Sample pages 1 PDF
... its function has not been demonstrated. The Arabidopsis genome encodes orthologs of animal clathrin-mediated vesicular trafficking proteins (Boehm and Bonifacino 2001). Adaptin orthologs in Arabidopsis identified by propeptide sequence alignments (Sanderfoot and Raikhel 2002; Boehm and Bonifacino 20 ...
... its function has not been demonstrated. The Arabidopsis genome encodes orthologs of animal clathrin-mediated vesicular trafficking proteins (Boehm and Bonifacino 2001). Adaptin orthologs in Arabidopsis identified by propeptide sequence alignments (Sanderfoot and Raikhel 2002; Boehm and Bonifacino 20 ...
Homology among (βα) 8 Barrels: Implications for the Evolution of
... from the phosphorylated Entner-Doudoroff pathway eda is also a Schiff base-dependent TIM barrel aldolase (Mavridis et al., 1982), and shows signi®cant sequence similarity to other phosphate-binding TIM barrels (Figure 1). Comparison of known structures shows that the Schiff base-forming catalytic ly ...
... from the phosphorylated Entner-Doudoroff pathway eda is also a Schiff base-dependent TIM barrel aldolase (Mavridis et al., 1982), and shows signi®cant sequence similarity to other phosphate-binding TIM barrels (Figure 1). Comparison of known structures shows that the Schiff base-forming catalytic ly ...
search1
... 2. Increase the Word Size to 20 - 25. With a default Word Size of 7, limiting the number small initial fragments to be extended to HSPs. ...
... 2. Increase the Word Size to 20 - 25. With a default Word Size of 7, limiting the number small initial fragments to be extended to HSPs. ...
Diversity of heterotrimeric G-protein γ subunits in plants | SpringerLink
... Background: Heterotrimeric G-proteins, consisting of three subunits Gα, Gβ and Gγ are present in most eukaryotes and mediate signaling in numerous biological processes. In plants, Gγ subunits were shown to provide functional selectivity to G-proteins. Three unconventional Gγ subunits were recently r ...
... Background: Heterotrimeric G-proteins, consisting of three subunits Gα, Gβ and Gγ are present in most eukaryotes and mediate signaling in numerous biological processes. In plants, Gγ subunits were shown to provide functional selectivity to G-proteins. Three unconventional Gγ subunits were recently r ...
EPIgeneousTM Binding Domain Assays
... with the substrate brings the donor and acceptor dyes into close proximity, enabling FRET to occur upon light excitation. The specific signal at 665 nm is inhibited when a specific compound prevents the reader domain protein from binding to its substrate. ...
... with the substrate brings the donor and acceptor dyes into close proximity, enabling FRET to occur upon light excitation. The specific signal at 665 nm is inhibited when a specific compound prevents the reader domain protein from binding to its substrate. ...
NAP57, a Mammalian Nucleolar Protein with a Putative Homolog
... complexes (Meier and Blobel, 1992). Similar tracks have now been observed with antibodies to the ribosomal protein S1 (Raska et al., 1992) and to the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nefprotein (Murti et al., 1993). These localization data are consistent with Nopp140 shuttling between the nucleol ...
... complexes (Meier and Blobel, 1992). Similar tracks have now been observed with antibodies to the ribosomal protein S1 (Raska et al., 1992) and to the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nefprotein (Murti et al., 1993). These localization data are consistent with Nopp140 shuttling between the nucleol ...
PDF Format - Kinexus Bioinformatics Corporation
... diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of human diseases. In particular, we track enzymes called protein kinases that control other proteins by carrying out their phosphorylation at regulatory sites known as phosphosites. Phosphosites act as on/off switches for proteins. Their malfunction has been linke ...
... diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of human diseases. In particular, we track enzymes called protein kinases that control other proteins by carrying out their phosphorylation at regulatory sites known as phosphosites. Phosphosites act as on/off switches for proteins. Their malfunction has been linke ...
C1qRP Is a Heavily O-Glycosylated Cell Surface Protein Involved in
... deduced from this cDNA indicates that the mature protein is composed of 631 amino acids, which is calculated to be 66,495 Da (14), while previous characterization of C1qRP demonstrated that it migrates in SDS-PAGE gels with a relative mobility of 100,000, which shifts upon reduction to 126,000. Whil ...
... deduced from this cDNA indicates that the mature protein is composed of 631 amino acids, which is calculated to be 66,495 Da (14), while previous characterization of C1qRP demonstrated that it migrates in SDS-PAGE gels with a relative mobility of 100,000, which shifts upon reduction to 126,000. Whil ...
