Powerpoint slides
... • Transcription of the mRNA that codes for the protein from DNA in the nucleus. • Export of the mRNA from the nucleus through pores in the nuclear envelope. • Translation of the mRNA on ribosomes on rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) to make the protein. •The protein is threaded into the lumen of the ...
... • Transcription of the mRNA that codes for the protein from DNA in the nucleus. • Export of the mRNA from the nucleus through pores in the nuclear envelope. • Translation of the mRNA on ribosomes on rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) to make the protein. •The protein is threaded into the lumen of the ...
The Three Dimensional Structure of Proteins
... Tertiary Structure The folding of a single polypeptide chain in three dimensional space is Tertiary Structure. Tertiary structures involves long range interactions within the polypeptide. The protein folds upon itself resulting in a tight compact shape, a conformation, that is at an energy minimum ...
... Tertiary Structure The folding of a single polypeptide chain in three dimensional space is Tertiary Structure. Tertiary structures involves long range interactions within the polypeptide. The protein folds upon itself resulting in a tight compact shape, a conformation, that is at an energy minimum ...
Membrane Proteins
... • Most of protein (N-terminal portion) on outside of cell, exposed to water; mainly hydrophilic residues, heavily glycosylated (carbohydrates in glycosidic bonds to Ser, Thr, and Asn) • Carbohydrates: ABO and MN blood group antigen-determining structures. • Extracellular part of protein also recepto ...
... • Most of protein (N-terminal portion) on outside of cell, exposed to water; mainly hydrophilic residues, heavily glycosylated (carbohydrates in glycosidic bonds to Ser, Thr, and Asn) • Carbohydrates: ABO and MN blood group antigen-determining structures. • Extracellular part of protein also recepto ...
Bioinformatics tools as JAWB (Just another Western Blot)
... Networks of “interactions” predict global function • Having the network of proteins/genes in which your protein/gene is inserted ...
... Networks of “interactions” predict global function • Having the network of proteins/genes in which your protein/gene is inserted ...
Fe-S
... Cristae – Highly folded inner membrane structure. Increase surface area. Matrix- “cytosol” of the mitochondria. Protein rich (500 mg/ml) Contains TCA cycle enzymes, pyruvate dehydrogenase, fatty and amino acid oxidation pathway, DNA, RNA, ribosomes Intermembrane Space – composition similar to cytoso ...
... Cristae – Highly folded inner membrane structure. Increase surface area. Matrix- “cytosol” of the mitochondria. Protein rich (500 mg/ml) Contains TCA cycle enzymes, pyruvate dehydrogenase, fatty and amino acid oxidation pathway, DNA, RNA, ribosomes Intermembrane Space – composition similar to cytoso ...
Subviral-Particle Biogenesis Hepatitis B Virus Small Surface
... gray line) proteins in the ER membrane (double horizontal lines). The numbers denote the suggested N- and C-terminal amino acid positions of the transmembrane domains (TM1 to -4). H, S derivative carrying a C-terminal addition of 11 aa (hatched box). All S mutants except mutant 2cn were generated in ...
... gray line) proteins in the ER membrane (double horizontal lines). The numbers denote the suggested N- and C-terminal amino acid positions of the transmembrane domains (TM1 to -4). H, S derivative carrying a C-terminal addition of 11 aa (hatched box). All S mutants except mutant 2cn were generated in ...
The reverse two
... detailed descriptions of the structure, function and control of biological systems in health and disease” Patterson & Aebersold Nat Genetics 33:S311 (2003) ...
... detailed descriptions of the structure, function and control of biological systems in health and disease” Patterson & Aebersold Nat Genetics 33:S311 (2003) ...
This exam has 8 pages, including this one.
... i) In the space below draw the structure of a dipeptide. The first amino acid can be any polar, but not charged, amino acid and the second amino acid can be any amino acid that is predominately or completely non-polar, except for Tyrosine. Provide the name for each amino acid that you have drawn (6 ...
... i) In the space below draw the structure of a dipeptide. The first amino acid can be any polar, but not charged, amino acid and the second amino acid can be any amino acid that is predominately or completely non-polar, except for Tyrosine. Provide the name for each amino acid that you have drawn (6 ...
