Lecture 2 Protein conformation Recap Recap… Proteins
... • The conformation of a protein determines its function • Proteins are made of polypeptides which are polymers of amino acids • Amino acid polymers are linked by peptide bonds • The amino acid sequence determines the 3-D shape of the Protein • There are four levels of protein structure ...
... • The conformation of a protein determines its function • Proteins are made of polypeptides which are polymers of amino acids • Amino acid polymers are linked by peptide bonds • The amino acid sequence determines the 3-D shape of the Protein • There are four levels of protein structure ...
Over Expression of IPTG inducible GST protein in E.coli BL21
... by glutathione on an electrophilic substrate [2]. The resulting glutathione S conjugate are more soluble than the original substrate and thus more easily transported from the cell, mediated by ATP dependent MAPEG family membrane glycoprotein belonging to multiple drug resistant protein family [3]. E ...
... by glutathione on an electrophilic substrate [2]. The resulting glutathione S conjugate are more soluble than the original substrate and thus more easily transported from the cell, mediated by ATP dependent MAPEG family membrane glycoprotein belonging to multiple drug resistant protein family [3]. E ...
Protein Purification 2003
... – What kind of cell is it coming from – What part of cell – What does it do ...
... – What kind of cell is it coming from – What part of cell – What does it do ...
Protein Data Bank Advisory Committee
... • Part I: small molecule drugs, nutraceuticals, and their targets ( DrugBank) - 2012 • Part II: peptide derived compounds (PRD)- tbd • Part III: toxins and toxin targets (T3DB), human metabolites (HMDB) • Part IV: biotherapeutics, i.e., monoclonal antibodies • Part V: veterinary drugs (FDA Green Boo ...
... • Part I: small molecule drugs, nutraceuticals, and their targets ( DrugBank) - 2012 • Part II: peptide derived compounds (PRD)- tbd • Part III: toxins and toxin targets (T3DB), human metabolites (HMDB) • Part IV: biotherapeutics, i.e., monoclonal antibodies • Part V: veterinary drugs (FDA Green Boo ...
Lecture 4 - Biological Molecules Part II
... The two backbones run in opposite 5→ 3 directions from each other, an arrangement referred to as antiparallel The nucleotide monomers are linked by ...
... The two backbones run in opposite 5→ 3 directions from each other, an arrangement referred to as antiparallel The nucleotide monomers are linked by ...
Boronophenyl analogs of phospholyrosines
... have from 4~10 carbon atoms in their ring structure. and more preferably have 5. 6 or 7 carbons in the ring structure. Moreover. the term alkyl as used throughout the speci? cation and claims is intended to include both “unsubstituted alkyls” and “substituted alkyls". the latter of which refers to ...
... have from 4~10 carbon atoms in their ring structure. and more preferably have 5. 6 or 7 carbons in the ring structure. Moreover. the term alkyl as used throughout the speci? cation and claims is intended to include both “unsubstituted alkyls” and “substituted alkyls". the latter of which refers to ...
BioExpress® 6000 Mammalian Cell Growth Media
... H; 15N HSQC spectrum plotted at different threshhold levels of 200 μM sample of rhodospin expressed in CIL’s 15N-labeled media. The tryptophan sidechain signals are clearly visible, and the protein is folded in its native conformation. The broad peaks observed are expected for a large membrane prote ...
... H; 15N HSQC spectrum plotted at different threshhold levels of 200 μM sample of rhodospin expressed in CIL’s 15N-labeled media. The tryptophan sidechain signals are clearly visible, and the protein is folded in its native conformation. The broad peaks observed are expected for a large membrane prote ...
Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy: The Molecular Signaling
... are adjacent to DUX4 [9,10]. FRG1 activation leads to increased activity of spliceosome. Also, with use of mouse model of FSHD, it was shown that FRG1 reduces the stability of mRNA of RBFOX1 [11], which plays an important role in alternative splicing - binds to exon-intron recognition motifs. Thus, ...
... are adjacent to DUX4 [9,10]. FRG1 activation leads to increased activity of spliceosome. Also, with use of mouse model of FSHD, it was shown that FRG1 reduces the stability of mRNA of RBFOX1 [11], which plays an important role in alternative splicing - binds to exon-intron recognition motifs. Thus, ...
