to Ch. 8 Notes
... 1. earthquake: the vibration of earth produced by the rapid release of energy 2. focus: the point within Earth where an earthquake originates 3. epicenter: the location on Earth’s surface directly above the focus, or origin, of an earthquake 4. fault: a fracture in Earth along which movement has occ ...
... 1. earthquake: the vibration of earth produced by the rapid release of energy 2. focus: the point within Earth where an earthquake originates 3. epicenter: the location on Earth’s surface directly above the focus, or origin, of an earthquake 4. fault: a fracture in Earth along which movement has occ ...
GLY 3171 Geomorphology of the United States Course Description
... a. Compare and contrast the processes of physical and chemical weathering, including examples of each process. a. Describe the processes of mass wasting and give examples of structures developed by mass wasting. b. Examine the erosional and depositional activities of streams, and give examples of st ...
... a. Compare and contrast the processes of physical and chemical weathering, including examples of each process. a. Describe the processes of mass wasting and give examples of structures developed by mass wasting. b. Examine the erosional and depositional activities of streams, and give examples of st ...
earth`s history practice test
... c. They exist along the same line of latitude. d. They have the same climate today. 19. A scientist finds a fossil of the same organism in both India and Africa. These fossils provide evidence for which scientific theory below. a. Adaptation b. Continental drift c. Climate change d. Law of superposi ...
... c. They exist along the same line of latitude. d. They have the same climate today. 19. A scientist finds a fossil of the same organism in both India and Africa. These fossils provide evidence for which scientific theory below. a. Adaptation b. Continental drift c. Climate change d. Law of superposi ...
Dynamic Earth Webquest
... 8. Plate Tectonics Theory has been widely accepted since the ___________’s. It states that Earth’s outer layer or _________________ is broken up into ________________. These plates hold ______________________ and _____________________. They are constantly _________________. 9. Continents over time ...
... 8. Plate Tectonics Theory has been widely accepted since the ___________’s. It states that Earth’s outer layer or _________________ is broken up into ________________. These plates hold ______________________ and _____________________. They are constantly _________________. 9. Continents over time ...
Earthquakes
... of an earthquake with that magnitude would look like. Record information about your earthquake simulations so that you can draw conclusions about how the change in measurements affects the magnitude of an earthquake. ...
... of an earthquake with that magnitude would look like. Record information about your earthquake simulations so that you can draw conclusions about how the change in measurements affects the magnitude of an earthquake. ...
How did Alfred find fossilised sea animals high up in the Alps
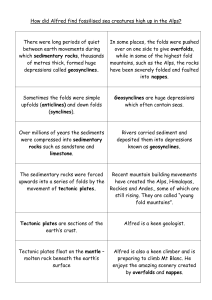
... How did Alfred find fossilised sea creatures high up in the Alps? ...
... How did Alfred find fossilised sea creatures high up in the Alps? ...
Earth`s Structure Test
... D Magma hardens into granite sediment. 18. Most geologists rejected Alfred Wegener’s idea of continental drift because A they were afraid of a new idea. B Wegener was interested in what Earth was like millions of years ago. C Wegener used several different types of evidence to support his hypothesis ...
... D Magma hardens into granite sediment. 18. Most geologists rejected Alfred Wegener’s idea of continental drift because A they were afraid of a new idea. B Wegener was interested in what Earth was like millions of years ago. C Wegener used several different types of evidence to support his hypothesis ...
Sample 5.3.B.2 Complete
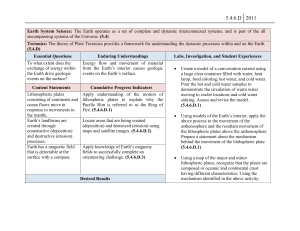
... showing how the continents might look 100 million years from now. Students must consider that the earth’s lithosphere is made up of moving plates and must take into account the directions in which major plates are moving. (5.4.6.D.1) ...
... showing how the continents might look 100 million years from now. Students must consider that the earth’s lithosphere is made up of moving plates and must take into account the directions in which major plates are moving. (5.4.6.D.1) ...
Grade 3 Rocks and Minerals Review
... Rocks that have changed due to intense heat and pressure Created from sedimentary, igneous or other metamorphic rocks. ...
... Rocks that have changed due to intense heat and pressure Created from sedimentary, igneous or other metamorphic rocks. ...
The Terrestrial Planets Chapter 6:
... interior and the lowest density material has risen to the surface ...
... interior and the lowest density material has risen to the surface ...
