Earth and Moon Review
... Why is the inner core solid even though it is hotter than the outer liquid core? A) This is not unusual: hotter things tend to be more solid. B) The great pressure at Earth's center forces the atoms in the core together, causing it to solidify. C) Radioactivity cause liquid materials to become soli ...
... Why is the inner core solid even though it is hotter than the outer liquid core? A) This is not unusual: hotter things tend to be more solid. B) The great pressure at Earth's center forces the atoms in the core together, causing it to solidify. C) Radioactivity cause liquid materials to become soli ...
Name___________________________ Date: Plate Tectonics
... 7. Describe what happens when a plate carrying oceanic crust collides with a plate carrying continental crust. When an oceanic crust collides with a continental crust, the ocean crust sinks (subducts) because it is thinner and more dense. 8. What happens along a subduction zone? Subduction zones occ ...
... 7. Describe what happens when a plate carrying oceanic crust collides with a plate carrying continental crust. When an oceanic crust collides with a continental crust, the ocean crust sinks (subducts) because it is thinner and more dense. 8. What happens along a subduction zone? Subduction zones occ ...
Isostasy and Large Scale Gravity Chap. 9 Homework Answers (Dec
... The false paradox here is that how can the mantle both undergo ‘solid-state’ creep (i.e., flow like a liquid) due the application of loads (e.g., ice sheets, erosion) over millions of years AND transmit earthquake induced shear waves with wave periods of <100 s. The logic goes, if the earth behaves ...
... The false paradox here is that how can the mantle both undergo ‘solid-state’ creep (i.e., flow like a liquid) due the application of loads (e.g., ice sheets, erosion) over millions of years AND transmit earthquake induced shear waves with wave periods of <100 s. The logic goes, if the earth behaves ...
When hawk-sized dragonflies ruled the air
... Radioisotope dating methods have been expanded and refined Sedimentary rocks are formed from materials that existed for varying lengths of time before being transported, sometimes over long distances, to the site of their deposition. Therefore, the inorganic isotopes in a sedimentary rock do not con ...
... Radioisotope dating methods have been expanded and refined Sedimentary rocks are formed from materials that existed for varying lengths of time before being transported, sometimes over long distances, to the site of their deposition. Therefore, the inorganic isotopes in a sedimentary rock do not con ...
Continental Drift through Plate Tectonics
... Read the section in the book, and then answer the following questions in your notebook: 1. What was Alfred Wegener’s theory of Continental Drift? 2. Explain the three types of evidence Wegener used to support his theory that continents move. 3. What is the main reason scientists rejected Wegener’s t ...
... Read the section in the book, and then answer the following questions in your notebook: 1. What was Alfred Wegener’s theory of Continental Drift? 2. Explain the three types of evidence Wegener used to support his theory that continents move. 3. What is the main reason scientists rejected Wegener’s t ...
VISUALIZING GLOBAL EARTHQUAKES
... • Causes of earthquakes: Earthquakes are places where rocks break and move; strain accumulates as there is movement of rock, and then the strain releases all at once as the rock breaks during an earthquake. • Plate tectonics: The lithosphere is made up of tectonic plates that fit together covering t ...
... • Causes of earthquakes: Earthquakes are places where rocks break and move; strain accumulates as there is movement of rock, and then the strain releases all at once as the rock breaks during an earthquake. • Plate tectonics: The lithosphere is made up of tectonic plates that fit together covering t ...
Calvin Pinson
... The causes of earthquakes are the vibrations from rocks breaking after exceeding their elastic limit. The forces that cause this are heat from the earth’s core and some radioactive decay in the mantle. This causes the plates of earth’s crust to move causing three forces to occur at their boundaries: ...
... The causes of earthquakes are the vibrations from rocks breaking after exceeding their elastic limit. The forces that cause this are heat from the earth’s core and some radioactive decay in the mantle. This causes the plates of earth’s crust to move causing three forces to occur at their boundaries: ...
plateboundariesstressesfaults
... and Faults 1. What is the theory of plate tectonics? 2. What are the three types of plate boundaries? ...
... and Faults 1. What is the theory of plate tectonics? 2. What are the three types of plate boundaries? ...
Earth`s History - Ms. Clark`s Science
... The four layers are the inner core, outer core, mantle, and crust. The crust and top of the mantle are further classified by their properties into the lithosphere and the asthenosphere. ...
... The four layers are the inner core, outer core, mantle, and crust. The crust and top of the mantle are further classified by their properties into the lithosphere and the asthenosphere. ...
Basement Sucks - School of Earth and Environment
... That groundwaters can penetrate crystalline rocks to mid-crustal depths was first appreciated from stable isotope studies of altered granite batholiths, and reinforced by examples of water inflows encountered during deep crustal drilling. Nevertheless, fluid flow modelling of sedimentary basins has ...
... That groundwaters can penetrate crystalline rocks to mid-crustal depths was first appreciated from stable isotope studies of altered granite batholiths, and reinforced by examples of water inflows encountered during deep crustal drilling. Nevertheless, fluid flow modelling of sedimentary basins has ...
Review Worksheet – Mechanical and Chemical Weathering and
... 2. The following forces can change the rate at which rocks weather: _______________________, ______________________________, and _____________________________. ...
... 2. The following forces can change the rate at which rocks weather: _______________________, ______________________________, and _____________________________. ...
Introducing Volcanoes - Ysgol Rhyngrwyd IGCSE Geography
... characteristic set of Earth structures or “tectonic” features. The word, tectonic, refers to the *deformation of the crust as a consequence of plate interaction. * deform = change shape ...
... characteristic set of Earth structures or “tectonic” features. The word, tectonic, refers to the *deformation of the crust as a consequence of plate interaction. * deform = change shape ...