Protein Chemistry
... increasing the rates of final stage in folding process. Many proteins contain chaperons “signals” (specific a.a. sequence). ...
... increasing the rates of final stage in folding process. Many proteins contain chaperons “signals” (specific a.a. sequence). ...
Review Cell Death Signalling Pathways in the
... malignancies, are associated with defects in the cell death mechanism. These defects are not only important for the growth advantage of malignant clones, but when understood can be used for specific therapeutic targeting of malignant cells while sparing normal cells. The cellular and molecular mecha ...
... malignancies, are associated with defects in the cell death mechanism. These defects are not only important for the growth advantage of malignant clones, but when understood can be used for specific therapeutic targeting of malignant cells while sparing normal cells. The cellular and molecular mecha ...
Important Factors Influencing Protein Crystallization (PDF
... High homogeneity and purity of the sample are crucial for the crystallization to be successful, the presence of different aggregates or oligomeric forms in the protein solution it well effect, we need to use Dynamic light scattering (DLS) to check that or small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS). ...
... High homogeneity and purity of the sample are crucial for the crystallization to be successful, the presence of different aggregates or oligomeric forms in the protein solution it well effect, we need to use Dynamic light scattering (DLS) to check that or small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS). ...
Theory_2004
... One gram of fat releases over twice as much energy than the same amount of glycogen The total mass of fat in the human body is about 1000-fold higher than that the total mass of body glycogen If all our energy was stored as glycogen, we would weigh at least 40 kg more than we do now Fat, but not gly ...
... One gram of fat releases over twice as much energy than the same amount of glycogen The total mass of fat in the human body is about 1000-fold higher than that the total mass of body glycogen If all our energy was stored as glycogen, we would weigh at least 40 kg more than we do now Fat, but not gly ...
+SDS - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... Serum albumin - protein used to transport nonsoluble molecules through the bloodstream Carries: bilirubin, fatty acids, hormones, dyes ...
... Serum albumin - protein used to transport nonsoluble molecules through the bloodstream Carries: bilirubin, fatty acids, hormones, dyes ...
poster PDF
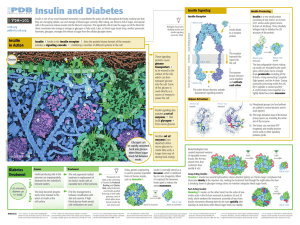
... Insulin is one of our most important hormones. It coordinates the action of cells throughout the body, making sure that they are managing uptake, use and storage of blood sugar correctly. After eating, our blood is full of sugar, and special cells in the pancreas release insulin into the blood in re ...
... Insulin is one of our most important hormones. It coordinates the action of cells throughout the body, making sure that they are managing uptake, use and storage of blood sugar correctly. After eating, our blood is full of sugar, and special cells in the pancreas release insulin into the blood in re ...
Identification of NaHCO3 Stress Responsive Proteins in Dunaliella
... process, single-organism process, response to stimulus and cellular component organization or biogenesis. The most highly-enriched GOBP category was metabolic process (20.53%), the second highly-enriched GO-BP category was cellular process (19.91%). This demonstrated that these processes were of fun ...
... process, single-organism process, response to stimulus and cellular component organization or biogenesis. The most highly-enriched GOBP category was metabolic process (20.53%), the second highly-enriched GO-BP category was cellular process (19.91%). This demonstrated that these processes were of fun ...
Addition of the keto functional group to the genetic
... specificity of the TyrRS so that it charges p-acetyl- L phenylalanine and not any of the common 20 amino acids, a library of M. jannaschii TyrRS mutants was generated and screened. The crystal structure of the homologous Bacillus stearothermophilus TyrRS (31) was used to identify those residues that ...
... specificity of the TyrRS so that it charges p-acetyl- L phenylalanine and not any of the common 20 amino acids, a library of M. jannaschii TyrRS mutants was generated and screened. The crystal structure of the homologous Bacillus stearothermophilus TyrRS (31) was used to identify those residues that ...
Feeding silage to pigs
... • Peas and faba beans have lower levels of crude protein and amino acids than SBM • Protein, amino acid, and energy content differs between varieties ...
