Program - Harvard Medical School
... thresholds and conductive hearing loss (due to supersensitivity to bone-conducted acoustic stimuli and increased air-conduction thresholds) at low frequencies are common indicators of a possible SCD, but is not always present in all SCD patients. Mechanically speaking, a decreased sensitivity to air ...
... thresholds and conductive hearing loss (due to supersensitivity to bone-conducted acoustic stimuli and increased air-conduction thresholds) at low frequencies are common indicators of a possible SCD, but is not always present in all SCD patients. Mechanically speaking, a decreased sensitivity to air ...
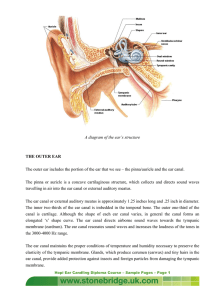
A diagram of the ear`s structure THE OUTER EAR The outer ear
... it to vibrate. The vibrations are passed to the small bones of the middle ear (ossicles), which form a system of interlinked mechanical levers: First, vibrations pass to the malleus (hammer), which pushes the incus (anvil), which pushes the stapes (stirrup). The base of the stapes rocks in and out a ...
... it to vibrate. The vibrations are passed to the small bones of the middle ear (ossicles), which form a system of interlinked mechanical levers: First, vibrations pass to the malleus (hammer), which pushes the incus (anvil), which pushes the stapes (stirrup). The base of the stapes rocks in and out a ...
ER-20 High-Fidelity Earplugs
... loss, depending on the intensity and duration of the noise. Some persons are more susceptible to hearing loss from high-level sound than others. The majority of eight-hour equivalent noise exposures fall between 85 and 95 dB. Many musicians and industrial workers can be adequately protected with as ...
... loss, depending on the intensity and duration of the noise. Some persons are more susceptible to hearing loss from high-level sound than others. The majority of eight-hour equivalent noise exposures fall between 85 and 95 dB. Many musicians and industrial workers can be adequately protected with as ...
PERCEPTION OF MUSIC BY PATIENTS WITH COCHLEAR
... hearing sensation to individuals with severe-to-profound hearing loss who do not benefit from hearing aids People with hearing losses in such range have absent or malfunctioning sensory cells in the cochlea ...
... hearing sensation to individuals with severe-to-profound hearing loss who do not benefit from hearing aids People with hearing losses in such range have absent or malfunctioning sensory cells in the cochlea ...
The Science of Hearing- Student Information Sheet
... Hearing loss can be temporary or permanent. ...
... Hearing loss can be temporary or permanent. ...
The human eye and the sense of sight. Structure Anatomy and
... The density of the cornea, aqueous humor, lens and vitreous humor are similar to each other and all refract light that passes through the eye. The refractive power of air through which light travels to reach the eyes of terrestrial mammals is lower than the refractive power of parts of the eye. Ther ...
... The density of the cornea, aqueous humor, lens and vitreous humor are similar to each other and all refract light that passes through the eye. The refractive power of air through which light travels to reach the eyes of terrestrial mammals is lower than the refractive power of parts of the eye. Ther ...
Screening using OAEs - Department of Surgery, HKU
... common, with clinical symptoms such as impaired consciousness, focal motor symptoms, speech dysfunction, seizure and sensory disorders ...
... common, with clinical symptoms such as impaired consciousness, focal motor symptoms, speech dysfunction, seizure and sensory disorders ...
Application of otoacoustic emissions in the diagnosis of hearing loss
... common, with clinical symptoms such as impaired consciousness, focal motor symptoms, speech dysfunction, seizure and sensory disorders ...
... common, with clinical symptoms such as impaired consciousness, focal motor symptoms, speech dysfunction, seizure and sensory disorders ...
CHAPTER 8
... Olfactory Hairs Olfactory Neurons Olfactory Nerve in the Brain Neurons connect directly into the brain from the nasal epithelium through the cribriform plate ...
... Olfactory Hairs Olfactory Neurons Olfactory Nerve in the Brain Neurons connect directly into the brain from the nasal epithelium through the cribriform plate ...
Unit 04 Sensation and
... Retina = the light-sensitive inner surface of the eye, containing the receptor rods and cones plus layers of neurons that begin the processing of visual information. ...
... Retina = the light-sensitive inner surface of the eye, containing the receptor rods and cones plus layers of neurons that begin the processing of visual information. ...
Document
... Sweet – concentrated on the tip of the tongue Sour – concentrated on the sides of the tongue Salty – concentrated on the tip and sides of the tongue Bitter – concentrated on the back of the tongue ...
... Sweet – concentrated on the tip of the tongue Sour – concentrated on the sides of the tongue Salty – concentrated on the tip and sides of the tongue Bitter – concentrated on the back of the tongue ...
Study guide for exam 2
... these firing-rate limits have to do with absolute and relative refractory periods? Why are these facts important for understanding frequency analysis by the auditory system? 14. How do the physical characteristics of the basilar membrane vary from the base of the cochlea to the apex? Why is this fac ...
... these firing-rate limits have to do with absolute and relative refractory periods? Why are these facts important for understanding frequency analysis by the auditory system? 14. How do the physical characteristics of the basilar membrane vary from the base of the cochlea to the apex? Why is this fac ...
Hearing
... known as sound waves • The ear consists of three portions, the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear • Each of these portions contain structures that help direct sound waves from the exterior to the receptors in the inner ear ...
