassium ions pass through more easily o Active transport (sodium/potassium pump) maintains balance ...
... • The membrane is electrically charged, “polarized” due to Na+ and K+ ions o Greater concentration of sodium ions outside and potassium ions inside. o Potassium ions pass through more easily o Active transport (sodium/potassium pump) maintains balance ...
Nervous Tissue - Northland Community & Technical College
... consists of cranial and spinal nerves that contain both sensory and motor fibers connects CNS to muscles, glands & all sensory ...
... consists of cranial and spinal nerves that contain both sensory and motor fibers connects CNS to muscles, glands & all sensory ...
Nerve Junctions
... 1. What is the function of Schwan cells in a neurone? 2. What is meant by a saltatory conduction? 3. What three factors speed up the rate of conduction of action potentials? ...
... 1. What is the function of Schwan cells in a neurone? 2. What is meant by a saltatory conduction? 3. What three factors speed up the rate of conduction of action potentials? ...
Overview Functions of the Nervous System
... – Chemical - specialized for release and reception of chemical neurotransmitters • travel across the synapse to the postsynaptic cells, where they are converted back into electrical signals • Axon terminal: contains many tiny, membrane-bounded sacs (synaptic vesicles) containing thousands of neurotr ...
... – Chemical - specialized for release and reception of chemical neurotransmitters • travel across the synapse to the postsynaptic cells, where they are converted back into electrical signals • Axon terminal: contains many tiny, membrane-bounded sacs (synaptic vesicles) containing thousands of neurotr ...
Neurons: Our Building Blocks
... -In some neurons, like those of the brain, the axons are very short. In others, like those in the leg, they can reach 3 feet long. ...
... -In some neurons, like those of the brain, the axons are very short. In others, like those in the leg, they can reach 3 feet long. ...
Control and Integration Nervous System Organization: Radial
... • slow increase until threshold is reached • voltage-gated Na+ channels open – Na+ enters cell → further depolarization → more channels open → further ...
... • slow increase until threshold is reached • voltage-gated Na+ channels open – Na+ enters cell → further depolarization → more channels open → further ...
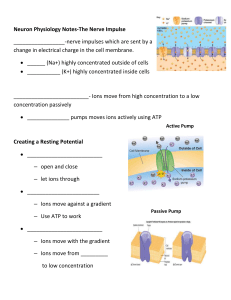
Neuron Physiology Notes
... by the influx of a neurotransmitters that causes sodium channels to open. Sodium moves inward causing neuron to depolarize. (-62mv) 3.) Threshold is reached when enough sodium enters the neuron to change the potential to (-55mv) which causes “trigger zone” to allow even more sodium into the neuron. ...
... by the influx of a neurotransmitters that causes sodium channels to open. Sodium moves inward causing neuron to depolarize. (-62mv) 3.) Threshold is reached when enough sodium enters the neuron to change the potential to (-55mv) which causes “trigger zone” to allow even more sodium into the neuron. ...
Neural Modeling
... • Cells that have the ability to transmit action potentials are called ‘excitable cells’. • The action potentials are initiated by inputs from the dendrites arriving at the axon hillock, where the axon meets the soma. • Then they travel down the axon to terminal branches which have synapses to the n ...
... • Cells that have the ability to transmit action potentials are called ‘excitable cells’. • The action potentials are initiated by inputs from the dendrites arriving at the axon hillock, where the axon meets the soma. • Then they travel down the axon to terminal branches which have synapses to the n ...
Neuroscience 3b – The Action Potential
... The depolarisation spreads along the axon by Na+ ions enter the cell and K+ ions leaving. Only a small number of ions cross causing a 0.1% concentration change. The current that is initiated induces depolarisation in the part of the axon just after (adjacent) to it. Just behind the action potential, ...
... The depolarisation spreads along the axon by Na+ ions enter the cell and K+ ions leaving. Only a small number of ions cross causing a 0.1% concentration change. The current that is initiated induces depolarisation in the part of the axon just after (adjacent) to it. Just behind the action potential, ...
The Nervous System - Ridgewood High School
... sheath, a wrapping of lipid which: – Protects the axon and electrically isolates it – Increases the rate of electrical action potential transmission ...
... sheath, a wrapping of lipid which: – Protects the axon and electrically isolates it – Increases the rate of electrical action potential transmission ...
Glial Cells
... The remaining two glial cells, Schwann cells and satellite cells are found solely in the peripheral nervous system. Schwann cells are analogous in function to oligodendrocytes (found in the CNS). They insulate the axons of peripheral nerves in one of two ways. A Schwann cell can wind its way round a ...
