Slide 1
... • In fact all T=3 RNA viruses have proteins that form “8 strand antiparallel b barrels”. • The structures form from the polypeptide by first forming a “jelly-roll barrel” that then goes on to form the wedge-shaped barrel when the capsid is being formed. ...
... • In fact all T=3 RNA viruses have proteins that form “8 strand antiparallel b barrels”. • The structures form from the polypeptide by first forming a “jelly-roll barrel” that then goes on to form the wedge-shaped barrel when the capsid is being formed. ...
Biochemistry 2000 Sample Question Protein
... (b) If a Trp residue has = 60º , = 120º, is it in an energetically favorable conformation? (c) If a Gly residue has = 120º , = 60º, is it in an energetically favorable conformation? (5) Pauling predicted the structures of both -helices and -sheets from modeling studies. What physiochemic ...
... (b) If a Trp residue has = 60º , = 120º, is it in an energetically favorable conformation? (c) If a Gly residue has = 120º , = 60º, is it in an energetically favorable conformation? (5) Pauling predicted the structures of both -helices and -sheets from modeling studies. What physiochemic ...
Endocrine Pharmacology
... How long a hormone stays high in blood? Depends on: - Extent of protein binding - Efficiency of degradable enzymes & clearance Metabolism & excretion - Efficiency of negative feedback mechanisms ...
... How long a hormone stays high in blood? Depends on: - Extent of protein binding - Efficiency of degradable enzymes & clearance Metabolism & excretion - Efficiency of negative feedback mechanisms ...
Section Slides
... of these cells. When you examine the membrane using a microscope, you find that the tag is distributed diffusely across the cell surface. To determine the mobility of this phospholipid in the membrane, you use ...
... of these cells. When you examine the membrane using a microscope, you find that the tag is distributed diffusely across the cell surface. To determine the mobility of this phospholipid in the membrane, you use ...
Protein - Rainbow Lunches
... protein is present in our body such as our muscles, nails and hair. Each is structured differently. In simple terms, proteins are made up of long chains of amino acids of which there are 22 different types. Our bodies need all of them in order to function properly. Of the 22 amino acids, your body c ...
... protein is present in our body such as our muscles, nails and hair. Each is structured differently. In simple terms, proteins are made up of long chains of amino acids of which there are 22 different types. Our bodies need all of them in order to function properly. Of the 22 amino acids, your body c ...
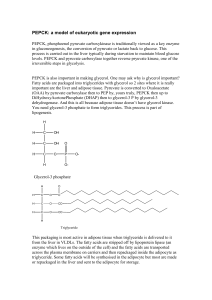
PEPCK: a model of eukaryotic gene expression
... In the normal fed state PEPCK mRNA in the liver is rapidly turned over. This is typical for a sequence which is regulated at the level of gene expression. Why? In the fed state insulin is released by the pancreas and this suppresses transcription of PEPCK, the mRNA is unstable so very little PEPCK p ...
... In the normal fed state PEPCK mRNA in the liver is rapidly turned over. This is typical for a sequence which is regulated at the level of gene expression. Why? In the fed state insulin is released by the pancreas and this suppresses transcription of PEPCK, the mRNA is unstable so very little PEPCK p ...
Cas_ProteinsFinal
... acids in length Are usually 210-265 amino acids long From: EMBL IPR013422 profile page (: http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/IEntry?ac=IPR013422) ...
... acids in length Are usually 210-265 amino acids long From: EMBL IPR013422 profile page (: http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/IEntry?ac=IPR013422) ...
5)qualitative_tests_of_proteins
... 2- Secondary structure: is the specific geometric shape caused by intramolecular and intermolecular hydrogen bonding of amide groups. Some combinations of amino acids will tend to form: Alpha Helix: In the alpha helix, the polypeptide chain is coiled tightly in the fashion of a spring. The "backbone ...
... 2- Secondary structure: is the specific geometric shape caused by intramolecular and intermolecular hydrogen bonding of amide groups. Some combinations of amino acids will tend to form: Alpha Helix: In the alpha helix, the polypeptide chain is coiled tightly in the fashion of a spring. The "backbone ...