Section 2: Rocks and Minerals
... Most earthquakes are so _____________ that only scientists notice them. However, every 50 to 100 years a big one comes along and does a lot of __________________. A __________________ is a scientist who studies rocks to learn about the history and structure of the Earth. They also study the ________ ...
... Most earthquakes are so _____________ that only scientists notice them. However, every 50 to 100 years a big one comes along and does a lot of __________________. A __________________ is a scientist who studies rocks to learn about the history and structure of the Earth. They also study the ________ ...
September 2005 - The Earth Institute
... The United Nations estimates that 2.6 billion people, including over 700 million in India, do not have the luxury of household toilets or the privacy of a secluded latrine. As a U.S. daily newspaper pointed out recently, hundreds of slum dwellers in the sprawling Indian city of Mumbai are forced to ...
... The United Nations estimates that 2.6 billion people, including over 700 million in India, do not have the luxury of household toilets or the privacy of a secluded latrine. As a U.S. daily newspaper pointed out recently, hundreds of slum dwellers in the sprawling Indian city of Mumbai are forced to ...
teacher name: room: week beginning
... To show a visual model of seafloor spreading-this shows how the seafloor “grows”, but isn’t getting any larger because the land is removed in trenches. ...
... To show a visual model of seafloor spreading-this shows how the seafloor “grows”, but isn’t getting any larger because the land is removed in trenches. ...
Chapter 1 – Plate Tectonics
... up with Earth’s magnetic field. The magnetite minerals in some of the bands were lined up with the current position of Earth’s magnetic north and south poles. These rocks had normal polarity. In the other bands, the magnetite minerals were lined up in the opposite direction, with the north end o ...
... up with Earth’s magnetic field. The magnetite minerals in some of the bands were lined up with the current position of Earth’s magnetic north and south poles. These rocks had normal polarity. In the other bands, the magnetite minerals were lined up in the opposite direction, with the north end o ...
Theory of Plate Tectonics
... • Using sensors embedded in Earth’s plates and using satellites we know that they move at a rate of about 1-15 cm per year depending on the plate • The following map shows in which direction the different plates are moving ...
... • Using sensors embedded in Earth’s plates and using satellites we know that they move at a rate of about 1-15 cm per year depending on the plate • The following map shows in which direction the different plates are moving ...
Obj - davis.k12.ut.us
... – the crust stretches but does not reach elastic limit and break, 3. ocean ridges – from seafloor spreading. 3. Transform boundary – the edges of the plates move side by side or back and forth to each other. The moving plates cause the crust to break creating friction that makes the rock melt and ro ...
... – the crust stretches but does not reach elastic limit and break, 3. ocean ridges – from seafloor spreading. 3. Transform boundary – the edges of the plates move side by side or back and forth to each other. The moving plates cause the crust to break creating friction that makes the rock melt and ro ...
Unit 3 Lesson 1 Geological History
... Chains of islands are found throughout the oceans and especially in the western Pacific margins: the Aleutians, Japan, Philippines, and Indonesia. These "Island arcs" are usually situated along deep-sea trenches and are situated on the continental side of the trench. These observations, along with m ...
... Chains of islands are found throughout the oceans and especially in the western Pacific margins: the Aleutians, Japan, Philippines, and Indonesia. These "Island arcs" are usually situated along deep-sea trenches and are situated on the continental side of the trench. These observations, along with m ...
Chapter1305.ppt
... can reveal the latitude of a continent in the past. Marine magnetic anomalies can tell us how an ocean basin has gotten smaller or larger over time (< 200 million years or Jurassic time period because of subduction of the ocean basin). Comparing fossils found in different global locations can tell s ...
... can reveal the latitude of a continent in the past. Marine magnetic anomalies can tell us how an ocean basin has gotten smaller or larger over time (< 200 million years or Jurassic time period because of subduction of the ocean basin). Comparing fossils found in different global locations can tell s ...
Handout
... can reveal the latitude of a continent in the past. Marine magnetic anomalies can tell us how an ocean basin has gotten smaller or larger over time (< 200 million years or Jurassic time period because of subduction of the ocean basin). Comparing fossils found in different global locations can tell s ...
... can reveal the latitude of a continent in the past. Marine magnetic anomalies can tell us how an ocean basin has gotten smaller or larger over time (< 200 million years or Jurassic time period because of subduction of the ocean basin). Comparing fossils found in different global locations can tell s ...
4. Seafloor Spreading Notes
... • Earth’s magnetic field has reversed many times since its creation ...
... • Earth’s magnetic field has reversed many times since its creation ...
Geophysics

Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins go back to ancient times. The first magnetic compasses were made from lodestones, while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 BC. Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the 20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. Geophysical survey data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.