... The remaining two glial cells, Schwann cells and satellite cells are found solely in the peripheral nervous system. Schwann cells are analogous in function to oligodendrocytes (found in the CNS). They insulate the axons of peripheral nerves in one of two ways. A Schwann cell can wind its way round a ...
Synapses - JNCASR Desktop
... Neurons are the basic data processing units of the brain. Each neuron receives electrical inputs from about 1000 other neurons. Impulses arriving simultaneously are added together and, if sufficiently strong, lead to the generation of an electrical discharge, known as an action potential (a 'nerve i ...
... Neurons are the basic data processing units of the brain. Each neuron receives electrical inputs from about 1000 other neurons. Impulses arriving simultaneously are added together and, if sufficiently strong, lead to the generation of an electrical discharge, known as an action potential (a 'nerve i ...
The Nervous System * Crash Course Biology
... ________________________ a fatty substance that covers the axon ____________________________ breaks in the myelin sheath that lets the signal hop down the neuron ___________________________________ this means leaping, as in the info jumps from node to node _______________________________ the space b ...
... ________________________ a fatty substance that covers the axon ____________________________ breaks in the myelin sheath that lets the signal hop down the neuron ___________________________________ this means leaping, as in the info jumps from node to node _______________________________ the space b ...
M.learning.hccs.edu
... 4. An action potential depolarizes the synaptic terminal at the presynaptic membrane. 5. The synaptic terminal reabsorbs choline. 6. Acetylcholine is released from storage vesicles by exocytosis. 7. Acetylcholine binds to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane. 8. Calcium ions are removed from the c ...
... 4. An action potential depolarizes the synaptic terminal at the presynaptic membrane. 5. The synaptic terminal reabsorbs choline. 6. Acetylcholine is released from storage vesicles by exocytosis. 7. Acetylcholine binds to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane. 8. Calcium ions are removed from the c ...
Resting Membrane Potential
... Excitable tissues of nerves and muscles cells have higher potentials than other cells (epithelial cells and connective tissue cells). Dead cells do not have membrane potentials. ...
... Excitable tissues of nerves and muscles cells have higher potentials than other cells (epithelial cells and connective tissue cells). Dead cells do not have membrane potentials. ...
Doktryna neuronu
... the membrane hyperpolarization that results from opening of voltage-gated K+ channels ...
... the membrane hyperpolarization that results from opening of voltage-gated K+ channels ...
chapt12-nervous system
... The action potential occurs in each successive portion of an axon. A refractory period ensures that the action potential will not move backwards. In myelinated fibers the action potential only occurs at the nodes of Ranvier. This is called saltatory conduction. The Synapse Transmission of the nerve ...
... The action potential occurs in each successive portion of an axon. A refractory period ensures that the action potential will not move backwards. In myelinated fibers the action potential only occurs at the nodes of Ranvier. This is called saltatory conduction. The Synapse Transmission of the nerve ...
7-Nerves - bloodhounds Incorporated
... Activation of α1-receptors usually results in a slow depolarization linked to the inhibition of K+ channels activation of α2-receptors produces a slow hyperpolarization due to the activation of a different type of K+ channel. ...
... Activation of α1-receptors usually results in a slow depolarization linked to the inhibition of K+ channels activation of α2-receptors produces a slow hyperpolarization due to the activation of a different type of K+ channel. ...
Nervous System - Emery
... Neuron Signalling How do electrical signals pass through cells? Membrane Potential glial cells provide insulation for electrical ...
... Neuron Signalling How do electrical signals pass through cells? Membrane Potential glial cells provide insulation for electrical ...
Nervous System
... Axon – single nerve fiber that carries impulses away from the cell body •Covered with lipid (fat) covering called a myelin sheath •Increases rate of transmission of an impulse •Insulates and maintains the axon ...
... Axon – single nerve fiber that carries impulses away from the cell body •Covered with lipid (fat) covering called a myelin sheath •Increases rate of transmission of an impulse •Insulates and maintains the axon ...
Node of Ranvier

The nodes of Ranvier also known as myelin sheath gaps, are the gaps (approximately 1 micrometer in length) formed between the myelin sheaths generated by different cells. A myelin sheath is a many-layered coating, largely composed of a fatty substance called myelin, that wraps around the axon of a neuron and very efficiently insulates it. At nodes of Ranvier, the axonal membrane is uninsulated and, therefore, capable of generating electrical activity.