Protein Labeling
... intein fused to its C-terminus. The second half of the split intein covalently linked to a small-molecule probe and a protein transduction domain (PTD) peptide is added to the cell growth media. Upon entering the cell, the PTD, linked to the probe-derivatized intein half via a disulfide bond, is rel ...
... intein fused to its C-terminus. The second half of the split intein covalently linked to a small-molecule probe and a protein transduction domain (PTD) peptide is added to the cell growth media. Upon entering the cell, the PTD, linked to the probe-derivatized intein half via a disulfide bond, is rel ...
Model Description Sheet
... TrxA whose function is unknown and TrxC, whose function has been well studied, have similar structures, thus it can be hypothesized that their functions are similar. Comparing binding sites between the proteins could provide insight if TrxA reacts with TrxR similarly to TrxC. By modeling TrxA and Tr ...
... TrxA whose function is unknown and TrxC, whose function has been well studied, have similar structures, thus it can be hypothesized that their functions are similar. Comparing binding sites between the proteins could provide insight if TrxA reacts with TrxR similarly to TrxC. By modeling TrxA and Tr ...
They do NOT like water!
... – Contains adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. – Sugar is deoxyribose. ...
... – Contains adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. – Sugar is deoxyribose. ...
Proteins and Protein Synthesis: A n Overview
... change in a key will allow it to open only one door. The protein molecule has highly specific binding sites, which are determined by the following: Electrical charges Number and strength of electrical attractions Three-dimensional considerations Essentially, all cellular function and regulation is d ...
... change in a key will allow it to open only one door. The protein molecule has highly specific binding sites, which are determined by the following: Electrical charges Number and strength of electrical attractions Three-dimensional considerations Essentially, all cellular function and regulation is d ...
Instructions for Mem-mEN Web-server
... Membrane proteins, which interact with the membranes of a cell or an organelle, play essential roles in a variety of vital biological processes. Because membrane proteins mediate many interactions between cells and extracellular surroundings as well as between the cytosol and membrane-bound organell ...
... Membrane proteins, which interact with the membranes of a cell or an organelle, play essential roles in a variety of vital biological processes. Because membrane proteins mediate many interactions between cells and extracellular surroundings as well as between the cytosol and membrane-bound organell ...
Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha
... replication, tumorigenesis, and autoimmune diseases; and in viral, bacterial, fungal, and parasitic infections. Besides inducing hemorrhagic necrosis of tumors, TNF was found to be involved in tumorigenesis, tumor metastasis, viral replication, septic shock, fever, inflammation, and autoimmune disea ...
... replication, tumorigenesis, and autoimmune diseases; and in viral, bacterial, fungal, and parasitic infections. Besides inducing hemorrhagic necrosis of tumors, TNF was found to be involved in tumorigenesis, tumor metastasis, viral replication, septic shock, fever, inflammation, and autoimmune disea ...
Chapter 11. Protein Structure and Function
... Four levels of protein structure • Primary structure The sequence of amino acids in a protein. • Secondary structure Way that chains of amino acids are coiled or folded (-helix, -sheet, random coil). • Tertiary structure Way -helix, -sheet, random coils fold and coil. ...
... Four levels of protein structure • Primary structure The sequence of amino acids in a protein. • Secondary structure Way that chains of amino acids are coiled or folded (-helix, -sheet, random coil). • Tertiary structure Way -helix, -sheet, random coils fold and coil. ...
Protein concentration measurement by UV
... will expose all aromatic residues to equivalent environment and minimize the effect of the folded protein on their absorbance, but at the same time it will also hide any problems with aggregation of the material as all protein will be denatured and solubilised. Depending on the method, the absorptio ...
... will expose all aromatic residues to equivalent environment and minimize the effect of the folded protein on their absorbance, but at the same time it will also hide any problems with aggregation of the material as all protein will be denatured and solubilised. Depending on the method, the absorptio ...