NTI Day 1 Article
... from the shallow mid-ocean ridges, it cools and sinks as it becomes more dense. This increases the volume of the ocean basin and decreases the sea level. For instance, a mid-ocean ridge system in Panthalassa—an ancient ocean that surrounded the supercontinent Pangaea—contributed to shallower oceans ...
... from the shallow mid-ocean ridges, it cools and sinks as it becomes more dense. This increases the volume of the ocean basin and decreases the sea level. For instance, a mid-ocean ridge system in Panthalassa—an ancient ocean that surrounded the supercontinent Pangaea—contributed to shallower oceans ...
Lecture 10
... How can plate tectonics help in earthquake prediction? We have seen that earthquakes occur at the following three kinds of plate boundary: ocean ridges where the plates are pulled apart, margins where the plates scrape past one another, and margins where one plate is thrust under the other. Thus, ...
... How can plate tectonics help in earthquake prediction? We have seen that earthquakes occur at the following three kinds of plate boundary: ocean ridges where the plates are pulled apart, margins where the plates scrape past one another, and margins where one plate is thrust under the other. Thus, ...
reprint
... oriented mantle material (characterized by a fast polarization direction φ and a delay time δt) that arise due to lattice-preferred orientation in olivine (Silver & Chan 1991). Russo & Silver’s (1994) used the pattern of shear-wave splitting observations and geoid features around South America to in ...
... oriented mantle material (characterized by a fast polarization direction φ and a delay time δt) that arise due to lattice-preferred orientation in olivine (Silver & Chan 1991). Russo & Silver’s (1994) used the pattern of shear-wave splitting observations and geoid features around South America to in ...
Component 4: Oils, Earth and Atmosphere
... The oil from these fruits and seeds can be used for f____________ or for fuel. To extract the oil the fruits or seeds need to be c____________ and then p____________. D____________ refines oil and removes water and any i____________. ...
... The oil from these fruits and seeds can be used for f____________ or for fuel. To extract the oil the fruits or seeds need to be c____________ and then p____________. D____________ refines oil and removes water and any i____________. ...
Power Point 9.5
... • A geological theory stating that pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant, slow motion. • As plates move they crash together, pull apart and grind past each other. Each movement along a plate boundary creates a different land feature. ...
... • A geological theory stating that pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant, slow motion. • As plates move they crash together, pull apart and grind past each other. Each movement along a plate boundary creates a different land feature. ...
Compared to the desolate surface of the Moon, Earth must
... I. Igneous Textures—refers to the size and shape of the minerals in the rock A. Phaneritic: contain crystals large enough to see with unaided eye. When magma cools slowly over hundreds to thousands of years the minerals crystallize slowly and have ample time to grow large. Intrusive Rocks (Plutonic ...
... I. Igneous Textures—refers to the size and shape of the minerals in the rock A. Phaneritic: contain crystals large enough to see with unaided eye. When magma cools slowly over hundreds to thousands of years the minerals crystallize slowly and have ample time to grow large. Intrusive Rocks (Plutonic ...
Earthquakes - TeacherWeb
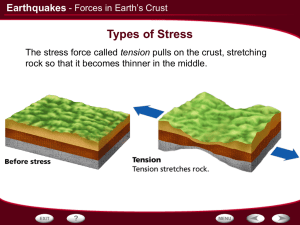
... fault slip past each other sideways, with little up or The stress force called compression squeezes rock down motion. until it folds or breaks. A fold inthat rock that bends upward into is an Stress pushes a mass of rock in an twoarch opposite anticline. directions is called shearing. A fold in in r ...
... fault slip past each other sideways, with little up or The stress force called compression squeezes rock down motion. until it folds or breaks. A fold inthat rock that bends upward into is an Stress pushes a mass of rock in an twoarch opposite anticline. directions is called shearing. A fold in in r ...
Name Date Period ______ Plate Tectonics Study Guide 1. Explain
... 2. What evidence is used to support the theory of continental drift? ...
... 2. What evidence is used to support the theory of continental drift? ...
Introduction to Oceanography 112
... 63. Although not absolutely true, a hotspot is generally thought to be fixed in its position (i.e. does not move inside the Earth) relative to the overlying plate. a. True b. False 64. The older seamounts are more submerged because: a. They continually erode as they age b. The seafloor on which they ...
... 63. Although not absolutely true, a hotspot is generally thought to be fixed in its position (i.e. does not move inside the Earth) relative to the overlying plate. a. True b. False 64. The older seamounts are more submerged because: a. They continually erode as they age b. The seafloor on which they ...
Chapter 17: Plate Tectonics
... seafloor is geologically young at about 180 million years old. Why are ocean-floor rocks so young compared to continental rocks, some of which are 3.8 billion years old? Geologists knew that oceans had existed for more than 180 million years. Where, then, they wondered, is the ocean crust from those ...
... seafloor is geologically young at about 180 million years old. Why are ocean-floor rocks so young compared to continental rocks, some of which are 3.8 billion years old? Geologists knew that oceans had existed for more than 180 million years. Where, then, they wondered, is the ocean crust from those ...
volcano - Cloudfront.net
... 1. How does magma form and move? 2. Where does magma form? 3. How does plate tectonics relate to volcanoes? 4. What methods do scientists use to predict volcanic eruptions? ...
... 1. How does magma form and move? 2. Where does magma form? 3. How does plate tectonics relate to volcanoes? 4. What methods do scientists use to predict volcanic eruptions? ...
Geophysics

Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins go back to ancient times. The first magnetic compasses were made from lodestones, while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 BC. Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the 20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. Geophysical survey data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.