... known as sound waves • The ear consists of three portions, the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear • Each of these portions contain structures that help direct sound waves from the exterior to the receptors in the inner ear ...
Chapter03-edited - Marie-Murphy-WIN13
... • Loudness and sequence in which sounds reach the ear provide cues – May turn head to clarify information ...
... • Loudness and sequence in which sounds reach the ear provide cues – May turn head to clarify information ...
Acting Out How the Ear Hears PPt Lesson Work
... that says, “Outer Ear.” The Outer Ear will get an envelope that is not to be opened by anyone but the Brain. So, the Outer Ear will just hold the envelope for now. ...
... that says, “Outer Ear.” The Outer Ear will get an envelope that is not to be opened by anyone but the Brain. So, the Outer Ear will just hold the envelope for now. ...
1 . If its wavelength is 1.5 cm, what is the frequency of the wave? Will
... 16. What is loudness of sound? What factors does it depend on? Answer The effect produced in the brain by the sound of different frequencies is called loudness of sound. Loudness depends on the amplitude of vibrations. In fact, loudness is proportional to the square of the amplitude of vibrations. 1 ...
... 16. What is loudness of sound? What factors does it depend on? Answer The effect produced in the brain by the sound of different frequencies is called loudness of sound. Loudness depends on the amplitude of vibrations. In fact, loudness is proportional to the square of the amplitude of vibrations. 1 ...
Auditory Neuroscience - University of Sunderland
... produce peaks and notches in the spectrum. • These serve as cues to location, particularly in elevation and resolving the front/back dimension. • You can apply filters to a sound to confuse this localization. • The types of confusion that occur give insight into how the cues are processed. ...
... produce peaks and notches in the spectrum. • These serve as cues to location, particularly in elevation and resolving the front/back dimension. • You can apply filters to a sound to confuse this localization. • The types of confusion that occur give insight into how the cues are processed. ...
A Brief History of Auditory Models
... The outer ear is the visible portion of the ear. It includes the pinna (also called auricle), the ear canal and the eardrum. The pinna collects the sounds and directs them down into the ear canal. Its shape also help us to extract directional information from sounds. The ear canal is a tube about 2. ...
... The outer ear is the visible portion of the ear. It includes the pinna (also called auricle), the ear canal and the eardrum. The pinna collects the sounds and directs them down into the ear canal. Its shape also help us to extract directional information from sounds. The ear canal is a tube about 2. ...
Sound and Music
... When the combination of the two straws is as long as possible, you can get the lowest sounds. Low pitch has a lower rate of vibration – lower frequency or less wiggles per second. However frequency and pitch are different things. Pitch is what your ear senses and frequency is the vibrations per seco ...
... When the combination of the two straws is as long as possible, you can get the lowest sounds. Low pitch has a lower rate of vibration – lower frequency or less wiggles per second. However frequency and pitch are different things. Pitch is what your ear senses and frequency is the vibrations per seco ...
13 ijmsci - Valley International Journals
... incus and stapes (and are also known as the hammer, anvil and stirrup). The ear drum and ossicles amplify the vibrations and carry them to the inner ear. The stirrup transmits the amplified vibrations through the oval window and into the fluid that fills the inner ear. The vibrations move through fl ...
... incus and stapes (and are also known as the hammer, anvil and stirrup). The ear drum and ossicles amplify the vibrations and carry them to the inner ear. The stirrup transmits the amplified vibrations through the oval window and into the fluid that fills the inner ear. The vibrations move through fl ...
ch._14-4
... the auricle. The auricle helps channel sound waves into the external auditory canal. The eardrum acts as a barrier between the outer and middle ear. ...
... the auricle. The auricle helps channel sound waves into the external auditory canal. The eardrum acts as a barrier between the outer and middle ear. ...
Listen Up! Better
... Hair cells help to convert sound vibrations into electrical signals that travel along nerves from the ear to the brain. These cells allow us to detect sounds. But when hair cells are damaged and then destroyed by too much noise, they don’t grow back. So hearing is permanently harmed. Sometimes loud ...
... Hair cells help to convert sound vibrations into electrical signals that travel along nerves from the ear to the brain. These cells allow us to detect sounds. But when hair cells are damaged and then destroyed by too much noise, they don’t grow back. So hearing is permanently harmed. Sometimes loud ...
Terms List
... The competency tests in Vocal Anatomy/Physiology and Voice Acoustics/Hearing will be drawn from these terms and questions. It is a good strategy to write down definitions and/or responses to each item on these lists as you engage in your weekly reading and web site explorations. These lists are also ...
... The competency tests in Vocal Anatomy/Physiology and Voice Acoustics/Hearing will be drawn from these terms and questions. It is a good strategy to write down definitions and/or responses to each item on these lists as you engage in your weekly reading and web site explorations. These lists are also ...
Neural Basis of the Ventriloquist
... Attention? Probably not Lateralization may be due to attentional orientation to perceived sound location No differential BOLD response in attentional areas (anterior cingulate, posterior parietal cortex) between illusion/noillusion trials Other behavioral results suggest visual attention has little ...
... Attention? Probably not Lateralization may be due to attentional orientation to perceived sound location No differential BOLD response in attentional areas (anterior cingulate, posterior parietal cortex) between illusion/noillusion trials Other behavioral results suggest visual attention has little ...