Caenorhabditis elegans genes sma-2, sma-3, and sma
... poorly conserved proline-rich linker of '90 aa. SMA-4 is the most divergent member of the family, distinguished by a 160-aa N-terminal extension and a 25-aa insert in DH2. Vertebrate Dwarfins Are Highly Homologous to SMA-2, SMA-3, and SMA-4. We were interested in whether vertebrate dwarfins exist, s ...
... poorly conserved proline-rich linker of '90 aa. SMA-4 is the most divergent member of the family, distinguished by a 160-aa N-terminal extension and a 25-aa insert in DH2. Vertebrate Dwarfins Are Highly Homologous to SMA-2, SMA-3, and SMA-4. We were interested in whether vertebrate dwarfins exist, s ...
Gene Section PTPN21 (protein tyrosine phosphatase, non- receptor type 21)
... ATP synthesis. PTPD1 has been also implicated in the regulation of the Tec family kinases and activation of Stat3 signaling pathway. ...
... ATP synthesis. PTPD1 has been also implicated in the regulation of the Tec family kinases and activation of Stat3 signaling pathway. ...
Appendix 3 Assessment of the effects of the observed variants We
... aligned for prediction. This enables estimation of the reliability of the analysis. In addition to sequence homology approaches, PolyPhen-2 (7) and SNPs3D (Yue, Melamud and Moult 2006) adds protein structure principles to its prediction models, which may give insights into protein stability, and pos ...
... aligned for prediction. This enables estimation of the reliability of the analysis. In addition to sequence homology approaches, PolyPhen-2 (7) and SNPs3D (Yue, Melamud and Moult 2006) adds protein structure principles to its prediction models, which may give insights into protein stability, and pos ...
Gene Section MAPK4 (mitogen-activated protein kinase 4) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... protein (MAP) kinase family of serine/threonine kinases. The human ERK4 protein is made of 587 amino acids and contains a typical kinase domain located at the N-terminal extremity. Another region with homology to the MAP kinase ERK3 (C34 domain) has been identified after the kinase domain. The funct ...
... protein (MAP) kinase family of serine/threonine kinases. The human ERK4 protein is made of 587 amino acids and contains a typical kinase domain located at the N-terminal extremity. Another region with homology to the MAP kinase ERK3 (C34 domain) has been identified after the kinase domain. The funct ...
Chapter01 Introduction Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins (绪论
... Due to weak interactions between side (R) groups as well as covalent disulfide bonds Weak interactions Hydrogen bonds Electrostatic interactions (ionic bonds) Hydrophobic interactions Van der Waals interactions Quaternary: arrangement of subunits (in multisubunit protein) Held together by weak inter ...
... Due to weak interactions between side (R) groups as well as covalent disulfide bonds Weak interactions Hydrogen bonds Electrostatic interactions (ionic bonds) Hydrophobic interactions Van der Waals interactions Quaternary: arrangement of subunits (in multisubunit protein) Held together by weak inter ...
Nutritional Requirements of Non
... Other plant and animal proteins are often used in combination with SBM. • Fishmeal (60-70% CP) (Crude Protein) • Milk products, such as dried skimmed milk (33% CP) and dried whey (13.3% CP) • Meat and bone meal (50% CP) • Spray dried plasma protein and bloodmeal (86% CP) ...
... Other plant and animal proteins are often used in combination with SBM. • Fishmeal (60-70% CP) (Crude Protein) • Milk products, such as dried skimmed milk (33% CP) and dried whey (13.3% CP) • Meat and bone meal (50% CP) • Spray dried plasma protein and bloodmeal (86% CP) ...
Nutritional Requirements of Non
... Other plant and animal proteins are often used in combination with SBM. • Fishmeal (60-70% CP) (Crude Protein) • Milk products, such as dried skimmed milk (33% CP) and dried whey (13.3% CP) • Meat and bone meal (50% CP) • Spray dried plasma protein and bloodmeal (86% CP) ...
... Other plant and animal proteins are often used in combination with SBM. • Fishmeal (60-70% CP) (Crude Protein) • Milk products, such as dried skimmed milk (33% CP) and dried whey (13.3% CP) • Meat and bone meal (50% CP) • Spray dried plasma protein and bloodmeal (86% CP) ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).