Test Results - Oregon State University
... • Fill in high points questions if you know the answers • Rapidly go through MC and fill ins and answer the ones you know • Use remaining time to use the process of elimination to better statistical chances on the remaining multiple choice • Revisit high point questions and try to garner some partia ...
... • Fill in high points questions if you know the answers • Rapidly go through MC and fill ins and answer the ones you know • Use remaining time to use the process of elimination to better statistical chances on the remaining multiple choice • Revisit high point questions and try to garner some partia ...
Study Guide for Chapter 11 in Fox
... 9. Hormones affect the _________ of their TT 10. We can “classify” hormones (H) in 2 ways: by their chemical structure and by their actions in TT 11. What are the 2 types of “lipid soluble” Hormones? What glands produce them? 12. When looking at Fig. 11.2, understand why different tissues release di ...
... 9. Hormones affect the _________ of their TT 10. We can “classify” hormones (H) in 2 ways: by their chemical structure and by their actions in TT 11. What are the 2 types of “lipid soluble” Hormones? What glands produce them? 12. When looking at Fig. 11.2, understand why different tissues release di ...
Actin - WordPress.com
... o Gelsolin? Caps + end to prevent further growth What is the difference between Lamellipodia and Filipodia? o Lamellipodia push the cell forwards for movement o Filipodia act as sensors that respond to chemotaxic factors What type of Myosin is used for Contractile Muscles? o Type II Myosin Actin i ...
... o Gelsolin? Caps + end to prevent further growth What is the difference between Lamellipodia and Filipodia? o Lamellipodia push the cell forwards for movement o Filipodia act as sensors that respond to chemotaxic factors What type of Myosin is used for Contractile Muscles? o Type II Myosin Actin i ...
Principles of Life
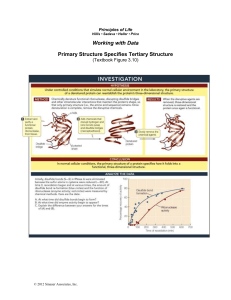
... After the tertiary structures of proteins were first shown to be highly specific, the question arose as to how the order of amino acids determined the three-dimensional structure. The second protein whose structure was determined was ribonuclease A, an enzyme from cows that was readily available fro ...
... After the tertiary structures of proteins were first shown to be highly specific, the question arose as to how the order of amino acids determined the three-dimensional structure. The second protein whose structure was determined was ribonuclease A, an enzyme from cows that was readily available fro ...
28P PROCEEDINGS OF THE BIOCHEMICAL SOCIETY
... to yield a first-order velocity constant for the rate of approach to pH equilibrium. Between pH6 and pH7 mitochondria in distilled water increased the rate constant for the approach to equilibrium from the alkaline side (002 hydration predominating). At pH6.4 the rate constant was doubled by 1.2mg o ...
... to yield a first-order velocity constant for the rate of approach to pH equilibrium. Between pH6 and pH7 mitochondria in distilled water increased the rate constant for the approach to equilibrium from the alkaline side (002 hydration predominating). At pH6.4 the rate constant was doubled by 1.2mg o ...
Kravitz_Symposium
... Open ocean, estuary, embayment, upwelling, fringing reef, atoll, warm seep, mangrove, fresh water, biofilms, sediments, soils ...
... Open ocean, estuary, embayment, upwelling, fringing reef, atoll, warm seep, mangrove, fresh water, biofilms, sediments, soils ...
Phosphorylation and concomitant structural changes in human 2
... [19] and HSP27 [20] were negatively regulated by phosphorylation, causing dissociation of large oligomers into small molecules and reducing their chaperone activity. Notably, protein structure of HSP33 in E. coli is regulated in a manner similar to the 2-Cys Prxs [6,21]. Under oxidative stress, HSP3 ...
... [19] and HSP27 [20] were negatively regulated by phosphorylation, causing dissociation of large oligomers into small molecules and reducing their chaperone activity. Notably, protein structure of HSP33 in E. coli is regulated in a manner similar to the 2-Cys Prxs [6,21]. Under oxidative stress, HSP3 ...
MB207_15 - MB207Jan2010
... • A single MT is comprised of 10-15 protofilaments (usually 13 in mammalian cells) that associate laterally to form a 24nm wide hollow cylinder. • Different polymerization rates at two ends: → In each protofilament, the heterodimers are oriented with their β-tubulin monomer pointing towards the fast ...