... • Peas and faba beans have lower levels of crude protein and amino acids than SBM • Protein, amino acid, and energy content differs between varieties ...
Anti-TYK2 (JTK1)
... Rabbit polyclonal TYK2 antibody was raised against a 17 amino acid peptide near the amino terminus of human TYK2 ...
... Rabbit polyclonal TYK2 antibody was raised against a 17 amino acid peptide near the amino terminus of human TYK2 ...
The role of P2 receptors in controlling infections by intracellular
... such as mycobacteria and chlamydiae. A conserved mechanism appears to be involved in controlling infection by both of these pathogens, as a role for phospholipase D in inducing fusion between lysosomes and the vacuoles has been demonstrated. Other P2-dependent mechanisms are most likely operative in ...
... such as mycobacteria and chlamydiae. A conserved mechanism appears to be involved in controlling infection by both of these pathogens, as a role for phospholipase D in inducing fusion between lysosomes and the vacuoles has been demonstrated. Other P2-dependent mechanisms are most likely operative in ...
Proteins with
... We’ve got the lots of sequences, now how do we score/search? First, we need a way to assign numbers to “shades of grey” matches. Genetic code scoring system – This assumes that changes in protein sequence arise from mutations. If only one point mutation is needed to change a given AA to another (at ...
... We’ve got the lots of sequences, now how do we score/search? First, we need a way to assign numbers to “shades of grey” matches. Genetic code scoring system – This assumes that changes in protein sequence arise from mutations. If only one point mutation is needed to change a given AA to another (at ...
Regulation and Control of Metabolism in Bacteria
... to a decrease in the rate of transcription of proteins. Catabolite repression is considered a form of positive control because it affects an increase in rates of transcription of proteins. ...
... to a decrease in the rate of transcription of proteins. Catabolite repression is considered a form of positive control because it affects an increase in rates of transcription of proteins. ...
Seasonal regulation of a 24-kDa protein from red
... change during CA in some species. Alterations in amounts of lignin and suberin (Griffith and Brown 1982), extracellular soluble and pectic polysaccharides, callose (Wallner et al. 1986) and cell-wall-associated proteins (e.g., Jian et al. 1987, Weiser et al. 1990, Kozbial et al. 1998) have been obse ...
... change during CA in some species. Alterations in amounts of lignin and suberin (Griffith and Brown 1982), extracellular soluble and pectic polysaccharides, callose (Wallner et al. 1986) and cell-wall-associated proteins (e.g., Jian et al. 1987, Weiser et al. 1990, Kozbial et al. 1998) have been obse ...
Ferrara et al, Nat Med 2003 - Kashyap Memorial Eye Hospital
... DAG, diacylglycerol; ET, endothelin; LPO, lypoxygenase; MMP, matrix metalloproteinases; NO, nitric oxide; PKC, protein kinase C; PPVP, posterior precortical vitreous pocket; RAS, renin-angiotensin system ...
... DAG, diacylglycerol; ET, endothelin; LPO, lypoxygenase; MMP, matrix metalloproteinases; NO, nitric oxide; PKC, protein kinase C; PPVP, posterior precortical vitreous pocket; RAS, renin-angiotensin system ...
Basic concepts of molecular biology and proteins I
... Many rodlike collagen molecules are cross-linked together in the extracellular space to form unextendable collagen fibrils (top) that have the tensile strength of steel. The striping on the collagen fibril is caused by the regular repeating arrangement of the collagen molecules within the fibril. (B ...
... Many rodlike collagen molecules are cross-linked together in the extracellular space to form unextendable collagen fibrils (top) that have the tensile strength of steel. The striping on the collagen fibril is caused by the regular repeating arrangement of the collagen molecules within the fibril. (B ...
Expression and transcriptional activity of progesterone receptor A
... one PR isoform, usually PRA, is seen in cancers, suggests that disrupted progesterone signaling may play a role in development or progression of breast cancer. ...
... one PR isoform, usually PRA, is seen in cancers, suggests that disrupted progesterone signaling may play a role in development or progression of breast cancer. ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).