4. Seafloor Spreading Notes
... • Earth’s magnetic field has reversed many times since its creation ...
... • Earth’s magnetic field has reversed many times since its creation ...
ppt: Plate Tectonics Intro- Theory and History
... 1. Convergent (aka subduction zone) boundaries – where one plate overrides another plate. Each plate is bounded by some combination of these three plate boundary types. 2. Divergent (aka spreading) boundaries – where plates are moving apart 3. Transform fault boundaries – where plates are moving pa ...
... 1. Convergent (aka subduction zone) boundaries – where one plate overrides another plate. Each plate is bounded by some combination of these three plate boundary types. 2. Divergent (aka spreading) boundaries – where plates are moving apart 3. Transform fault boundaries – where plates are moving pa ...
Glossary for the Lithosphere
... a theory that considers the Earth to be a single, self-regulating system. the combined processes that maintain balance in a living organism or the environment. processes or deposits associated with hot water rocks or processes involving molten rock. in the place where it is found liquids and dissolv ...
... a theory that considers the Earth to be a single, self-regulating system. the combined processes that maintain balance in a living organism or the environment. processes or deposits associated with hot water rocks or processes involving molten rock. in the place where it is found liquids and dissolv ...
earthquake
... Earthquake Waves Body Waves • Identified as P waves or S waves • P waves - Are push-pull waves that push (compress) and pull (expand) in the direction that the waves travel - Travel through solids, liquids, and gases - Have the greatest velocity of all earthquake waves ...
... Earthquake Waves Body Waves • Identified as P waves or S waves • P waves - Are push-pull waves that push (compress) and pull (expand) in the direction that the waves travel - Travel through solids, liquids, and gases - Have the greatest velocity of all earthquake waves ...
THIRD QUARTER II. UNIT 4: Landforms and Constructive and
... 1. Earth’s surface features, such as mountains, volcanoes and continents, are the constantlychanging result of dynamic processes and forces at work inside the Earth. 2. Earth is formed of three basic layers, with the densest being the iron and nickel core. The middle layer, the mantle, of the Earth ...
... 1. Earth’s surface features, such as mountains, volcanoes and continents, are the constantlychanging result of dynamic processes and forces at work inside the Earth. 2. Earth is formed of three basic layers, with the densest being the iron and nickel core. The middle layer, the mantle, of the Earth ...
Word - New Haven Science
... 1. Earth’s surface features, such as mountains, volcanoes and continents, are the constantlychanging result of dynamic processes and forces at work inside the Earth. 2. Earth is formed of three basic layers, with the densest being the iron and nickel core. The middle layer, the mantle, of the Earth ...
... 1. Earth’s surface features, such as mountains, volcanoes and continents, are the constantlychanging result of dynamic processes and forces at work inside the Earth. 2. Earth is formed of three basic layers, with the densest being the iron and nickel core. The middle layer, the mantle, of the Earth ...
Chapter C-1 Lesson 2
... It is very thin compared to the other layers. If the Earth was an egg, the crust would be thinner than the egg’s shell. ...
... It is very thin compared to the other layers. If the Earth was an egg, the crust would be thinner than the egg’s shell. ...
Earth Science!!!!!! Chapter 1 – Intro to Earth Science Section 1.1
... o Constructive forces = such as mountain building and volcanism build up the surface by raising the land and depositing new material in the form of lava Depend on Earth’s internal heat for energy In the early 20th century, the idea that the continents had moved about the face of the Earth This beg ...
... o Constructive forces = such as mountain building and volcanism build up the surface by raising the land and depositing new material in the form of lava Depend on Earth’s internal heat for energy In the early 20th century, the idea that the continents had moved about the face of the Earth This beg ...
Plate Tectonics DQ - Biloxi Public Schools
... 2. Alfred Wegner’s Theory of Continental Drift was not well accepted because he couldn’t say what force could be big enough to move continents. Current theories explain this movement with---A. subduction zones at continental margins. B. hot spots forming under continents. C. magnetic reversals of th ...
... 2. Alfred Wegner’s Theory of Continental Drift was not well accepted because he couldn’t say what force could be big enough to move continents. Current theories explain this movement with---A. subduction zones at continental margins. B. hot spots forming under continents. C. magnetic reversals of th ...
Plate Boundaries
... Area of Interaction: Environment Learner Profile: Thinker Standard: Investigate the scientific process of how the Earth's surface is made. Learning Target: Today I’m learning about plate boundaries because I need to understand the forces that change Earth’s surface. Opening: Discovering Plate Tecton ...
... Area of Interaction: Environment Learner Profile: Thinker Standard: Investigate the scientific process of how the Earth's surface is made. Learning Target: Today I’m learning about plate boundaries because I need to understand the forces that change Earth’s surface. Opening: Discovering Plate Tecton ...