... • A single MT is comprised of 10-15 protofilaments (usually 13 in mammalian cells) that associate laterally to form a 24nm wide hollow cylinder. • Different polymerization rates at two ends: → In each protofilament, the heterodimers are oriented with their β-tubulin monomer pointing towards the fast ...
1 - PLOS
... genes associated with signal transduction, more specifically, transcripts associated with cell-cycle control (prohibitin B cell receptor), regulation of intracellular ion levels (sodium/potassium transporting ATPase) and vision (CRALBP). Transcripts coding for an adenylate cyclase type protein were ...
... genes associated with signal transduction, more specifically, transcripts associated with cell-cycle control (prohibitin B cell receptor), regulation of intracellular ion levels (sodium/potassium transporting ATPase) and vision (CRALBP). Transcripts coding for an adenylate cyclase type protein were ...
Feb 24 exam all parts
... d) What vitamin is necessary for effective blood clotting _______Vit K__________ (1 mark) e) What special behaviour is associated with this amino acid, and how does it promote activation of prothrombin on negative phospholipid or glass surfaces? (3 marks) ...
... d) What vitamin is necessary for effective blood clotting _______Vit K__________ (1 mark) e) What special behaviour is associated with this amino acid, and how does it promote activation of prothrombin on negative phospholipid or glass surfaces? (3 marks) ...
2 -1 -2 -1 1 2 K
... generate multi-domain proteins Domains are not only structurally, but also functionally, discrete units – domain family members are structurally and functionally conserved and recombined in complex ways during evolution Domains can be seen as the units of evolution Novelty in protein function ...
... generate multi-domain proteins Domains are not only structurally, but also functionally, discrete units – domain family members are structurally and functionally conserved and recombined in complex ways during evolution Domains can be seen as the units of evolution Novelty in protein function ...
Organization: The 6 Essential Elements
... Proteins (made of CHON) All six essential elements may be used in the production of small subunits called amino acids. There are 20 different amino acids, each with a specific side chain of chemicals. Amino acids bond to other amino acids to form a long chain called a protein. These chains of amino ...
... Proteins (made of CHON) All six essential elements may be used in the production of small subunits called amino acids. There are 20 different amino acids, each with a specific side chain of chemicals. Amino acids bond to other amino acids to form a long chain called a protein. These chains of amino ...
Autonomic Nervous System 5
... Stimulation • Depending upon tissue, either a subunit or bg-complex produces the effects • Alpha subunitActivates adenylate cyclase Producing cAMP cAMP activates protein kinase Opening ion channels ...
... Stimulation • Depending upon tissue, either a subunit or bg-complex produces the effects • Alpha subunitActivates adenylate cyclase Producing cAMP cAMP activates protein kinase Opening ion channels ...
slide
... B)- Membrane carbohydrates are important for cell-cell recognition • The membrane plays the key role in cell-cell recognition. • Cell-cell recognition is the ability of a cell to distinguish one type of neighboring المجاورةcell from another. • It is the basis for rejection of foreign cells by th ...
... B)- Membrane carbohydrates are important for cell-cell recognition • The membrane plays the key role in cell-cell recognition. • Cell-cell recognition is the ability of a cell to distinguish one type of neighboring المجاورةcell from another. • It is the basis for rejection of foreign cells by th ...
Interaction of a 14-3-3 protein with the plant
... Subcellular localization of green fluorescent protein (GFP) – EDE1 fusions on the microtubules of the spindle and spindle poles during mitosis and on the phragmoplast during cytokinesis indicates that EDE1 has a key role in microtubule function during mitosis. Also, its expression pattern is strictl ...
... Subcellular localization of green fluorescent protein (GFP) – EDE1 fusions on the microtubules of the spindle and spindle poles during mitosis and on the phragmoplast during cytokinesis indicates that EDE1 has a key role in microtubule function during mitosis. Also, its expression pattern is strictl ...
SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION
... If the synapse is between an axon and a muscle cell, then the muscle will contract. If the synapse is between an axon and a gland, then the gland will release a hormone. STEP 8: The synaptic gap contains enzymes that will destroy the neurotransmitters, thus returning the synapse to it ...
... If the synapse is between an axon and a muscle cell, then the muscle will contract. If the synapse is between an axon and a gland, then the gland will release a hormone. STEP 8: The synaptic gap contains enzymes that will destroy the neurotransmitters, thus returning the synapse to it ...
