A Statistical Analysis of the Linear Interaction Energy Method
... relevant flexible targets (some 30 systems!) • Consequences of protein flexibility for ligand design – One site, several ligand binding modes possible ...
... relevant flexible targets (some 30 systems!) • Consequences of protein flexibility for ligand design – One site, several ligand binding modes possible ...
Post-translational modifications on human cell expressed
... cells as opposed to non-human cells. These methods determine not only the differences in glycosylation but may also give some insight into the possible differences in function of the protein. ...
... cells as opposed to non-human cells. These methods determine not only the differences in glycosylation but may also give some insight into the possible differences in function of the protein. ...
15.Flexible_Protein_Docking_Jonathan
... relevant flexible targets (some 30 systems!) • Consequences of protein flexibility for ligand design – One site, several ligand binding modes possible ...
... relevant flexible targets (some 30 systems!) • Consequences of protein flexibility for ligand design – One site, several ligand binding modes possible ...
ER, Golgi and Vesicles :
... beyond just keeping them from being active is not exclusive to assembly. A major class of cleaved peptide sequences is signal peptides. Signal peptides direct the protein from the cytoplasm into a particular cellular compartment. In the case of prokaryotes, this essentially means the cell membrane, ...
... beyond just keeping them from being active is not exclusive to assembly. A major class of cleaved peptide sequences is signal peptides. Signal peptides direct the protein from the cytoplasm into a particular cellular compartment. In the case of prokaryotes, this essentially means the cell membrane, ...
BCL-2 Family Proteins: Critical Checkpoints of Apoptotic
... 1) operates downstream of death receptors 2) Fas, TNFR(Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor) family 3) leads to the recruitment of a DISC (death inducing signaling complex) ...
... 1) operates downstream of death receptors 2) Fas, TNFR(Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor) family 3) leads to the recruitment of a DISC (death inducing signaling complex) ...
Protein-Misfolding Diseases
... General facts on protein folding Chaperones The concentration of chaperones is genetically selfregulated and increases with the presence of misfolded proteins. They possess an ATPase domain that reversibly binds with the hydrophobic parts of partially folded proteins ...
... General facts on protein folding Chaperones The concentration of chaperones is genetically selfregulated and increases with the presence of misfolded proteins. They possess an ATPase domain that reversibly binds with the hydrophobic parts of partially folded proteins ...
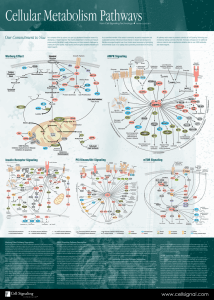
Cellular Metabolism Pathways
... Cancer cells frequently use glutamine as a secondary fuel source, which enters the mitochondria and can be used to replenish Krebs Cycle intermediates or can be used to produce more pyruvate through the action of malic enzyme. Highly proliferative cells need to produce excess lipid, nucleotide, and ...
... Cancer cells frequently use glutamine as a secondary fuel source, which enters the mitochondria and can be used to replenish Krebs Cycle intermediates or can be used to produce more pyruvate through the action of malic enzyme. Highly proliferative cells need to produce excess lipid, nucleotide, and ...
Team Publications
... Exosomes are small membrane vesicles, secreted by most cell types from multivesicular endosomes, and thought to play important roles in intercellular communications. Initially described in 1983, as specifically secreted by reticulocytes, exosomes became of interest for immunologists in 1996, when the ...
... Exosomes are small membrane vesicles, secreted by most cell types from multivesicular endosomes, and thought to play important roles in intercellular communications. Initially described in 1983, as specifically secreted by reticulocytes, exosomes became of interest for immunologists in 1996, when the ...
Cell Signaling and Cancer
... Signaling pathways work through the interaction of a series of proteins. The message received by the cell is transmitted through the cell by activating these proteins. The receptor is activated by changing its shape in response to the binding of the chemical messenger. Once activated, the receptor ...
... Signaling pathways work through the interaction of a series of proteins. The message received by the cell is transmitted through the cell by activating these proteins. The receptor is activated by changing its shape in response to the binding of the chemical messenger. Once activated, the receptor ...
Eukaryotic transcriptional control
... monomers form a coiled-coil dimer. Basic amino acid residues N-terminal to the leucine zipper form the DNA-binding domain. ...
... monomers form a coiled-coil dimer. Basic amino acid residues N-terminal to the leucine zipper form the DNA-binding domain. ...
The SPFH domain - Tavernarakis Lab
... arrowheads denote mutations that disrupt the function of MEC-2 or UNC-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans. The green arrowbar denotes the region that has been shown to be important for oligomerization of vertebrate stomatin. Amino acid positions are indicated in the margins of the alignment. Numbers in pare ...
... arrowheads denote mutations that disrupt the function of MEC-2 or UNC-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans. The green arrowbar denotes the region that has been shown to be important for oligomerization of vertebrate stomatin. Amino acid positions are indicated in the margins of the alignment. Numbers in pare ...
Lecture 5
... Aspartic acid, asparagine, and serine have in common that they have short side chains that can form hydrogen bonds with the own backbone. These hydrogen bonds compensate the energy loss caused by bending the chain into a b-turn. ...