Chapter 3: Enzymes: Structure and Function
... (catch and release). It is usually proposed that the transition state complex is stabilized, lowering the activation energy which accelerates the reaction rate. Rather than the old 'lock and key' model, it is proposed that the enzyme and substrate influence one another to form a stronger interaction ...
... (catch and release). It is usually proposed that the transition state complex is stabilized, lowering the activation energy which accelerates the reaction rate. Rather than the old 'lock and key' model, it is proposed that the enzyme and substrate influence one another to form a stronger interaction ...
bbr052online 329..336 - Oxford Academic
... In recent years, numerous biocomputational tools have been designed to extract functional and evolutionary information from multiple sequence alignments (MSAs) of proteins and genes. Most biologists working actively on the characterization of proteins from a single or family perspective use the MSA ...
... In recent years, numerous biocomputational tools have been designed to extract functional and evolutionary information from multiple sequence alignments (MSAs) of proteins and genes. Most biologists working actively on the characterization of proteins from a single or family perspective use the MSA ...
Human/Mouse/Rat PP2A Catalytic Subunit Antibody
... Protein Phosphatase 2A (PP2A) dephosphorylates serine and threonine residues in proteins. This ubiquitously expressed enzyme plays a critical role in modulating cell survival, growth factor responses, and neurotransmission. Phosphorylation near the Cterminus at Y307 of the catalytic subunit decrea ...
... Protein Phosphatase 2A (PP2A) dephosphorylates serine and threonine residues in proteins. This ubiquitously expressed enzyme plays a critical role in modulating cell survival, growth factor responses, and neurotransmission. Phosphorylation near the Cterminus at Y307 of the catalytic subunit decrea ...
Full-Text PDF
... included MAPK1, SKIV2L2, Sec24D, Cct4, PDIA3, CORO1C. These proteins are involved in DNA transcription, mRNA translation, cell cycle, cell motility, and morphological processes. For the purposes of this study, those proteins involved in transcriptional and translational control were of particular in ...
... included MAPK1, SKIV2L2, Sec24D, Cct4, PDIA3, CORO1C. These proteins are involved in DNA transcription, mRNA translation, cell cycle, cell motility, and morphological processes. For the purposes of this study, those proteins involved in transcriptional and translational control were of particular in ...
The potato NLR immune receptor R3a does not contain
... Plants use immune receptors to recognize invading pathogens and pests. The largest family of intracellular immune receptors is the nucleotide binding-leucine rich repeat (NB-LRR or NLR) protein family - an important element of defense against pathogens in both plants and animals (Maekawa et al. 2011 ...
... Plants use immune receptors to recognize invading pathogens and pests. The largest family of intracellular immune receptors is the nucleotide binding-leucine rich repeat (NB-LRR or NLR) protein family - an important element of defense against pathogens in both plants and animals (Maekawa et al. 2011 ...
analysis of membrane protein dimerization
... from Escherichia coli as previously described in detail.(5) Prior to sedimentation equilibrium analysis, the protein was exchanged into either C12E8 or C8E5 by adsorption to an ion exchange column, washing with 10 volumes of buffer containing the appropriate detergent, and eluting with high salt. Sa ...
... from Escherichia coli as previously described in detail.(5) Prior to sedimentation equilibrium analysis, the protein was exchanged into either C12E8 or C8E5 by adsorption to an ion exchange column, washing with 10 volumes of buffer containing the appropriate detergent, and eluting with high salt. Sa ...
Gene Section TMPRSS2 (transmembrane protease, serine 2) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Youngwoo Park Therapeutic Antibody Research Center, Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Daejon, ...
... Youngwoo Park Therapeutic Antibody Research Center, Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Daejon, ...
the ask1-map kinase cascades in mammalian stress response
... Oxidative Stress and ASK1 interacting Proteins ROS --- super oxide and H2O2 produced through cellular processes or derived from exogenous sources play imp role in normal cell-proliferation, survival and immune response. Excessive Production of ROS causes: Severe damage to cellular components. ...
... Oxidative Stress and ASK1 interacting Proteins ROS --- super oxide and H2O2 produced through cellular processes or derived from exogenous sources play imp role in normal cell-proliferation, survival and immune response. Excessive Production of ROS causes: Severe damage to cellular components. ...