1 1 2 bez pyt lecture chemistryofaminoacids 7 fin
... • The α helix is a common type of secondary structure in proteins. • It is the predominant structure in α-keratins. • In globular proteins, about one-fourth of all amino acid residues are found in α helices ...
... • The α helix is a common type of secondary structure in proteins. • It is the predominant structure in α-keratins. • In globular proteins, about one-fourth of all amino acid residues are found in α helices ...
Molecular Graphics for Ligand Binding Experiment
... help understand the nature of the binding of ligands to avidin and to correlate those structures to the values for the Kd’s that you will obtain for HABA and desthiobiotin binding to egg white avidin. The relevant PDB files that you can download from the RCSB (www.pdb.org/pdb/home/home.do) web site ...
... help understand the nature of the binding of ligands to avidin and to correlate those structures to the values for the Kd’s that you will obtain for HABA and desthiobiotin binding to egg white avidin. The relevant PDB files that you can download from the RCSB (www.pdb.org/pdb/home/home.do) web site ...
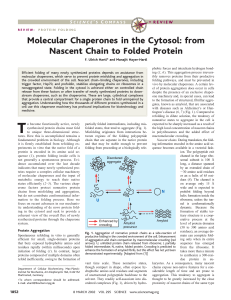
Molecular Chaperones in the Cytosol: from Nascent Chain to Folded
... to the formation of structured, fibrillar aggregates, known as amyloid, that are associated with diseases such as Alzheimer’s or Huntington’s disease (6, 7) (Fig. 1). Compared to refolding in dilute solution, the tendency of nonnative states to aggregate in the cell is partially folded intermediates ...
... to the formation of structured, fibrillar aggregates, known as amyloid, that are associated with diseases such as Alzheimer’s or Huntington’s disease (6, 7) (Fig. 1). Compared to refolding in dilute solution, the tendency of nonnative states to aggregate in the cell is partially folded intermediates ...
Phosphoproteomic analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana Hanna Klang Årstrand
... Medicine in 1974 for this discovery. Ribosomes are large protein and rRNA complexes which are made up from one small and one large subunit that work together to translate mRNA into a protein chain. Eukaryotic translation is mainly controlled during the ...
... Medicine in 1974 for this discovery. Ribosomes are large protein and rRNA complexes which are made up from one small and one large subunit that work together to translate mRNA into a protein chain. Eukaryotic translation is mainly controlled during the ...
Task - The British Association of Sport and Exercise Sciences
... Muscle protein synthesis in response to amino acids In this important study by Cutherbertson, Smith and Rennie, young and elderly subjects were given up to 40 g of essential amino acids (EAA). The data show that the maximal rate of protein synthesis is lower in the elderly. ...
... Muscle protein synthesis in response to amino acids In this important study by Cutherbertson, Smith and Rennie, young and elderly subjects were given up to 40 g of essential amino acids (EAA). The data show that the maximal rate of protein synthesis is lower in the elderly. ...
Alvin_20.385_Presentation
... Paper goes overboard in proclaiming its success (at most just 1 of 8 mutants successful) ...
... Paper goes overboard in proclaiming its success (at most just 1 of 8 mutants successful) ...
Protein Synthesis, Processing, and Regulation
... form. These processing steps, particularly in eukaryotes, are intimately related to the sorting and transport of different proteins to their appropriate destinations within the cell. Although the expression of most genes is regulated primarily at the level of transcription, gene expression can also ...
... form. These processing steps, particularly in eukaryotes, are intimately related to the sorting and transport of different proteins to their appropriate destinations within the cell. Although the expression of most genes is regulated primarily at the level of transcription, gene expression can also ...
Intrinsically Disordered Proteins as Drug Targets
... instance, the determined conformations of a protein often differ in its ligand-bound and -unbound forms. Protein conformational changes can open new ligand binding sites, whose exploration is key to fully assess the efficacy of a drug as well as to identify nonspecific targeting with possible undesi ...
... instance, the determined conformations of a protein often differ in its ligand-bound and -unbound forms. Protein conformational changes can open new ligand binding sites, whose exploration is key to fully assess the efficacy of a drug as well as to identify nonspecific targeting with possible undesi ...
Page 1 - Biochemistry
... 29. What is the advantage of having 20 different amino acids available to form proteins? Answer: The amino acids provide a rich diversity of functional groups, which can independently contribute to protein structure and function. In addition, many can be modified, increasing the diversity of functio ...