... Aspartic acid, asparagine, and serine have in common that they have short side chains that can form hydrogen bonds with the own backbone. These hydrogen bonds compensate the energy loss caused by bending the chain into a b-turn. ...
protein range - Absolute Organix Lifematrix
... all nine essential aminos and the branched-chain aminos. Research shows that egg white protein has similar effects on stimulating muscle development as whey. Lifematrix Egg White Protein Powder is manufactured in Belgium. The powder has a mild, neutral flavour. As with all Lifematrix protein powders ...
... all nine essential aminos and the branched-chain aminos. Research shows that egg white protein has similar effects on stimulating muscle development as whey. Lifematrix Egg White Protein Powder is manufactured in Belgium. The powder has a mild, neutral flavour. As with all Lifematrix protein powders ...
In Silico Salinispora Dinesh Kumar K. Waheeta Hopper
... extracellular domain, which binds to ligands that activate the receptor, (b) the transmembrane domain that is involved in dimerization interaction between receptors, and (c) the intracellular tyrosine kinase domain that phosphorylates tyrosine residues on substrate proteins. The crystal structures o ...
... extracellular domain, which binds to ligands that activate the receptor, (b) the transmembrane domain that is involved in dimerization interaction between receptors, and (c) the intracellular tyrosine kinase domain that phosphorylates tyrosine residues on substrate proteins. The crystal structures o ...
Lecture 3 - ISpatula
... - mole = g\ molecular weight . - 1 mole of all substances have the same number of molecules - Membrane is a bilayer of phospholipids that have charged heads & hydrophobic tails & that’s good (subhan allah ) because both the ECF & ICF are aqueous solutions ( water environment). - The bilayer is the m ...
... - mole = g\ molecular weight . - 1 mole of all substances have the same number of molecules - Membrane is a bilayer of phospholipids that have charged heads & hydrophobic tails & that’s good (subhan allah ) because both the ECF & ICF are aqueous solutions ( water environment). - The bilayer is the m ...
Super ShieldTM HRP Conjugate Stabilizer
... HRPZRTM is specially formulated for stabilize the activity of HRP conjugates. HRPZRTM also preserves proteins in various other assay systems. It is often used in ELISA, Western Blot, Southern/Northern Blots, and lateral flow. Super Shield can be used directly as an assay buffer. The product is suppl ...
... HRPZRTM is specially formulated for stabilize the activity of HRP conjugates. HRPZRTM also preserves proteins in various other assay systems. It is often used in ELISA, Western Blot, Southern/Northern Blots, and lateral flow. Super Shield can be used directly as an assay buffer. The product is suppl ...
Poster
... Signal transduction is an essential process in cells. One critical signaling molecule, protein kinase A (PKA), phosphorylates target proteins, thereby changing their conformations and modifying their functions. PKA is a component of multiple signaling pathways that regulate a variety of proteins. Si ...
... Signal transduction is an essential process in cells. One critical signaling molecule, protein kinase A (PKA), phosphorylates target proteins, thereby changing their conformations and modifying their functions. PKA is a component of multiple signaling pathways that regulate a variety of proteins. Si ...
Introduction
... one polypeptide chain(a-helical and b-sheet structure) Tertiary structure: Ionic interaction, hydrophobic interaction, hydrogen bonding and Van der Waals attraction formed among moieties within one polypeptide chain Quaternary structure: Weak chemical interactions among different polypeptide chains ...
... one polypeptide chain(a-helical and b-sheet structure) Tertiary structure: Ionic interaction, hydrophobic interaction, hydrogen bonding and Van der Waals attraction formed among moieties within one polypeptide chain Quaternary structure: Weak chemical interactions among different polypeptide chains ...
MS Word File
... Primary structure is the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide (Usually read N-C) Secondary structures are localized folds or helices that form within a region of a polypeptide Tertiary structures are larger folding events that are stabilized by interactions between R groups Quaternary structure ...
... Primary structure is the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide (Usually read N-C) Secondary structures are localized folds or helices that form within a region of a polypeptide Tertiary structures are larger folding events that are stabilized by interactions between R groups Quaternary structure ...
bio12_sm_02_2
... chemicals used in cellular communication. Attachment and recognition proteins act as attachment points for structural elements such as the cytoskeleton or as recognition sites for foreign substances such as microbes. 10. They both detect molecules and perform an action in response. They both recogni ...
... chemicals used in cellular communication. Attachment and recognition proteins act as attachment points for structural elements such as the cytoskeleton or as recognition sites for foreign substances such as microbes. 10. They both detect molecules and perform an action in response. They both recogni ...
Cellular activity - Our eclass community
... outside the cell, and when those molecules are present they bind with the receptor protein The receptor and the bound molecule then trigger changes in the cell. ...
... outside the cell, and when those molecules are present they bind with the receptor protein The receptor and the bound molecule then trigger changes in the cell. ...
(A) and B chains - Michael P. Ready
... Connected by disulfides In order to sequence the protein, the chains have to be separated ...
... Connected by disulfides In order to sequence the protein, the chains have to be separated ...
file1
... - eliminate covariance by finding eigenvectors/eigenvalues of covariance matrix - largest eigenvalues and corresponding eigenvectors give you principal components - ie the largest factors determining distribution of your dataset - they take the three largest (the largest of which represents consensu ...
... - eliminate covariance by finding eigenvectors/eigenvalues of covariance matrix - largest eigenvalues and corresponding eigenvectors give you principal components - ie the largest factors determining distribution of your dataset - they take the three largest (the largest of which represents consensu ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).