Mid Term Review Sample Questions
... 10. What kind of rock is formed by heat and pressure (but without melting)? ________________________ 11. Why can slate be used for roofing shingles? _______________________________________________ 12. If granite is subjected to high heat and pressure, what type of rock does it turn into? ___________ ...
... 10. What kind of rock is formed by heat and pressure (but without melting)? ________________________ 11. Why can slate be used for roofing shingles? _______________________________________________ 12. If granite is subjected to high heat and pressure, what type of rock does it turn into? ___________ ...
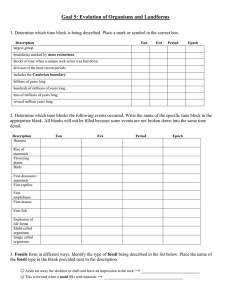
Goal 5: Evolution of Organisms and Landforms
... 23. Answer the following questions about mass extinctions: ...
... 23. Answer the following questions about mass extinctions: ...
Slide 1
... Francisco. Buildings such as this are designed to absorb the energy of an earthquake and to withstand the movement of the Earth. • Roads and bridges can also be designed to withstand the power of earthquakes. ...
... Francisco. Buildings such as this are designed to absorb the energy of an earthquake and to withstand the movement of the Earth. • Roads and bridges can also be designed to withstand the power of earthquakes. ...
Chapter 1 – Plate Tectonics
... The ocean floor is renewed every 200 million years or so. Seafloor spreading and subduction can change the size and shape of Earth’s oceans. ~ The Atlantic Ocean has been steadily expanding over the past 250 million years ...
... The ocean floor is renewed every 200 million years or so. Seafloor spreading and subduction can change the size and shape of Earth’s oceans. ~ The Atlantic Ocean has been steadily expanding over the past 250 million years ...
Plate Tectonics
... move the crustal plates in different directions. •The source of heat driving the convection currents is radioactivity deep in the Earth's mantle. ...
... move the crustal plates in different directions. •The source of heat driving the convection currents is radioactivity deep in the Earth's mantle. ...
Mountain Building
... melts, some material is forced up to the surface as magma and results in a volcano. The volcano grows until a volcanic mountain is formed. What would the soil or rock be like on this mountain? ...
... melts, some material is forced up to the surface as magma and results in a volcano. The volcano grows until a volcanic mountain is formed. What would the soil or rock be like on this mountain? ...
L10
... Magma rises to surface and forms new oceanic crust. Occur in oceanic crust (oceanic ridges) and in continental crust (rift valleys). Continental rift valleys may eventually flood to form a new ocean basin. ...
... Magma rises to surface and forms new oceanic crust. Occur in oceanic crust (oceanic ridges) and in continental crust (rift valleys). Continental rift valleys may eventually flood to form a new ocean basin. ...
Plate Tectonics Continental Drift
... • A few scientists agreed and continued to look for evidence to support his idea ...
... • A few scientists agreed and continued to look for evidence to support his idea ...
No Slide Title
... Long-term: consider how Earth’s climate has changed over last few hundred m.y. Why study long-term changes? ...
... Long-term: consider how Earth’s climate has changed over last few hundred m.y. Why study long-term changes? ...
Plate Tectonics Unit:
... move from side to side and up and down. S waves, unlike P waves, can not travel through liquids. 3. Surface waves: P or S waves that have reached the surface. These are the waves that cause the most damage, although they are slower than the other two. ...
... move from side to side and up and down. S waves, unlike P waves, can not travel through liquids. 3. Surface waves: P or S waves that have reached the surface. These are the waves that cause the most damage, although they are slower than the other two. ...
Volcanoes-Earthquakes
... The plates, which make up Earth's lithosphere, float on a semi-solid layer of molten rock called the mantle or the asthenosphere. The mantle has two layers: (1) the upper mantle which is more solid and (2) the lower mantle which is more liquid. ...
... The plates, which make up Earth's lithosphere, float on a semi-solid layer of molten rock called the mantle or the asthenosphere. The mantle has two layers: (1) the upper mantle which is more solid and (2) the lower mantle which is more liquid. ...
earthquake
... Debri from the Tsunami has to go somewhere… • Debris from the massive tsunami that struck Japan in March is on its way: Up to 20 million tons of trash, like "confetti soup," is slowly drifting across the Pacific Ocean and heading toward the United States. • Already garbage has been found 2,000 mile ...
... Debri from the Tsunami has to go somewhere… • Debris from the massive tsunami that struck Japan in March is on its way: Up to 20 million tons of trash, like "confetti soup," is slowly drifting across the Pacific Ocean and heading toward the United States. • Already garbage has been found 2,000 mile ...
Geophysics

Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins go back to ancient times. The first magnetic compasses were made from lodestones, while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 BC. Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the 20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. Geophysical survey data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.