1MBO Lopez kin
... catalyzes the insertion of ferrous iron into protoporphyrin IX to form protoheme IX (heme). Due to the many critical roles of heme, synthesis of heme is required by the vast majority of organisms. Despite significant investigation of both the microbial and eucaryotic enzyme, details of metal chelati ...
... catalyzes the insertion of ferrous iron into protoporphyrin IX to form protoheme IX (heme). Due to the many critical roles of heme, synthesis of heme is required by the vast majority of organisms. Despite significant investigation of both the microbial and eucaryotic enzyme, details of metal chelati ...
fibulins: a versatile family of extracellular matrix proteins
... sequence for calcium ligation, and they are known as calcium-binding EGF (cbEGF)-like modules. The carboxy-terminal domain III, which is ∼120–140 residues long with only two extra cysteine residues, resembles a new protein module (FC; fibulin-type carboxyl terminus) that is shared by fibulins and fi ...
... sequence for calcium ligation, and they are known as calcium-binding EGF (cbEGF)-like modules. The carboxy-terminal domain III, which is ∼120–140 residues long with only two extra cysteine residues, resembles a new protein module (FC; fibulin-type carboxyl terminus) that is shared by fibulins and fi ...
Detection of a New Radical and FeMo
... All three signals are observed at C2H2 concentrations as low as 0.001 atm and the amplitude ratio of the individual inflections remain unchanged. In other words, there are no hi-/lo-C2H2 signals analogous to the aforementioned hi-CO and lo-CO CO signals. A plot of signal amplitude vs C2H2 at low con ...
... All three signals are observed at C2H2 concentrations as low as 0.001 atm and the amplitude ratio of the individual inflections remain unchanged. In other words, there are no hi-/lo-C2H2 signals analogous to the aforementioned hi-CO and lo-CO CO signals. A plot of signal amplitude vs C2H2 at low con ...
FYVE-dependent endosomal targeting of an arrestin-related
... interior and the extracellular environment. Appropriate physiological responses to external stimuli rely on receptors, transporters and other intrinsic protein equipment located at the membrane boundary. The activity of some of these protein families, of which the GPCRs have been described in most d ...
... interior and the extracellular environment. Appropriate physiological responses to external stimuli rely on receptors, transporters and other intrinsic protein equipment located at the membrane boundary. The activity of some of these protein families, of which the GPCRs have been described in most d ...
FYVE-Dependent Endosomal Targeting of an Arrestin
... interior and the extracellular environment. Appropriate physiological responses to external stimuli rely on receptors, transporters and other intrinsic protein equipment located at the membrane boundary. The activity of some of these protein families, of which the GPCRs have been described in most d ...
... interior and the extracellular environment. Appropriate physiological responses to external stimuli rely on receptors, transporters and other intrinsic protein equipment located at the membrane boundary. The activity of some of these protein families, of which the GPCRs have been described in most d ...
Essential Cell Biology Chapter 4 excerpt
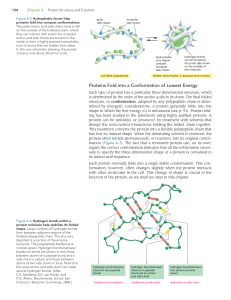
... The a helix and the b Sheet are common folding patterns When the three-dimensional structures of many different protein molecules are compared, it becomes clear that, although the overall conformation of each protein is unique, two regular folding patterns are often present. Both were discovered mor ...
... The a helix and the b Sheet are common folding patterns When the three-dimensional structures of many different protein molecules are compared, it becomes clear that, although the overall conformation of each protein is unique, two regular folding patterns are often present. Both were discovered mor ...
here
... are known as motifs or supersecondary structures A motif is usually smaller than a domain but can encompass an entire domain. Sometimes the structures of domains are partly named after motifs that they contain, e.g. “greek key beta barrel” It should be noted that the term motif, when used in conjunc ...
... are known as motifs or supersecondary structures A motif is usually smaller than a domain but can encompass an entire domain. Sometimes the structures of domains are partly named after motifs that they contain, e.g. “greek key beta barrel” It should be noted that the term motif, when used in conjunc ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).