Coronavirus JHM: a Virion-assoeiated Protein Kinase
... precursor to pp60, and one phosphoamino acid linkage to this protein is phosphoserine. Associated with JHMV is a protein kinase which is independent of cyclic AMP stimulation, has a requirement for divalent cations, phosphorylates serine residues and has a broad substrate specificity in vitro, phosp ...
... precursor to pp60, and one phosphoamino acid linkage to this protein is phosphoserine. Associated with JHMV is a protein kinase which is independent of cyclic AMP stimulation, has a requirement for divalent cations, phosphorylates serine residues and has a broad substrate specificity in vitro, phosp ...
Expression and activity of platelet-derived growth factor receptor
... autophosphorylation at tyrosine residues. Kinase activity of the receptor is upregulated by phosphorylation at the specific tyrosine residue in the activation loop of the receptor tyrosine kinase domain. Other autophosphorylated tyrosine residues outside the kinase domain provide binding sites for v ...
... autophosphorylation at tyrosine residues. Kinase activity of the receptor is upregulated by phosphorylation at the specific tyrosine residue in the activation loop of the receptor tyrosine kinase domain. Other autophosphorylated tyrosine residues outside the kinase domain provide binding sites for v ...
Bending membranes
... It is widely assumed that peripheral membrane proteins induce intracellular membrane curvature by the asymmetric insertion of a protein segment into the lipid bilayer, or by imposing shape by adhesion of a curved protein domain to the membrane surface. Two papers now provide convincing evidence chal ...
... It is widely assumed that peripheral membrane proteins induce intracellular membrane curvature by the asymmetric insertion of a protein segment into the lipid bilayer, or by imposing shape by adhesion of a curved protein domain to the membrane surface. Two papers now provide convincing evidence chal ...
Membrane Lipids in the Function of Serotonin and Adrenergic
... 1. INTRODUCTION The G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily is the largest and most diverse protein family in mammals, involved in signal transduction across membranes [1, 2]. GPCRs are typically seven transmembrane domain proteins and include >800 members which are encoded by ~5% of human gen ...
... 1. INTRODUCTION The G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily is the largest and most diverse protein family in mammals, involved in signal transduction across membranes [1, 2]. GPCRs are typically seven transmembrane domain proteins and include >800 members which are encoded by ~5% of human gen ...
Wheel Runnin Alters Serotonin (5-HT) Transporter, 5
... In situ hybridization Measures mRNA levels Assumed there is a direct correlation with protein ...
... In situ hybridization Measures mRNA levels Assumed there is a direct correlation with protein ...
Structures of
... - Example: hemoglobin is a dimer of αβ protomers - Contact region between subunits resembles the interior of a single subunit protein: closely packed nonpolar residues, hydrogen bonding, interchain disulfide bridges, but generally less hydrophobic than the hydrophobic core of a single subunit prot ...
... - Example: hemoglobin is a dimer of αβ protomers - Contact region between subunits resembles the interior of a single subunit protein: closely packed nonpolar residues, hydrogen bonding, interchain disulfide bridges, but generally less hydrophobic than the hydrophobic core of a single subunit prot ...
Instructions for Gram-LocEN Web-server
... Proteins must be transported to the correct organelles of a cell and folded into correct 3-D structures to properly perform their functions. Therefore, knowing the subcellular localization is one step towards understanding its functions. Proteins can exist in different locations within a cell, and s ...
... Proteins must be transported to the correct organelles of a cell and folded into correct 3-D structures to properly perform their functions. Therefore, knowing the subcellular localization is one step towards understanding its functions. Proteins can exist in different locations within a cell, and s ...
Antibodies for Unfolded Protein Response
... Activating Transcription Factor 6 (ATF6) ATF6 is a transmembrane glycoprotein and transcription activator, which functions to initiate the UPR during ER stress. The predicted molecular weight of the canonical form of ATF6 is 74.5 kDa. However, ATF6 may be detected at approximately 90 kDa in Western ...
... Activating Transcription Factor 6 (ATF6) ATF6 is a transmembrane glycoprotein and transcription activator, which functions to initiate the UPR during ER stress. The predicted molecular weight of the canonical form of ATF6 is 74.5 kDa. However, ATF6 may be detected at approximately 90 kDa in Western ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).