... 29. What is the advantage of having 20 different amino acids available to form proteins? Answer: The amino acids provide a rich diversity of functional groups, which can independently contribute to protein structure and function. In addition, many can be modified, increasing the diversity of functio ...
Functional analysis of an interspecies chimera of acyl carrier
... signals between the bacterium and the plant. Plants secrete ¯avonoids that are recognized by the bacteria. This leads to the production of bacterial signals called Nod factors. These Nod factors are synthesized by proteins encoded by nod, nol or noe genes (DeÂnarie et al. 1996). ...
... signals between the bacterium and the plant. Plants secrete ¯avonoids that are recognized by the bacteria. This leads to the production of bacterial signals called Nod factors. These Nod factors are synthesized by proteins encoded by nod, nol or noe genes (DeÂnarie et al. 1996). ...
Introduction to Bioinformatics Protein Structure and
... dipeptides (two amino acids joined together by a peptide bond). There are 20 possible amino acids in the first position and 20 possible amino acids in the second position. That makes 202 = 400 possible dipeptides. Similarly, there are 203 = 8000 possible tripeptides. Proteins range in size from a sm ...
... dipeptides (two amino acids joined together by a peptide bond). There are 20 possible amino acids in the first position and 20 possible amino acids in the second position. That makes 202 = 400 possible dipeptides. Similarly, there are 203 = 8000 possible tripeptides. Proteins range in size from a sm ...
Amino Acids - Angelo State University
... Vasopressin and Oxytocin • More than 200 peptides have been identified as being essential to the body’s proper functioning. • Vasopressin and oxytocin are nonapeptide hormones secreted by the pituitary gland. Six of the amino acid residues are held in a loop by disulfide bridges formed by the oxidat ...
... Vasopressin and Oxytocin • More than 200 peptides have been identified as being essential to the body’s proper functioning. • Vasopressin and oxytocin are nonapeptide hormones secreted by the pituitary gland. Six of the amino acid residues are held in a loop by disulfide bridges formed by the oxidat ...
University of Birmingham Armadillo
... them to be functionally very versatile. Are the ARMrepeat proteins in ‘little creatures’ as multifunctional as their better-studied relatives? The time is now right to start analysing ARM-repeat proteins in these new systems to better understand their cell biology. Here, we review recent advances in ...
... them to be functionally very versatile. Are the ARMrepeat proteins in ‘little creatures’ as multifunctional as their better-studied relatives? The time is now right to start analysing ARM-repeat proteins in these new systems to better understand their cell biology. Here, we review recent advances in ...
Chapter Five - DORAS
... Analysis of the HmuU amino acid sequence using the Pfam database indicated that it shared close homology to the FecCD transport family, which is a sub-family of the bacterial binding-protein dependent transport systems family (Staudenmaier et al., 1989). This suggests a common ancestry with that of ...
... Analysis of the HmuU amino acid sequence using the Pfam database indicated that it shared close homology to the FecCD transport family, which is a sub-family of the bacterial binding-protein dependent transport systems family (Staudenmaier et al., 1989). This suggests a common ancestry with that of ...
Lecture Notes BS1090
... down the second messenger into an inactive product (AMP). The activity of this enzyme also acts as a switch and a timer that acts to terminate the signal. This enzyme may also be activated by the hormone, resulting in only a very rapid, transient increase in cAMP. An increase in extracellular hormon ...
... down the second messenger into an inactive product (AMP). The activity of this enzyme also acts as a switch and a timer that acts to terminate the signal. This enzyme may also be activated by the hormone, resulting in only a very rapid, transient increase in cAMP. An increase in extracellular hormon ...
MB207_10 - MB207Jan2010
... - Only very small uncharged molecules can readily diffuse i.e.. O2, CO2 & water. - Hydrophobic molecules pass through more readily than hydrophilic ones. Membrane possess transport proteins - Facilitating and regulating the movement of substances into and out of the cell and its organelles against a ...
... - Only very small uncharged molecules can readily diffuse i.e.. O2, CO2 & water. - Hydrophobic molecules pass through more readily than hydrophilic ones. Membrane possess transport proteins - Facilitating and regulating the movement of substances into and out of the cell and its organelles against a ...
PSI - European Bioinformatics Institute
... • Given a set of uncharacterised sequences, we usually want to know: ...
... • Given a set of uncharacterised sequences, we usually want to know: ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).